Arithmetic Logic Unit
What Is Arithmetic Logic Unit ( ALU ) ?
In computer architecture, the arithmetic logic unit ( ALU ) is an combinational digital electronic circuit and fundamental building block of all microprocessor chips.
The ALU essentially works as a mathematical brain of the all processor chips. It performs all the arithmetic and logical operations performed by the processor. It performs arithmetic and logical operations on binary data, enabling the CPU to execute complex computations and make logical decisions to execute the computer program.
The main function microprocessor ( CPU ) is to execute the computer program. The computer program contains set of machine instructions. The CPU executes the program.
In order to execute the program, the CPU has to perform number of arithmetic and logical operations as per the program instructions. These operations are performed by the ALU.
The ALU is an essential part of each central processing unit ( CPU ). The CPU is also alternately referred to as processor or a microprocessor.
The ALU is responsible for executing basic arithmetic operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. It also performs logical operations, including AND, OR, NOT, and XOR, on binary numbers. These operations are fundamental for carrying out calculations, comparisons, and data manipulation within a computer system.
The ALU is also a crucial component of the Graphics Processing Unit ( GPU ) . A GPU is a dedicated processor used for handling the graphics processing which improves the system performance.
Depending upon the microprocessor architecture, the CPU and GPU can contain one or more Arithmetic and logic units. The ALU for the GPU is optimized for rapid graphics processing.
The ALU is a fundamental building block of all microprocessor. From simple to highly advanced microprocessor, all the processor chips, the ALU is a essential component.
In this article, you will learn what is arithmetic logic unit, how ALU works, functions of the ALU, logic gates and other important topics related to the central processing unit ( CPU ) and ALU.
Arithmetic Logic Unit ( ALU ) In Computer Architecture
ALUs are designed with different word sizes (the number of bits they can process in a single operation), and their performance plays a critical role in determining the overall speed and capabilities of a CPU.
Modern CPUs often have ALUs with 32-bit or 64-bit word sizes, though other configurations are possible depending on the specific application and design requirements. Additionally, CPUs can have multiple ALUs, allowing them to perform multiple operations simultaneously, which enhances their overall performance.
The Arithmetic Logic Unit is an essential building block of a CPU, responsible for carrying out the core arithmetic and logical operations required to execute computer programs and perform various computations.
Arithmetic Logic Unit In Computer Architecture
Table Of Contents
Types Of ALU Functions
The Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) is a fundamental component of the central processing unit (CPU) in a computer. It is responsible for performing arithmetic and logic operations on binary numbers, the basic language of computer processing. The ALU is a critical part of the CPU that executes the instructions provided by a computer program.
Arithmetic Operations:
The ALU performs basic arithmetic operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. These operations are fundamental for mathematical calculations and numerical processing.
Logic Operations:
In addition to arithmetic operations, the ALU performs logic operations such as AND, OR, NOT, and XOR. These operations are crucial for decision-making processes and data manipulation.
Comparison Operations:
The ALU compares two binary numbers to determine if they are equal, less than, or greater than each other. This is essential for branching and decision-making in program execution.
Shift Operations:
The ALU can shift the bits of a binary number left or right, facilitating data movement and manipulation.
Components Of ALU
Registers:
The ALU typically contains a set of registers, small storage units within the CPU, where data is temporarily held for processing. These registers include the accumulator, which stores the results of arithmetic operations.
Control Unit:
The control unit coordinates the operations of the ALU, directing it to perform specific tasks based on the instructions received from the computer program.
Multiplexers:
Multiplexers are used to select input data for the ALU, determining which data will be processed in a particular operation.
Flags:
Flags are status indicators that signal conditions resulting from arithmetic and logic operations. Common flags include zero flag (Z), carry flag (C), sign flag (S), and overflow flag (V).
ALU And CPU Architecture
The ALU is a crucial component of all the microprocessor chips. And therefore, The ALU operations can be best understood in the context of how CPU works.
The CPU stands for the central processing unit and it functions as a brain of the computer system. The CPU is an integrated circuit chip and crucial component of the computer system.
It is CPU is responsible to process the data as per the program instructions. The CPU provides the processing power to the computer by performing complex calculations.
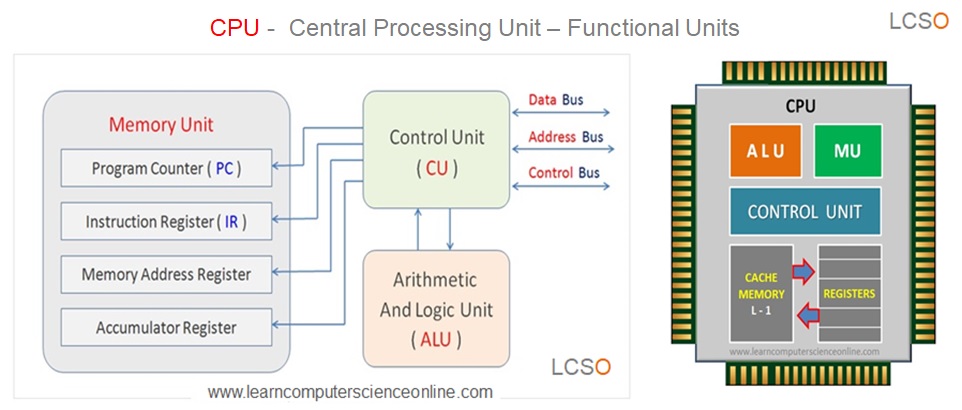
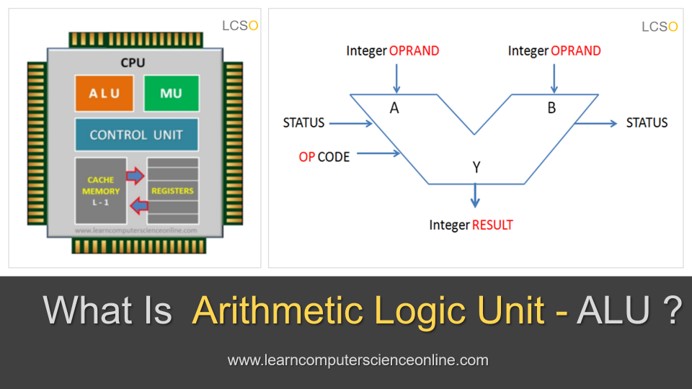
The processor internally consists of three functional units. These functional units are control unit ( CU ), arithmetic and logic unit ( ALU ) and the memory unit ( MU ).
The control unit ( CU ) decodes the operation code ( Opcode ) part of the machine instruction. The CU then directs the arithmetic logic unit ( ALU ) to perform a specific operation as per the operation code.
The ALU operates on the data ( Operand ) part of the machine instruction and processed data is stored into the memory unit ( MU ).
During the program execution, the CPU stores the program instructions and data into the internal high speed memory unit of the CPU. The memory unit consists of CPU registers.
What Are Arithmetic And Logic Operations ?
The ALU is a part of the processor and the number of operations supported by the processor ( operations performed by the ALU ) depends upon the instruction set architecture of the processor.
The modern processor contains highly advanced ALU circuit that is capable of performing complex arithmetic and logic operations.
The ALU is said to be a combinational circuit because the ALU circuit internally consists of combination of both arithmetic Unit and the logic unit.
Arithmetic Operations
The ALU performs both arithmetic and logic operations. The arithmetic operations of the ALU include all the basic mathematical operations.
For example, the ALU arithmetic operations includes addition, subtraction, division multiplication and raise to the power.
Logic Operations
All the decision making operations based on the conditional logic are said to be the logical operations.
The ALU logical operations include the grater than ( ≥ ) less than ( ≤ ) , comparison, equal to shifting operations, Boolean operations comparisons ( XOR, OR, AND, and NOT operations ).
The ALU supports only binary operations. The arithmetic and logic unit internally consists of AU ( arithmetic unit ) and the LU ( logic unit ).
ALU Arithmetic Operations | ALU Logic Operations |
+ Addition | = Equal To , ≠ Not Equal To |
- Subtracition | > Greater Than |
÷ Division | < Less Than |
× Multiplication | ≥ Greater Than Or Equal To |
Raise By A Power | ≤ Less Than Or Equal To |
Arithmetic Logic Unit And Boolean Algebra
The arithmetic logic unit ( ALU ) handles three types of operations performed by the CPU. These three basic operations of the ALU include arithmetic, logical and shift operations.
The ALU circuits consists of different types of logic gates that allows the ALU to perform the logical operations. The logic gates are digital circuits and fundamental building block of all the digital circuits.
The computer system is a digital electronic machine. Since all the electronic components of the computer system works on the principles of digital electronic.
And therefore, the computer can execute the machine instructions in the binary format. The machine instructions are represented in binary that contains only two digits that is either zero or one.
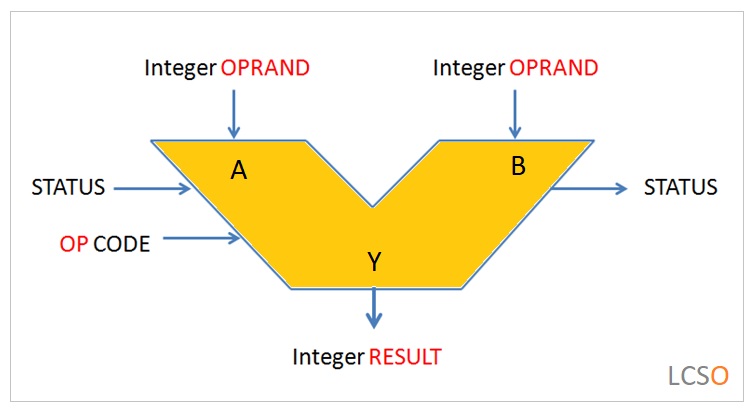
The ALU performs the logical operations with the help of logic gates. The ALU makes use of different types of logic gates to execute different logic operations.
A logic gate is an electronic device that works as a building block for all the digital electronic circuits. The logic gates perform basic logical functions that are essential for the digital circuits.
In a digital circuit, the logic gates will make decisions based on a combination of digital signals received from its inputs. Most logic gates have two inputs and one output.
Logic gates are based on the principles of the Boolean algebra. In mathematics, the Boolean algebra is the branch of algebra in which the values of the variables are the truth values.
The Boolean algebra is based on the binary number system. The truth value is either true and false and it is denoted 1 and 0, respectively in the binary.
The logic gates take binary inputs and provide one single binary output. There are seven basic logic gates represented by specific symbol. There seven basic logic gates are AND, OR, XOR, NOT, NAND, NOR, and XNOR.
What Are Logic Gates ?
The arithmetic logic unit internally consists of two sub functional units which includes the arithmetic unit and the logic unit.
The arithmetic unit performs the arithmetic operations. Whereas, the logic unit performs the logic operations such as decision making.
When the program instruction contains the conditional logic, the CPU has to first evaluate the condition. The CPU further operation depends upon the result of the conditional expression.
The arithmetic logic unit executes the conditional statements with the help of the logic gates.
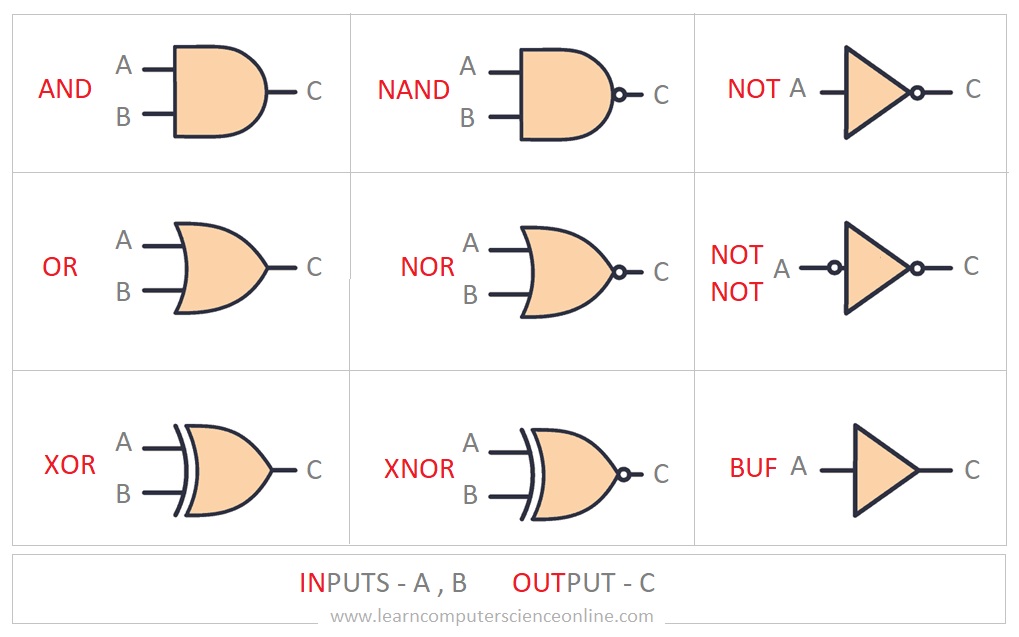
The logic gates are used in the ALU to make decisions during the program execution. The logic gates allow the electrical outputs are only ‘turn on’ when the correct logic sequence has been applied.
The logic gate has a specific name that helps to describe how different inputs will determine the possible outputs.
In order to understand how a logic gate works, the table of logic possibilities needs to be studied. In Boolean algebra , this table is called a ‘truth table’ .
In digital electronics, truth tables are used for planning and designing the logic gates.
ALU Functions
What Are The Functions Of ALU ?
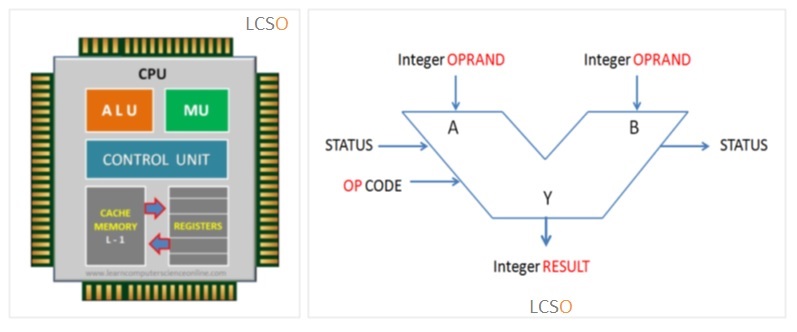
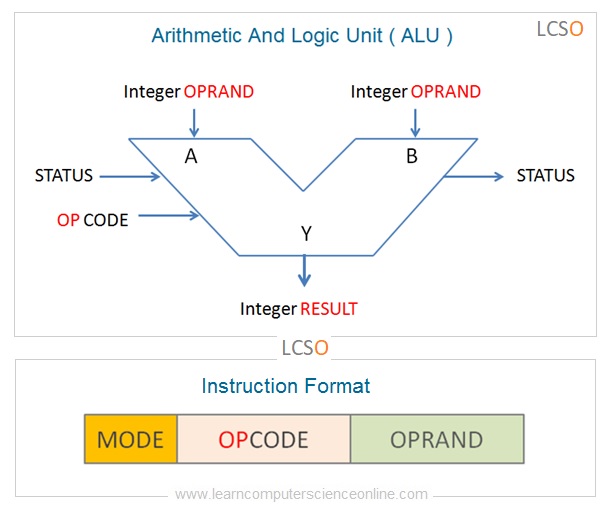
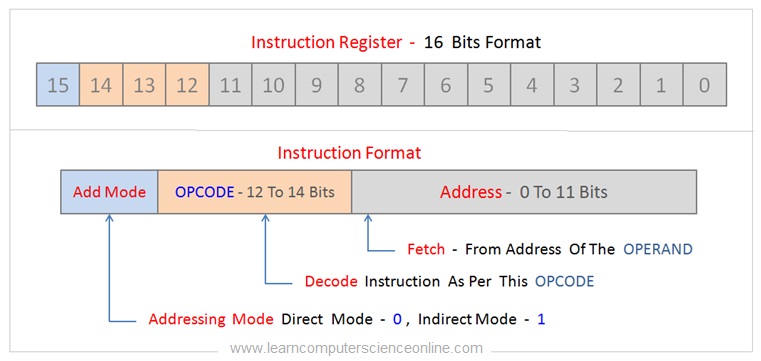
The ALU is that functional part of the processor that operates on the data. The Opcode part of the instruction format defines the operation to be performed.
Whereas, the data is represented by Operand into the instruction format. The addressing mode part directs the control unit regarding the manner in which data is represented into the instruction format.
The arithmetic logic unit performs three types of functions.
- To operate on data as per the program instruction decoded by control unit.
- ALU performs arithmetic operations such as ; addition, subtraction, increment, multiplication etc.
- ALU performs logical operations such as ; AND , OR , X-OR , NOT etc.
- ALU accepts operands from accumulator and temporary register.
- ALU after performing operation, it stores the result in accumulator or temporary register.
- It performs Bitwise Logical and Bit Shift operations
- It provides states of result to the flag register.
- ALU also handles the branching decisions.
Bitwise Logic Operations
The bitwise logic operations include all the basic decision making operations such as AND , OR , Exclusive-OR bitwise XOR,
Bit Shift Operations
The bit shift operations are used to move the bits to either the left or right in an instruction word.
There are three types of bit shift operations performed by the ALU. These bit shift operations are logical shift, arithmetic shift and rotate. A logical bit shift operation moves bits to the left or right.
The bits which ‘fall off’ the end of the instruction word are discarded. The falling bit in the instruction word is replaced by 0’s from the opposite end.
Important ALU Functions
Types Of Operations Performed By ALU
An Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) is a fundamental component of a computer’s central processing unit (CPU). It is responsible for performing arithmetic operations (such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division) as well as logical operations (such as AND, OR, NOT, and XOR).
The ALU takes input data from registers or memory, processes the data according to the instructions provided by the CPU, and produces output data based on the result of the operation.
Key functions of an ALU include:
1. Arithmetic Operations
An Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) is a fundamental component of a computer’s central processing unit (CPU). It is responsible for performing arithmetic operations (such as addition, subtraction,
2. Logical Operations
Logical operation are necessary to execute the program instructions. The ALU performs logical operations on binary data, such as bitwise AND, OR, NOT, and XOR. These operations are fundamental for manipulating and comparing binary data.
3. Data Comparison
The ALU can compare two binary numbers and generate signals to indicate if they are equal, not equal, greater than, less than, etc. These comparisons are crucial for decision-making processes in programs.
4. Shifting Operations
The ALU can shift the bits of a binary number left or right, which is used in various operations, including multiplication and division, as well as bitwise manipulation.
5. Carry and Overflow Handling
The ALU is equipped to handle carry (when the result of an addition exceeds the maximum representable value) and overflow (when a signed operation produces a result that is too large to represent) conditions.
How ALU Works ?
The arithmetic logic unit ALU plays an important role in the program execution. The ALU is part of the processor which performs the mathematical calculations and decision-making logical operations.
The program execution starts when operating system loads the program into the main memory RAM. The microprocessor is responsible to execute the program.
The CPU initiates the program execution by its internal execution mechanism called an instruction cycle. The instruction cycle is the basic CPU operation which consists of four steps.
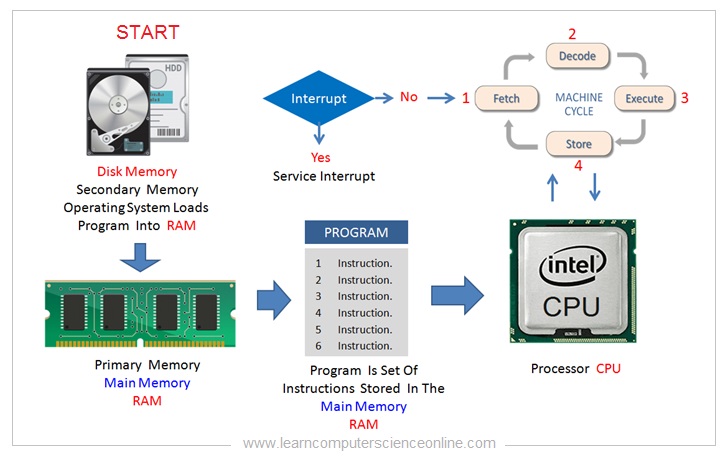
The instruction cycle is a four stage CPU operation and it is also called as fetch, decode and execute cycle.
The CPU initiates the program execution by fetching the program instructions one by one. The program instruction is also referred as machine instruction or instruction word.
Each time the instruction is fetched, the program counter ( PC ) register is incremented so that it points to the address of the next instruction.
Each processor has three functional units which includes control unit, arithmetic logic unit and the memory unit.
The control unit ( CU ) inside the processor controls the entire execution cycle performed by the processor and generates the necessary control signals.
The control unit is also responsible to decode the program instruction stored into the instruction register. The decoding part of the instruction takes place in the control unit as per the instruction format.
The operation code ( Opcode ) part of the instruction format is decoded by the control unit CU to decode which operation is to be performed. The CU also decodes the Operand to fetch the data.
After the decode operation is completed, the control unit generates the necessary control signals and directs the ALU to perform the desired operation as specified in the Opcode.
The arithmetic logic unit ( ALU ) then performs the necessary mathematical and logical operations on the data. The processed data is stored into the output register and then transferred to the main memory.
The operating system regains the control of the processed data stored into the main memory RAM for further action.
ALU Architecture
How ALU Executes Operations ?
The ALU consists of combinational logic circuits that are designed to process binary data. It takes two binary inputs, performs the specified operation, and produces an output based on the operation’s result. The size of the ALU is typically determined by the word size of the computer architecture it belongs to. For example, a 32-bit ALU is designed to handle 32-bit data inputs and produce 32-bit outputs.
The ALU’s design includes various components, such as registers, multiplexers, adders, and logic gates. Registers are used to store temporary data during calculations, while multiplexers select the appropriate inputs based on control signals. Adders are responsible for performing addition operations, and logic gates implement logical operations.
To perform arithmetic operations, the ALU uses adders and subtractors. The input operands are fed into the adders, and the carry-out or borrow-out signals are used to indicate overflow or underflow conditions. Multiplication and division operations are achieved through a series of repeated addition and subtraction operations.
Logical operations in the ALU are implemented using logic gates. For example, the AND operation is performed by combining the input bits with AND gates, while the OR operation uses OR gates. The NOT operation is achieved through inverters.
The ALU’s output is usually connected to other components, such as registers or memory units, enabling the CPU to store and manipulate data. The ALU’s output can also affect the control flow of a program, as it determines the outcome of conditional statements and influences program branching.
How ALU Operates
the ALU’s functionality is determined by the CPU’s microarchitecture and instruction set, which defines the specific operations the ALU can perform and how it interacts with other components of the CPU. The ALU’s speed and efficiency significantly impact the overall performance of the CPU in executing instructions and processing data.
1. Input Data
the ALU’s functionality is determined by the CPU’s microarchitecture and instruction set, which defines the specific operations the ALU can perform and how it interacts with other components of the CPU. The ALU’s speed and efficiency significantly impact the overall performance of the CPU in executing instructions and processing data.
1. Input Data
- The ALU takes input data from CPU registers, which are small, high-speed memory locations within the CPU. Registers store the data temporarily during the execution of instructions.
- The data in the registers can be fetched from memory or generated as a result of previous operations.
2. Control Signals
- The CPU sends control signals to the ALU, indicating the type of operation to be performed (e.g., addition, subtraction, AND, OR, etc.).
- These control signals also dictate other aspects of the operation, such as whether to perform arithmetic or logical operations, whether to set or reset certain flags (e.g., carry flag, overflow flag), and the direction of shifting operations.
3. Arithmetic Operations
- For arithmetic operations like addition and subtraction, the ALU takes two binary numbers as inputs and performs the specified operation.
- It operates bit by bit, starting from the least significant bit (LSB) to the most significant bit (MSB), while considering any carry generated from the previous bit.
- The ALU can handle both unsigned and signed numbers, using two’s complement representation for signed numbers.
4. Logical Operations
- For logical operations like AND, OR, NOT, and XOR, the ALU also operates bit by bit on corresponding bits of the input data.
- For example, in an AND operation, the ALU checks if both bits in the corresponding positions of the input numbers are set to 1, and if so, sets the corresponding bit in the output to 1; otherwise, it sets it to 0.
5. Carry And Overflow Handling
- During arithmetic operations, the ALU must handle carry-in and carry-out. The carry-in represents any carry from a previous bit, and the carry-out indicates if there’s a carry to the next bit.
- For subtraction, the ALU performs addition using the two’s complement method, where it adds the negated value of the second operand to the first operand.
- It also checks for overflow, which occurs when the result of a signed operation is too large (positive overflow) or too negative (negative overflow) to be represented with the given number of bits.
6. Shifting
- For shifting operations, the ALU moves the bits of a binary number left or right by a specified number of positions.
- Left shifts are equivalent to multiplication by powers of 2, while right shifts are equivalent to division by powers of 2.
7. Output Data
- The ALU produces the result of the operation, which is stored back in a register for further processing or use in subsequent instructions.
8. Flags
- The ALU sets or resets various status flags, such as carry flag, overflow flag, zero flag, and sign flag, based on the result of the operation.
- These flags provide important information to the CPU, which enables it to make decisions during program execution.
ALU Configurations
Arithmetic logic unit (ALU) is one functional unit of the CPU architecture. During the program execution, ALU interacts with other functional units of the CPU and performs various operations as per the program instructions.
Depending upon the CPU architecture, Each arithmetic logic unit (ALU) can include the following configurations.
Based on the internal storage of operands, the ISA can be classified as: Stack, Accumulator and General Purpose Register Architecture.
- Instruction Set Architecture.
- Accumulator.
- Stack.
- Register to Register.
- Register Stack.
- Register Memory.
Instruction Set Architecture
The instruction set architecture (ISA) is a part of the processor architecture. The ISA define set of commands supported by the processor and implemented into the processor’s microarchitecture.
Each microprocessor supports a group of commands that are hardwired into the processor circuitry. The ISA defines the set of commands that the processor can perform to execute the program instructions.
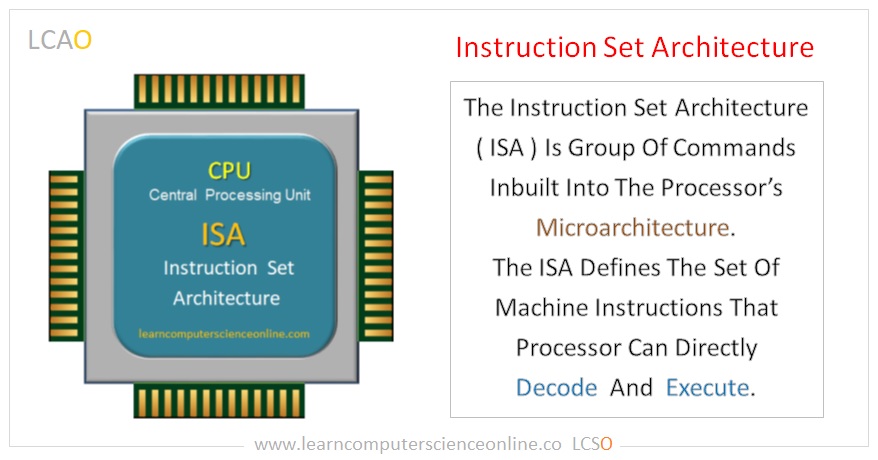
In other words, the instruction set architecture is group of commands and operations used by the software to communicate and direct the processor. These commands are implemented into the processor circuitry that is microarchitecture.
Accumulator
In computing, an accumulator is a type of register used by the processor to store the short-term and intermediate data related to mathematical and logical operations during the program execution.
The CPU makes use of number of high-speed internal memory called registers. In modern CPUs, accumulators are replaced by general-purpose registers because they offer more flexibility. However, accumulator may still be in some special-purpose processors.
Stack Architecture
In computing, the computers that are based on the Stack-based CPU Organization use data structure called a stack. The stack is a list of data words. A word is a unit of data in bits of a defined bit length that can be addressed and moved between various memory storage devices and the processor.
Stack system uses the Last In First Out (LIFO) access method which is the most commonly used data access method in most of the processor. A CPU register is used to store the address of the topmost element of the stack which is known as Stack pointer (SP) register.
In stack-based CPU organization, ALU operations are performed on stack data. It means both the operands are always required on the stack. After manipulation, the result is placed in the stack.
The two main operations that are performed on the operators of the stack are Push and Pop. These two operations are performed from one end only.
Register To Register Architecture
In this type of register-based CPU organization, the processor makes use of multiple general-purpose registers, instead of a single accumulator register.
This CPU Organization is also known as General register-based CPU Organization. In this type of CPU organization, the computer uses two or three address fields in their instruction format.
Each address field points to a general register or a memory word. The CPU will make use of available registers for heavily used variables and intermediate results. The register being the fastest memory results increased CPU execution speed.
Register Memory Architecture
In this type of register and memory based CPU organization, the processor makes use of both multiple general-purpose registers as well as memory referencing instead of a single accumulator register.
This CPU Organization is also known as register memory CPU Organization. In this type of CPU organization, the processor uses one or two register address fields and memory referencing in their instruction format.
Each address field in the instruction format might point to either a general register or a memory word. The CPU will make use of either available registers or memory address for storing variables and intermediate results for optimal CPU performance.
Register Stack Architecture
The register-stack architecture is the combination of register and accumulator operations. In the register-stack architecture, all the ALU operations that must be done are pushed to the top of the stack. Whereas the output of the ALU operation is kept at the top of the stack.
More difficult mathematical operations can be simplified using the reverse polish method. Another approach is to utilize the concept of a binary tree to represent operands. This means that the reverse polish process may be simple for these programmers but challenging for others. To carry out push-and-pop operations, new hardware must be developed.
ALU FAQ
Arithmetic Logic Unit FAQ
What Is Arithmetic Logic Unit ?
In computer architecture, the arithmetic logic unit ( ALU ) is an combinational electronic circuit which handles arithmetic and logical operations of the processor. The ALU is a fundamental building block of all the microprocessor chips.
The ALU essentially works as a mathematical brain for the central processing unit ( processor chip ) that performs the arithmetic and logical operations performed by the processor.
What Are the Components Of ALU ?
The ALU components depending upon its architecture can consists of arithmetic unit and logic unit. The arithmetic unit performs all arithmetic operations.
The logic unit handles all decision making logical operations of the CPU. For example, logic functions are AND , OR , Exclusive-OR bitwise XOR.
What Is CPU ?
A processor ( CPU ) is an integrated circuit ( IC ). The processor consist of millions of IC chips and each IC chip consist of millions of tiny component called transistor. The Transistor is madeup of silicon which is a semiconductor material .
The processor ( CPU ) controls all the activities of the computer system. And therefore it is referred as brain of the computer system. There are two main computer processor manufacturers Intel and Advanced Micro Devices ( AMD ). These two companies produce most of the processors used in desktop, laptops and notebooks.
A Central Processing Unit ( CPU ) performs millions tasks per second to execute a computer program by performing the basic arithmetic, logical, control and input / output ( I / O ) operations as specified by the program instructions.
A CPU is placed on the motherboard in a processor socket with locking liver mechanism in order to fix the processor chip properly into the processor socket . The processor socket contains a IC socket in which the processor chip is firmly mounted . A heatsink is mounted on the top of the processor chip which protects the processor from excessive heat generated.
What are Functions Of Arithmetic Logic Unit?
The arithmetic logic unit performs three important functions to execute the program instructions and operate on the data.
The control unit decodes the machine instructions and directs the ALU to perform specific operation.
- To perform The Arithmetical Operations.
- To perform The Bitwise Logic Operations.
- To perform The Bit Shift Operations.
What are Logic Gates ?
The Logic gates are electronic components used in the digital electronics to handle logical functionality.
The logic gate is an electronic circuit used in the ALU to compute a function on a two valued signal. Logic gates are the basic building block of digital circuits.
The logic gates accept two inputs and produce one output. Some logic gates like NOT gate has only one input and one output.
The logic gate being a digital electronic component, can handle inputs only in the binary format (only low 0, or high 1) by receiving the input voltage.
Join The Best Seller
Computer Science Online Course
This is the most comprehensive and unique Computer Science And Programming Fundamentals course Online which will give you in depth understanding of most important fundamental concepts in computer science And Programming .