
Java Programming Tutorial For Beginners
Java programming basics are easy to understand and the language syntax is similar to other programming languages . And therefore , it is relatively much easier to learn the java programming basics .
Java is one of the most popular , versatile and widely used programming language . Java powers over three billion devices . One of the biggest advantage of java is the platform independence which makes it suitable for wide range of applications.
Java is said to be platform independent because java program once written can run on any platform as long as that device has Java Runtime Environment ( JRE ) .
Java language is simple , powerful , secure , object oriented and versatile high level programming language which makes it perfectly suitable for creating different types of applications .
Java Programming Basics

If you are a student who wants to learn java especially for android development then this tutorial guide you step by step for learning the java programming essential skills for mobile app development using the android studio.
This java tutorial has been specially designed for absolute beginner as well as for experienced programmers . This tutorial is a comprehensive resource to learn all the java fundamental programming concepts , java language syntax and its practical implementation.
Java Programming
Table Of Contents
- Programming Paradigms.
- Object Oriented Programming ( OOP )
- Java Programming Basics.
- Java Program Compilation.
- Java Program Examples.
Java Programming Basics
Table Of Contents
History Of Java
Java was developed by James Gosling and his colleagues while working on a project at Sun Microsystems in year 1991. The Java language was initially developed for developing embedded software for electronic gadgets .
The Java language development project started as a project called “Oak” by James Gosling . However , due to some legal issues this language was later on renamed as Java . Java was officially released in year 1995.
The Java language syntax is quite similar to the syntax of C language and C++ . However , some crucial features of these languages were excluded in Java syntax in order to make the java more secure language .
The primary motive of the development of java was to create language that is platform independent . This means java program should have the capability of “Write Once, Run Anywhere”.
The java’s birth also coincided with the advent of smart mobile handsets . The java’s capabilities were tailor made for mobile and touch screen devices . Java soon became one of the most popular , versatile and widely used language which now powers over 3 Billion devices .
Java Programming Basics
Introduction To Computer Programming
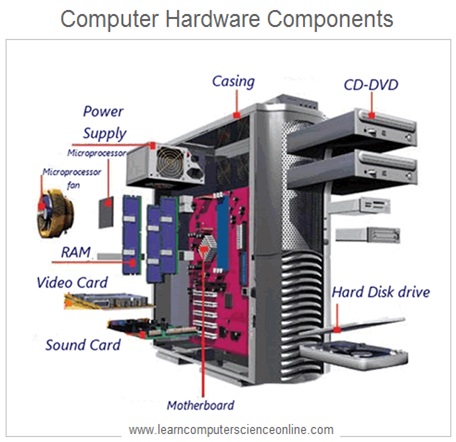
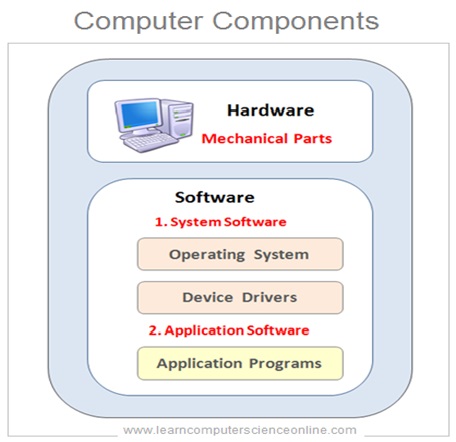
The computer system consist of both software and hardware components . The operating system is a system software that manages all the crucial functions of the computer system.
A computer system is a digital electronic device that needs to be programmed to perform any meaningful task . The computer program directs the computer microprocessor ( CPU ) to perform the desired operations as per the program instructions .
The computer program consist of set of program instructions and each of these instruction performs a specific task . The computer program can be written using any high level programming language .
Some of the most popular and commonly used programming languages include C language , C++ , Java , Python , JavaScript , C # ( C Sharp ) , MS .Net and many other high level languages.
However , the computer system can understand and execute only machine code instructions in binary . The binary code consist of only two numbers that is 0 ( zero ) and 1 ( One ) .
Java Programming Basics
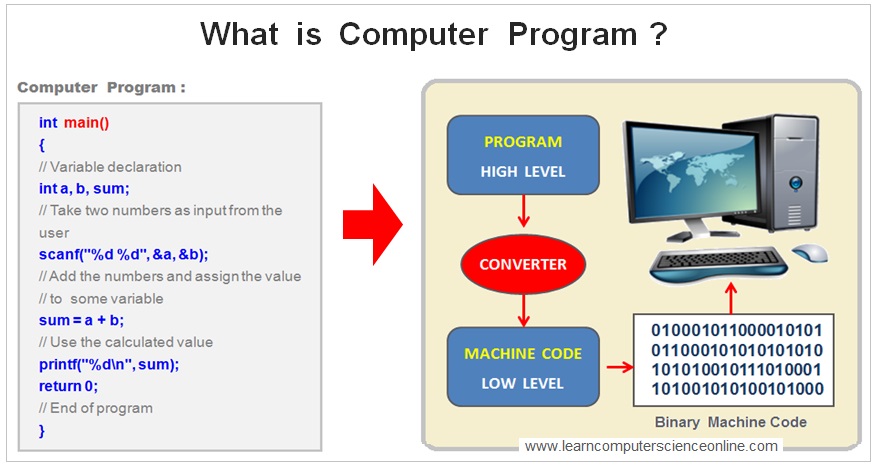
And therefore , all the programs written in any programming language must be first converted to machine code instructions in binary which computer CPU can interpret and execute .This conversion process is known as program compilation.
When the user initiates the program execution , the operating system allocates the necessary resources in terms of processor time and the main memory ( RAM ) . The CPU is the brain of the computer system . The CPU reads these instructions from the memory and executes the program instructions one by one .
What Is A Computer Program ?
Java Programming Basics
What Is Java ?
Java is high level , platform independent , object oriented programming language. Java was developed by James Gosling at Sun Microsystems in year 1991 .
The Sun Microsystems where Java originated defines java as simple , object oriented , network-savvy , interpreted , robust , secure , architecture-neutral , portable, high-performance , multi threaded ,dynamic computer language.
We can think of Java as a general-purpose , object-oriented language that looks a lot like C and C++, but Java is much easier to use and far more versatile . Java lets you create more secure and robust programs that can run on multiple platforms.
Java comes in three editions . Java standard edition is used to create general purpose software . The enterprise edition of java is used to create far more complex and distributed enterprise level applications.
Whereas the micro edition of java is a light weight that is optimized for mobile app and embedded system development .
Java Programming Basics



Java Programming Basics
Why Java Is Preferred For Android Development ?
Android is a Linux based open source software platform and operating system that is optimized for the touch screen and mobile devices. Android applications can be developed by using the Java programming language and the Android SDK.
Java has now become a default choice for android development for all types of mobile application development . Android apps are extensively used on all android devices .
Android is now owned and managed by Google in association with Open Handset Alliance ( OHA ) . The OHA consortium is led by Google.
Android has lion’s market share of over 86% in the mobile operating systems . In addition to Java , android application development can be done in other languages such as JavaScript and Google promoted Kotlin.

Java Programming Basics
However , Java still continues to be the most preferred programming language for android mobile app development . And therefore ,the Java programming professionals are in great demand in various industries and also in the job market.
The Java Platform Micro Edition ( Java ME ) is optimized for mobile applications . The Java ME provides a high performance , flexible and secure environment for creating applications that are suitable for embedded systems and mobile devices.
The mobile applications built with Java ME are portable, secure, and can take the advantage of the native capabilities of the mobile device.
The Android Studio which is most popular and extensively used Integrated Development Environment ( IDE ) has seamless integration with Java . And for this reason expertise in java programming basics is prerequisite for android development.
Java Programming Basics
Programming Paradigms
The programming paradigms are simply different approaches to organize and structure the program code . Alternately , paradigms can also be referred as methodology , approach or a particular style to write and organize the program code .
The computer science has evolved both in the hardware and software domain. Similarly , the computer programming approaches and problem solving techniques has also evolved over the period of last few decades .
There are a number of alternative approaches to program methodology and the manner in which the program is written and organized while building a software. Each of these programming style offers different advantages and limitations.
These different programming styles are referred to as programming paradigms. Each of these paradigm represent fundamentally different approaches to building solutions to specific types of problems using programming.
Different programming languages came in to existence which allow the programmers to write the code as per one paradigm. Most programming languages fall under one paradigm, but some languages have elements of multiple paradigms.
Before we start learning the java programming basics , let us first understand various programming methodologies . The programming paradigms can be broadly be grouped into three types .
Programming Paradigms
Non-Structured Programming
The non-structured programming paradigm was used in the first generation of programming languages . Basic , COBOL and Assembly language are examples of non-structured programming.
As per non-structured programming style of programming, the code is organized as collection of program statement which gets sequentially executed from first statement till the last statement.
In non-structured programming paradigm the code is written in a single continuous file . Each program statement has a statement number or label.
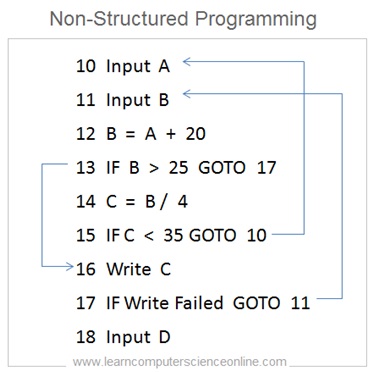

One of the major limitation of non-structured approach was the difficulties due to spaghetti code which makes the program code difficult to debug.
The spaghetti code is a badly entangled code due to liberal use of GOTO statement . In large and complex code it is difficult to track the flow of control due multiple use of GOTO statements.
The non–structured programming also had major limitation in terms of difficulty to reuse the program code. Further , it was not possible to secure the data from unintended changes in this approach.
Java Programming Basics
Structured Programming
The next generation of programming languages like C language and Pascal were based on the concept of structured programming.
In structured programming , the program code is modularized in the form of functions . The function once defined can be called number of times. A large chunk of code can be replaced by a single function .
The structured programming approach also made it easy to debug the program code . For example the logical errors in the program code can be easily fixed by making the necessary corrections in the function code .
A structured language has constructs like IF-THEN-ELSE condition statement , WHILE-NEXT conditional loop , SWITCH-CASE statements, DO-WHILE loop , and FOR-NEXT loop. These statements helps to simplify the program algorithm .
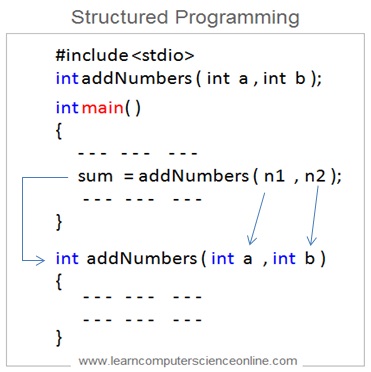

Limitations Of Structured Programming
Although structured programming approach was a major improvement over its predecessor. However , this approach also had some major limitations.
In structured programming approach , it was difficult to secure the data and it was difficult to protect the data was unwarranted operations. In large and complex code , it is difficult to track the operations of various functions operating on the same data which can lead to spaghetti code.
Further , in structured programming approach , it is difficult to perfectly model the real world objects ( Entities ) .
OOP
Object Oriented Programming
OOP Introduction
The object oriented programming ( OOP ) approach was next generation of programming paradigm developed to overcome the limitations of structured programming approach. The OOP methodology addressed two major limitations of the structured programming.
In structured programming , first it was difficult to secure the data and second , it was also difficult to model the real world entities .
The OOP methodology does not provide direct access to the program data . The OOP allows the data to be treated as private and the programmer can restrict the data access .
Further , with object oriented ( OOP ) approach , allows the programmers to easily and realistically model the real world entities .
A good understanding of OOP fundamental concepts is essential for learning the java programming basics.
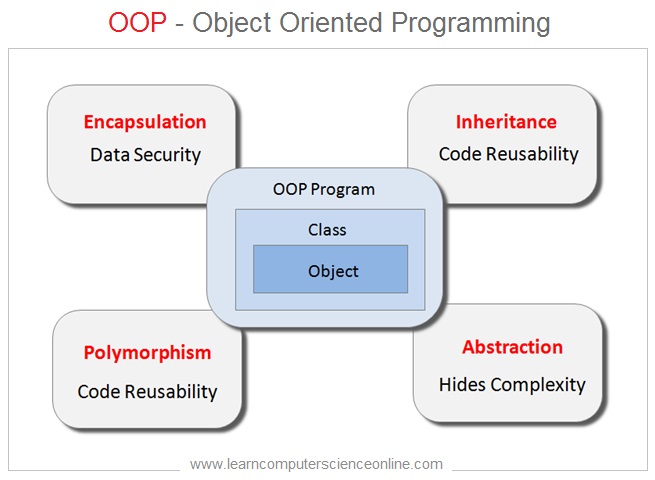
Java Programming Basics
What Is Object Oriented Programming ?
The object oriented programming is an approach to the software application development where all application components are treated as objects.
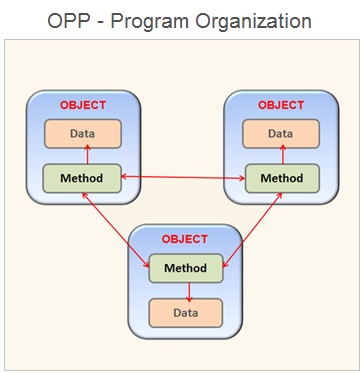
An object is a smallest component of a program that has some properties and behavior . The object behavior defines how to perform certain actions and interact with other elements of the program.
The objects are the basic units of object Oriented programming . In OOP methodology , the program code is organized in the form of set of classes . The class defines the object in the program code.
Each and every class represents a real world entity. In other words , the entities are objects that need to be represented in the program code .
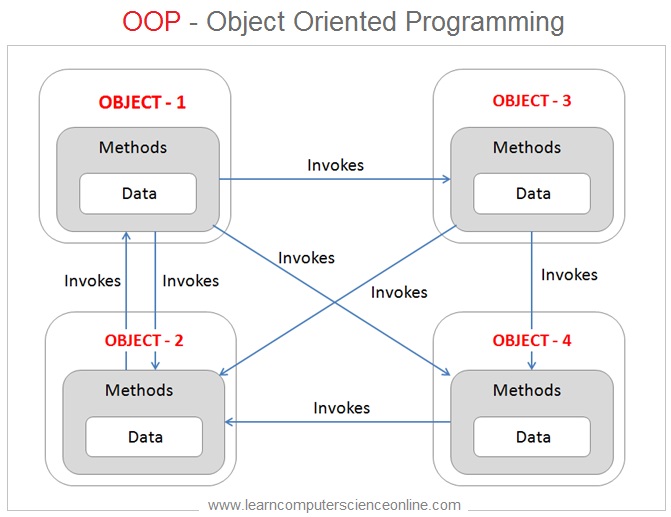
OOP Example
Android App Development
The java programming basics is essential skill for android developers . Let us consider one example of android application since java is the post popular and widely used programming language for android development.
Let us consider example of java programming used for an android app development to understand the OOP concept of an Object and class .
An android application consist of set of activities ( Screens ) through which user interacts with the android application. The activity is simply a screen displayed to the app user .
Various controls ( Views in android ) are placed on the each activity for user to give inputs or perform some actions on these controls .
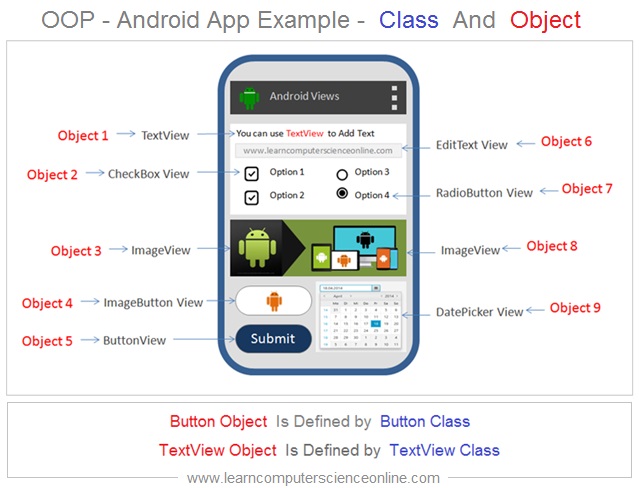
Object Oriented Programming Example
Each activity ( Screen ) and the various controls displayed to the user are objects . For example TextView is an object that displays text on the screen .
These TextView objects are created during the program runtime as defined in the TextView Class . Similarly , command button are objects of button class .
The various object used in the application program has corresponding classes . These classes defines the properties ( data ) and the behavior ( methods ) associated with that object .
You might find it a bit confusing initially but don’t worry , we are going to discuss all these OOP concepts much more in detail later on under java programming basics.
Java Programming Basics
Let us now start getting familiar with java programming basics and the object oriented programming fundamental concepts .
In order to get the best out of this java tutorial it is important for you to maintain a logical learning sequence . This will help you logically correlate various java programming and object oriented programming ( OOP ) fundamental concepts.
The following learning sequence in this java tutorial will guide you understand each topic step by step. So , lets dive in .
Java Programming Basics
Table Of Contents
Java Environment
The java environment refers to the runtime environment provided by the java platform needed for the development and the execution of java programs .
Java is a versatile language which is used for creating different types of software applications . Java is used for building desktop applications , enterprise level applications , web applications , android applications for mobile platforms and applets for web services .
The java developers would typically need all the three components required for the development and also for testing ( JDK = JRE + Tools ) the java applications.
Whereas the end user ( client ) machine would need only components ( JRE = JVM + Class Libraries ) necessary for execution of java program.
The java environment has three major components . These components include :
- Java Development Kit ( JDK ).
- Java Runtime Environment ( JRE ).
- Java Virtual Machine ( JVM ) .
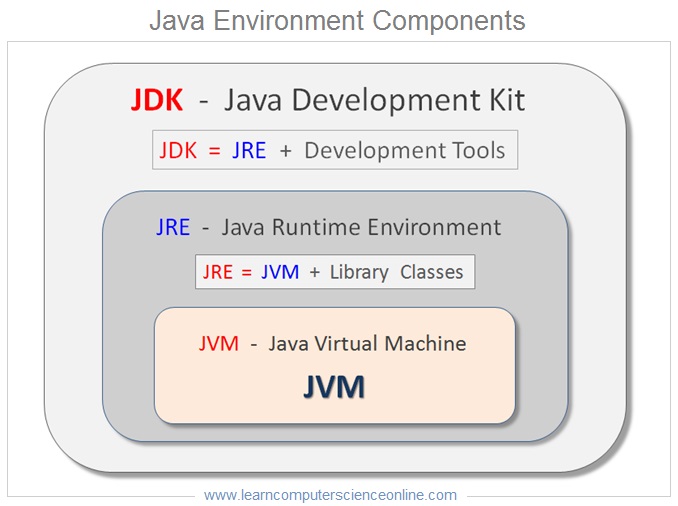
Java Development Kit ( JDK )
The Java Development Kit as the name suggest is primarily required for development of java applications . The JDK consist of two components . These two components are Java Runtime Environment ( JRE ) and some other application development tools.
The java development kit is intended for java developers . The JDK includes all the three components required for the development and also for testing ( JDK = JRE + Tools ) the java applications.
JDK = [ JRE + Development Tools ]
Java Runtime Environment ( JRE )
The Java Runtime Environment as the name suggest is primarily required for providing runtime environment to the java applications . The JRE consist of two components .
These two components are Java Virtual Machine ( JVM ) and some class libraries. The JRE is installed on the end user machines for providing runtime environment to the java software application needed for software deployment.
JRE = [ JVM + Library Classes ]
Java Virtual Machine ( JVM )
The JVM stands for Java Virtual Machine . The JVM is a vital component of the JRE which provides runtime environment to the java application.
The JVM accepts the platform independent bytecode ( dot class file ) generated by the java compiler ( javac.exe ) as input . The JVM converts the bytecode into platform specific native machine code and executes this code line by line .
Java Programming Basics

Java Programming Basics
How Java Program Works ?
Java is a high level programming language . The java program gets compiled in two stages . The java compiler does not directly compile the java program to native machine code .
Instead , the java program first gets compiled into a platform independent bytecode. In the first stage we use the java compiler ( javac.exe ) which compiles the high level java program code into intermediate bytecode ( dot class file ) .
This bytecode ( dot class file ) is a platform independent code that gets further compiled to native machine code. The JVM ( Java Virtual Machine ) then executes this platform specific native machine code line by line .
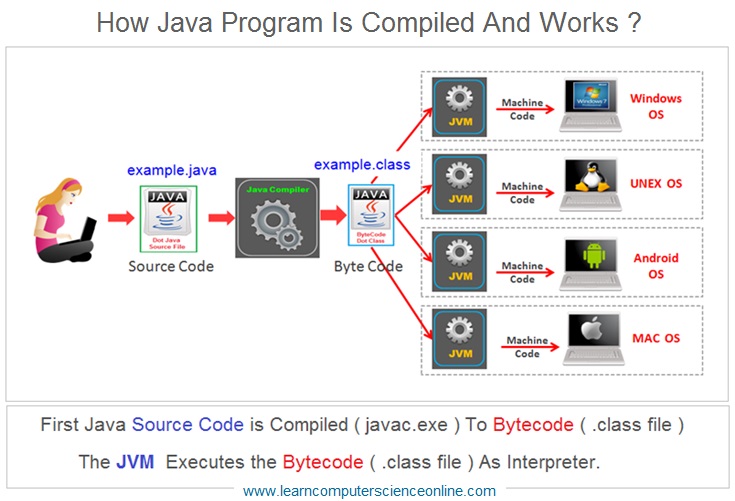
Java Program Compilation
The java program is said to be platform independent because the java program is compiled and executed in two stages .
In the first stage the java compiler ( javac.exe part of JDK ) converts the java program source code file ( YourProgram.java ) into a bytecode ( Also referred as dot class file YourProgram.class ) .
This java bytecode is a platform independent executable code that can run on any platform ( windows , mac , Linux , Unix ) which has Java Runtime Environment ( JER ) installed on it .
Java Program Compilation
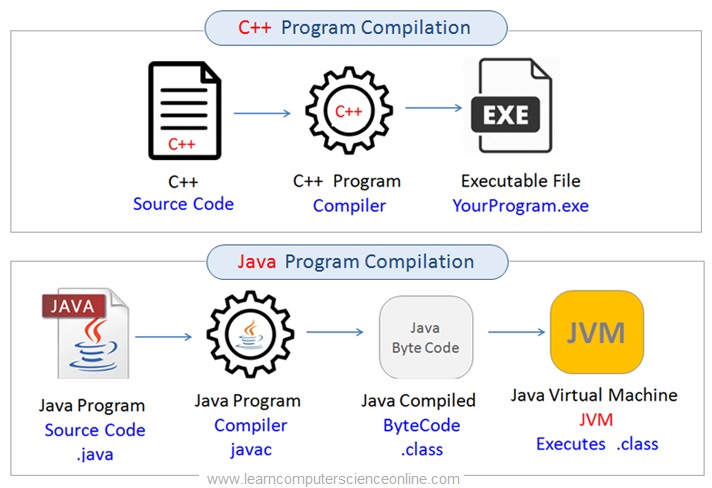
The JVM ( Java Virtual Machine ) is an essential component of the JRE. The JVM is an interpreter and responsible to execute the java bytecode ( .class file ) line by line.
And therefore , java program is platform independent but the JVM part of JRE is platform dependent . And for this reason we need to select the correct version java during the java download depending upon the platform .
Java Programming Basics
Java IDE
How To Write Java Program ?
Writing the java program is easy . In order to develop the java programs you need first install the java development kit ( JDK ) on your computer system . The java installation process has been explained in detail.
In addition to JDK you will also need a special software commonly referred as Integrated Development Environment ( IDE ) . Some of the popular and free Java IDE include :
NetBeans , Eclipse , IntelliJ IDEA Community Edition , Android Studio for android app development using java , Enide Studio 2014 and BlueJ.

How To Write Java Program ?
IMPORTANT
Although many java learners start writing the java programs using any IDE . However , if you are an absolute beginner then writing java programs with IDE may not be the best option .
It is highly recommended to initially start writing your java programs using any simple text editor and save this file as java program source code ( Example.java ). You can also compile these programs from the command prompt.
Writing the java program using any text editor will give far better understanding of how java program works , how java program is compiled and executed at the command prompt.
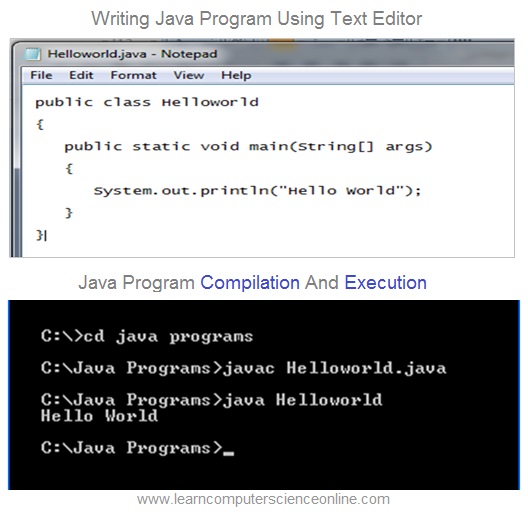
How To Write Java Program ?
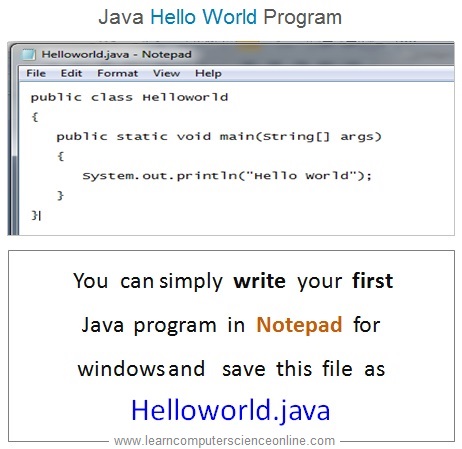
- In this example , we have used Notepad software as a text editor to write the Hello World java program .
- You can simply write your first Java program in Notepad which is commonly used as text editor for windows and save this file as Helloworld.java
- Java is case sensitive And the class name must start with the capital letter .
- Java being object oriented , the program code must be written inside a class.
- The source code Helloworld.java is compiled at command prompt using java compiler javac.exe
- The compilation will generate Bytecode Helloworld.class
- The JVM will start program execution with main method .
- Command Prompt is also known as cmd.exe OR cmd ( after its executable file name ) . The cmd is the command-line interpreter on Windows and for other operating systems.
Java Programming Basics
How To Write Java Program ?
The IDE provides fully automated environment for java program development. The IDE provides a complete set of software and tools to write , debug and deploy professional level Java software applications.
This is similar to learning the car driving either on a fully automatic car or on a manual transmission car. The manually driven car will teach you the judgment of clutch , gear and accelerator . Once you learn the driving then you can switch over to fully automatic car .
So , initially spend some time on the text editor writing your first few initial java programs. And once you understand the whole process of how java program works , then you can always switch over to any suitable IDE.
Java Programming Basics
Class And Object In Java
Java being a object oriented programming language views the various entities that needs to be represented in the program only in the form of objects .
The concept of class and object is a fundamental concept of Java programming basics . In object oriented programming the class contains the description of an object .
And therefore , as a programmer or a software developer , we must have a pretty good clarity about what is an object in the programming world and how to represent the objects in the program that we write .
What Is An Object In Java ?
We are all aware of the objects that exists in the real world . The world around us is full of objects such as house , car , pen , computer , cat , dog and also you as an individual .
We can recognize these objects in real world as per their properties such as shape , weight , height , color and also the behavior associated with these objects .
For example a dog is a real world object which has unique identity in terms of its breed , color , height , weight and other such properties . The dog also exhibits a behavior such as running , walking , sleeping and barking.
Java Programming Basics
What Is An Object In Java ?
However , in the programming world , the entities that we want to represent need to defined in the program while writing the program code .
When the program execution starts, the operating system allocates the necessary resources to the process in terms of processor time and the memory.
An object in object oriented programming ( OOP ) can either be either tangible or intangible entity . For example car is a tangible object whereas a bank account is also a valid object but an intangible object.
An Object Definition In OOP
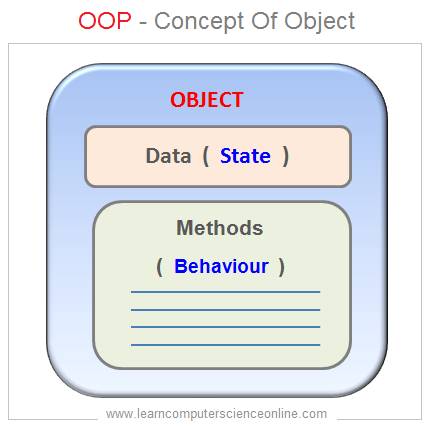
An object in OOP can be defined as an entity that is represented in the program which has a state , exhibits some well defined behavior and can be uniquely identified.
In OOP, an object is an entity that has properties ( data ) for identifies its state and methods that identifies its behavior or functionality . Every object is unique either by its state or because of its behavior. The events associated with object depicts the change of state.

Java Programming Basics
What Is Class In Java ?
As stated earlier , Java is a object oriented programming language and views the various entities that needs to be represented in the program only in the form of objects .
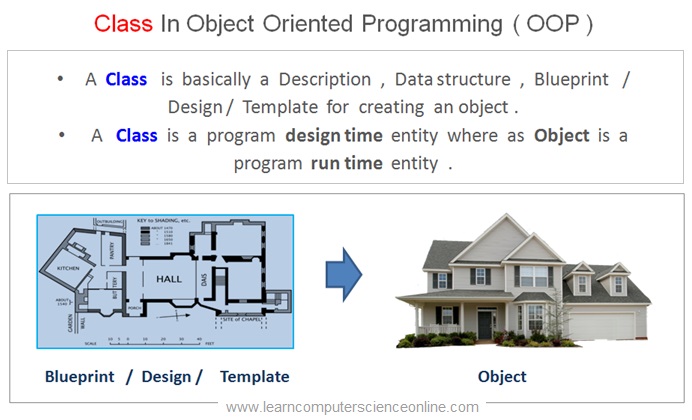
And therefore , the objects need to defined in the program code . In object oriented programming , a class is a description of an object . In other words , a class is a blue print or a template for creating the object .
In other words , an architect creates a blueprint for the house to be built . This architectural drawing defines the qualitative and quantitative dimensions of the house .
Similarly , the programmer needs to define the object in terms of its properties ( data ) and the behavior in terms of the methods .
For example , the android mobile app developer use Button class to create Button objects on the user interface ( activity ) and then defines the method in java code on button click event .
What Is Class In Java ?
What Is Class In Java ?
The programmer first identifies the various objects that need to be represented in the program . The programmer then define these objects in the form of classes in the program code .
And for this reason , the java program code essentially consist of number of classes . The classes are defined in the java program code as per the java language syntax and the object oriented programming design principles.
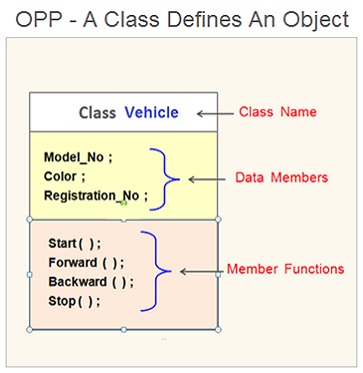
In the following example , we have created a class with class name as Vehicle . This class Vehicle has data members and also member functions . The class binds together the data related to an object and the methods ( functions ) which operates on the data .
In this class Vehicle the data members include Model No , Color and Registration No. Whereas the member methods include Start ( ) , Forward ( ) , Backward ( ) and Stop ( ) .
IMPORTANT
The Class Is a design-time entity . Whereas an Object is a run-time entity.
Java Programming Basics
What Is Class In Java ?

Java Programming Basics
Java Program Structure
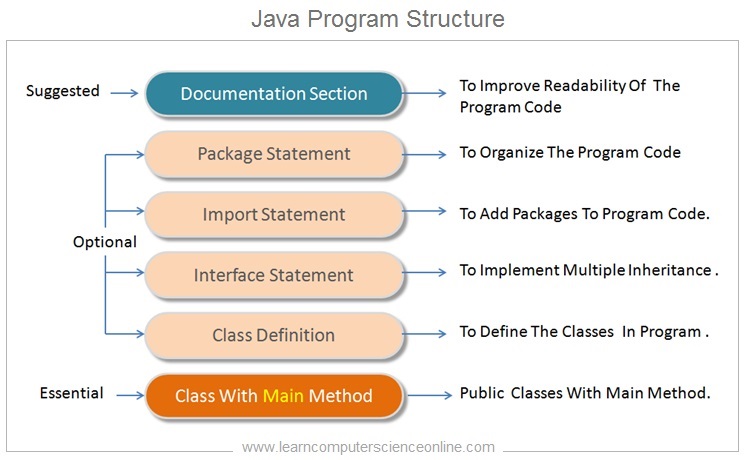
It is important to understand the java program structure . The java program structure consist of different sections. Each section in the java program code handles a specific part of the program .
The different sections in the java program structure improve the maintainability and the readability of the java program code . The Java program structure include six sections.
- Documentation Section.
- Package Statement
- Import Statements.
- Interface Statement.
- Class Definition.
- Class With Main Method.
Java Documentation Section
The documentation section is optional and contains the comments in the java program code . The comments are part of the program that are ignored and not compiled by the compiler.
The main purpose of the comments in the documentation section is to improve the readability and the maintainability of the java program code.
The comments are added to the program code especially in the large and complex project where number of programmers are writing the program code. The comments inserted in the program code makes it easier to understand the program code.
Java Documentation Example
Single Line Comment // Example Comment Text
Multiple Line Comment /* Example Multi-line Comment Line 1
This Is comment Line 2 */
Documentation Comment /** Example Documentation Comment
Generated Automatically */
Java Programming Basics
Java Package Statement
The java package allows the programmer to create a group of similar types of classes , interfaces and sub-packages . These packages once created can be easily imported into the program code .
The java packages allows the code re-usability and the programmer can simply add the required classes by importing the package that contains these classes . The java packages can be either built-in packages or user-defined package.
The package statement in java program is optional and identifies the package that a Java program is a part of that package. The program belongs to the default package If the java program does not include a package statement.
If program does not include the package statement then the program belongs to the default package, which is simply a package without any name.
Java Package Statement Declaration
package package_name;
Java Import Section
The java programmer can use the classes defined in other packages by directly importing the packages into the program code using import statement. The programmer can either import some classes or all the classes present in the package.
Java import statement is optional. The java programming language provide number of built-in packages which programmer can use to add additional functionality to the program .
Once the required package is imported, the classes in the package become available in the program code and can be referred to directly by using only its name. The import statement is very useful and frequently used in the Java program.
Java Import Statement Declaration
import java.io.* ;
Java Interface Section
Java interfaces are similar to class but contains methods without any implementation details. The interfaces contains only method declarations .Java language does not allow multiple inheritance . However , the programmer can use multiple inheritance using an interface.
Java interface is an optional section. Java interface statement is used when programmers want to implement multiple inheritances within a java program code.
Java Programming Basics
Java Class Definitions
In java program , all the entities that need to be represented in the program in the form of objects are included as class . And therefore , a Java program may contain several classes defined in the program.
The Class declarations are an important element of the java program code and the java program contains number of classes .
Java Class With Main Method
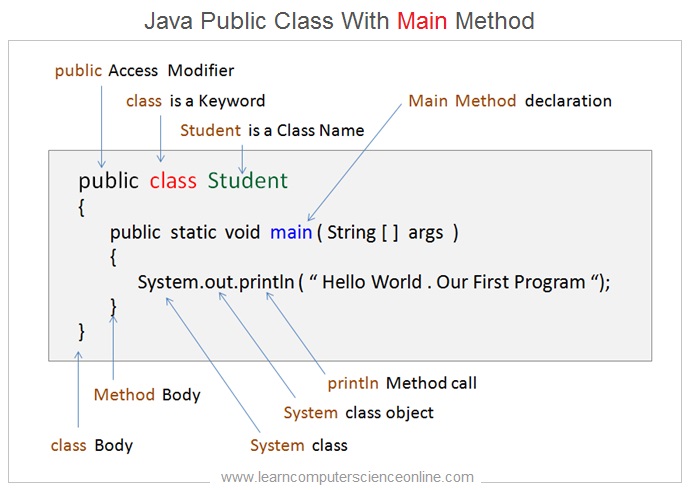
As we have discussed earlier , the java program can contain number of classes . However , the java program file which will be compiled to generate the bytecode ( Dot Class File ) must have one public class that contains the main method .
The java program file must be saved with the same class name that contains the main method . This main method is the starting point of the program execution .
The Java Virtual Machine ( JVM ) which executes the java program initiates the program execution by invoking the main method .
Java Programming Basics
Java Program Hello World
Let us now create and understand our first java program Hello World . You can write this program using any text editor ( such as Notepad ) and then compile this program on the command prompt .
In order to write and successfully execute the Java Program Hello World , you need to follow the following steps .
- Install the JDK on your computer .
- Set the JDK path with environment variable.
- Write the program in text editor .
- Save the program file with class name ( HelloWorld.java ).
- Compile the program : javac HelloWorld.java
- This will create java bytecode ( HelloWorld.class )
- Execute the program : java HelloWorld
- This will print Hello World
Java Programming Basics
How To Write Java Hello World Program ?
Java is object oriented and thus the Java program code is written inside a class . And therefore the first step is to create a class with class name HelloWorld .
A class is declared by using a java keyword class . The first letter of the class name should always be a capital letter ( HalloWorld ). The program code is written inside the class body enclosed within curly braces. For example class HelloWorld { Class Body } .
The file containing the program code should be saved same as class name with java extension . This program file should be saved in the directory that contains the JDK .
You need to download and install the JDK the correct version of java on your computer . Further , you also need to create an environment variable and set the path for JDK. This step is required only once after installing the JDK.
Java Program Hello World
Java Program Compilation And Execution

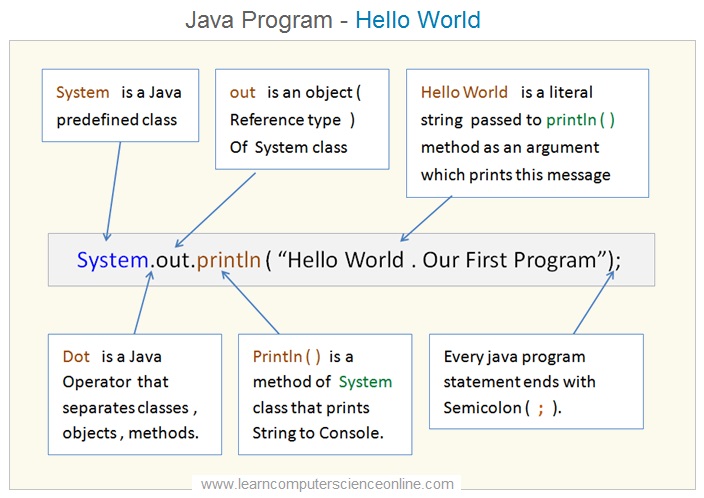
You can use the java compiler ( javac.exe ) to compile the java program . Now you can start the command prompt and change the directory where the java is installed .
For program compilation , start the command prompt. The Command Prompt is also known as cmd.exe OR cmd ( after its executable file name ) . The cmd is the command-line interpreter on Windows and for other operating systems.
To Compile the Program : javac HelloWorld.java
The HollowWorld.java after the compilation step will create a bytecode HelloWorld.class file in the same directory.
To Execute the Program : java HelloWorld
This command will execute the dot class file HelloWorld.class and Hello World will be displayed on the screen.
Java Programming Basics
Java Installation
How To Install Java ?
JDK Installation
Java Environment
Java installation process is simple . As a java developer , you need all the tools necessary tools for the development and execution of the java program.
For java development , we need to install the Java Development Kit ( JDK ) . The JDK includes the JRE ( Java Runtime Environment ) and essential tools used for java program development.
The JDK download and installation can be carried out in the following steps .
- Download Java JDK.
- Install Java JDK.
- Set the JDK Path With Environment Variable .
Download Java JDK
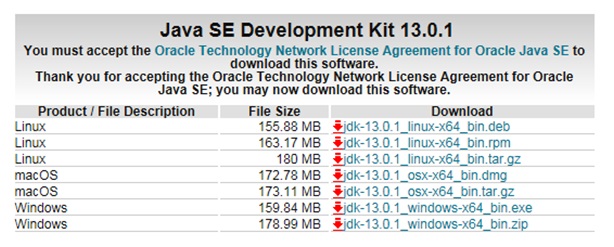
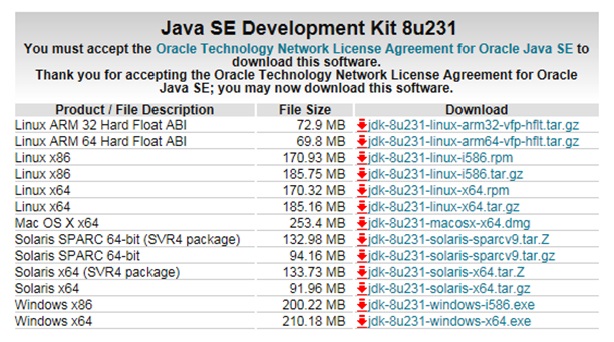
For java installation on your computer , we need to first download the correct version of java JDK from ORACLE official website . You can download the Java from Oracle official download page .
Depending upon the platform details of your computer ( Microsoft Windows , MacOS , Linux ) , you can select and download the correct version of the JDK.
Java Download Link : Download Java From Oracle Page
The JDK SE 8 supports both 64 Bit And 32 Bit Platforms .
Java JDK Installation
The java installation process is simple and similar to any other software installation process.
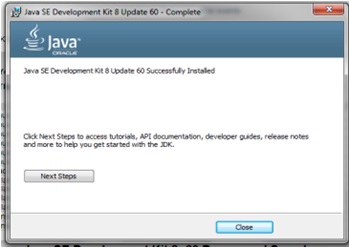
Java Programming Basics
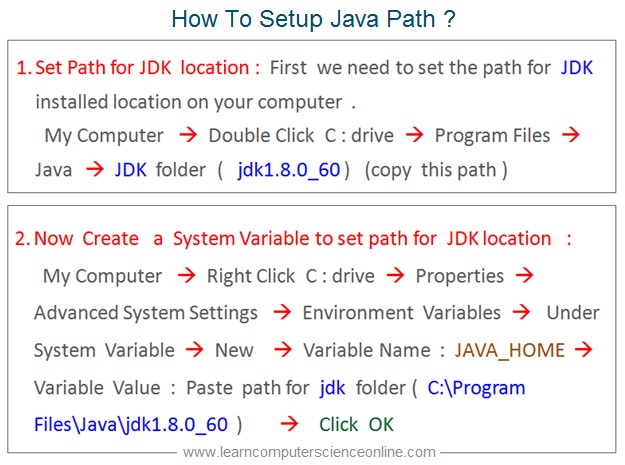
How To Setup Java Path ?
After the successful completion of java installation , the next step is to set up java path for JDK location.
The operating system needs to know the location of the JDK tools used for java program compilation and the application launcher . And for this reason we need to set the path for JDK .
The JDK path can be permanently defined either by appending the existing system environment variable or by creating a new system variable.
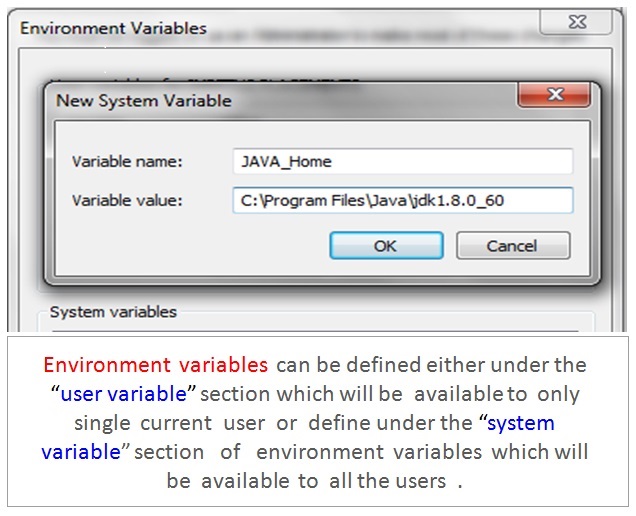
If you are saving the java source file inside the jdk / bin directory then path is not required to be set because all the tools will be available in the current directory .
However, If your java program source file is saved outside the jdk / bin folder then it is necessary to setup the path of the JDK folder.
The system variables JAVA_HOME and JRE_HOME maintain the locations of the JDK and JRE installed directory respectively.
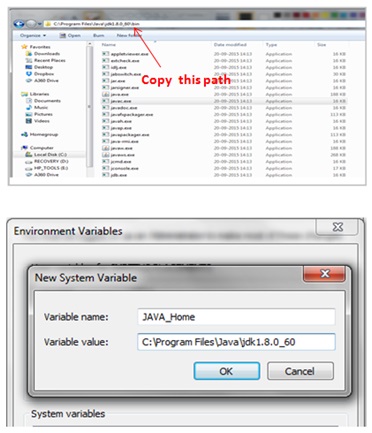
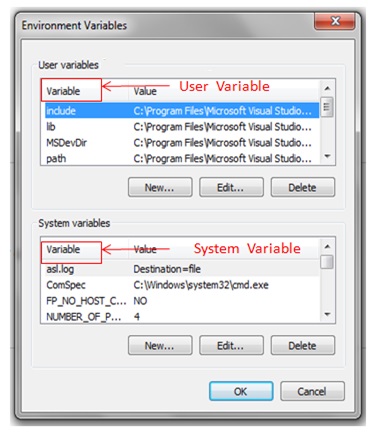
Let us now create a system variable to setup the path for JDK location . First go to my computer and right click on the C drive to select the properties option . Next select the advanced system settings .
Next select the environment variable . Now under system variable select new and type JAVA_HOME in Variable value . Now paste the path of the bin folder where java.exe and javac.exe are located in JDK folder and click OK.
Java Programming Basics
Java Syntax
Java Program Structure
Java Class Declaration
Java Methods
The java program is essentially a collection of objects which are represented in the program code in the form of a classes . These objects communicate with each other to perform the various tasks as per the program instructions.
Like any other programming language , the java program code must be written as per the set of rules and principles that govern the structure of the java program code and the statements .
The java syntax is verified and enforced by the Java Compiler ( javac.exe ) during the program compilation process . The java compiler will output the bytecode only after all the errors are resolved .
However , If you are writing your java program using any IDE ( Integrated Development Environment ) then the code editor will check and suggest the corrections if any .
Let us now learn the java syntax rules for various program elements.
Java Language Syntax
Table Of Contents
Java Program Structure
Java is a class based language . And therefore, all the program code is enclosed in a class except the package import statements , documentation statements and package declaration.
The java program code can be organized in various packages . The package is a collection of related classes . These pages can be imported into java program code using import keyword .
Java Is Strongly Types Language
Java is said to be a strongly typed language because as the java syntax rules all the variables used in the program code must be declared and the datatype should be specified .
Java Programming Basics
Java Class Declaration
Java program can have any number of classes . These classes are organized in packages to improve the readability of the program code.
The class should be declared as per java syntax rules . The class is declared using the java keyword class followed by the class name . The initial letter of the class name is capitalized by convention.
Example : class YourFirstClass { Class Body }
The java source code file with .java extension can contain only one public class . The java main method should be declared in this public class which is starting point of program execution. The java source code file should be saved with the same name as java public class name .
public class MyFirstJavaProgram
{
public static void main ( String [ ] args )
{
// Main Method Body
}
}
The java class can inherit only one parent class . The sub class can be created using the extend keyword . A class can inherit more than one interfaces using java keyword interface.
Example : class B extends class A { Class B Body }
Example : class C implements interface A , B { Class C Body }
Java Class Name
The class is an important element of the Java program . The java program can have any number of classes . The programmer can organize these classes into different packages .
As per standard naming convention , the first letter of the java class name should in upper case. When more than one word is combined for a class name then the first letter of the each inner word is also kept in uppercase .
The name of the public class that contains the main method must match the java source code file name.
Example : class StudentDetails { Class Body }
Java Programming Basics
Java Methods
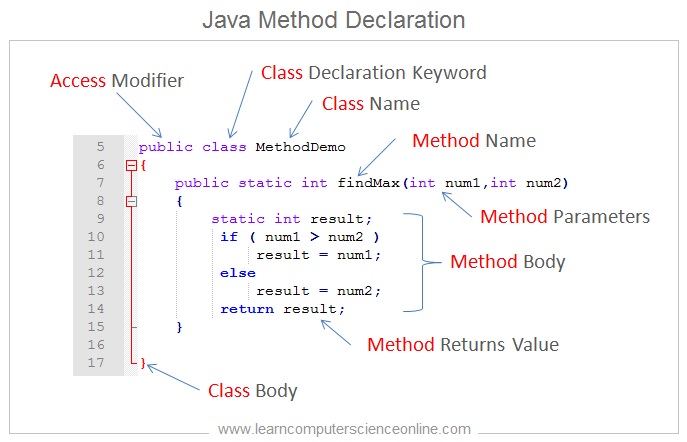
Java Method Declaration
The java program contains classes and a class contains member variables and functions ( methods ). A method is a named block of code which performs a specific task as per the program statements.
The variables within a class defines the state of an object whereas the methods defines the behavior of an object . The methods operate on the data ( variables ) to perform various operations.
The method needs to be explicitly called ( invoked ) in the program code along with the arguments. The methods are also alternately referred as functions in other language but both means the same.
The java programmer can make use of either built-in methods or user defined methods created as per the program needs .
The built-in methods are part of the classes that program can readily use by importing the package which contains the class in which these methods have been defined.
Java Method Types
The methods can be classified in java in number of ways . The java methods can either be standard library method ( built-in methods ) or user defined method .
The java languages provides extensive library of standard methods which are predefined in the java language . The programmer can simply import the package which contains the class in which the method is defined to use in the program.
The programmer can also create and define a method as per the program requirements . The programmer can use these methods by organizing the classes containing these methods into various packages .
- Pre-defined ( Builtin ) Methods.
- User-defined Methods.
- Instance Methods.
- Static Methods
The java methods can also be classified on the basis of scope of the method into two types such as instance method and static methods .
Instance Method
The programmer can also create a method by declaring a method within a class body . The method declared inside a class is referred as instance method . Which means each object ( instance ) of the class will have this method.
The instance method can be called ( Invoked ) by creating an object of the class and by using the object reference and the dot operator.
Static Method
A method can also be declared at the class level by using the java static keyword. The static method will be one single method common for all objects . The Static method can access only static member variables within a class.
The static method can be called ( Invoked ) without creating an object of the class and by using the class name and the dot operator. The main method is an example of the static method .
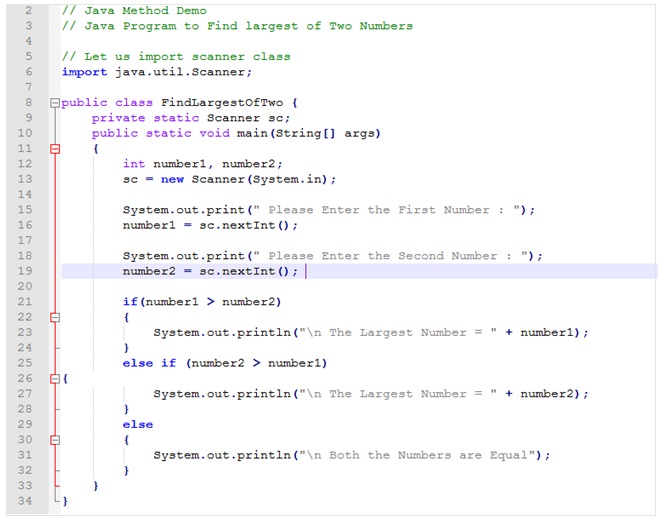
Java Method Example
Java Program To Find The Largest Of Two Numbers
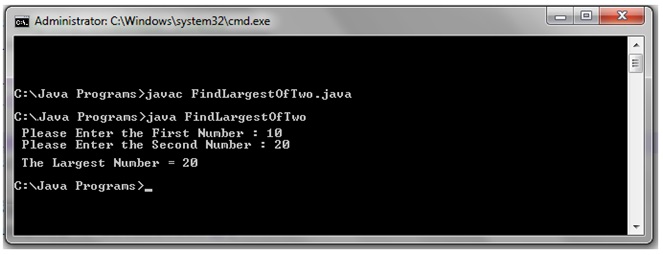
Java Programming Basics
Java Variables
What Is a Java Variable ?
The data is an important element of the java program. The class binds together the data and the methods which operate on the data .
The variables are named memory locations with specific datatype assigned to it which acts as a container for temporarily storing the values in the memory during the program execution.
The variable is temporary memory space created during the program execution that can store some value as per the datatype defined in a program instruction. This memory space can be accessed using a variable name as specified in the program code .
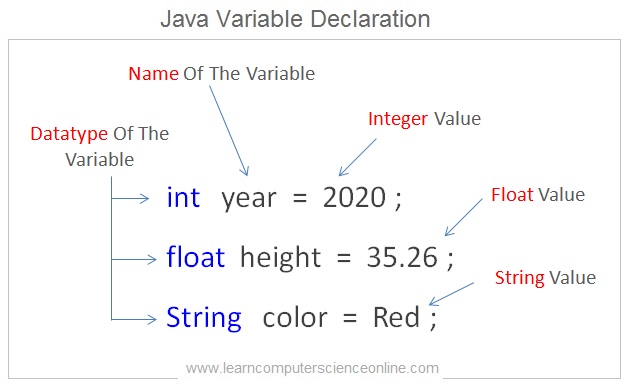
A variable can be declared with only one datatype. Once the variable is declared of a specific datatype then during the program execution different values of same datatype can be stored into the variable.
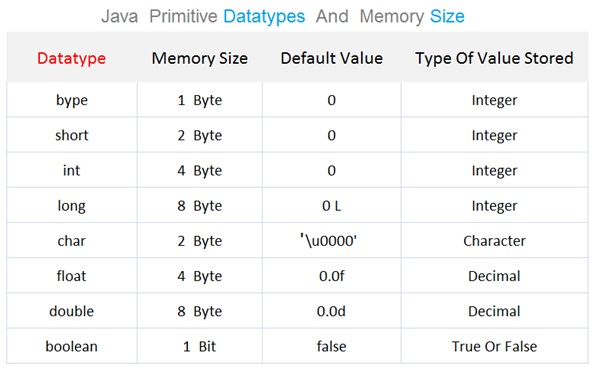
Each data type has specific range of the minimum and maximum value that can be stored into the variable. Depending upon the variable datatype the required bytes of memory is allocated by the operating system.
Java Variable Datatype And Size
Java Programming Basics
Java Variable Declaration
The variables are used to store the data during the program execution. The variables are referred in the program code by user specified variable names .
And therefore , the program defines the names to these memory locations and the specific datatype is also assigned to these named memory locations. The program data is stored into these named memory locations depending upon the datatype.
The java program variables must be declared in the program code along with its name and datatype. The suitable name is given to the variable as per the variable naming convention.
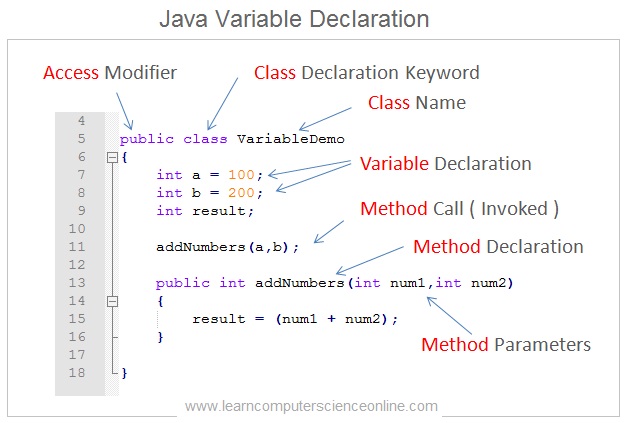
These variables are created during the program execution and the operating system allocates the required memory as per the datatype of the variable.
The scope and the visibility of the variable depends upon the type of the variable ( Local , Instance or static variable ) . The type of the variable depends upon where it is declared within a class and the type of the value assigned to the variable.
Java Programming Basics
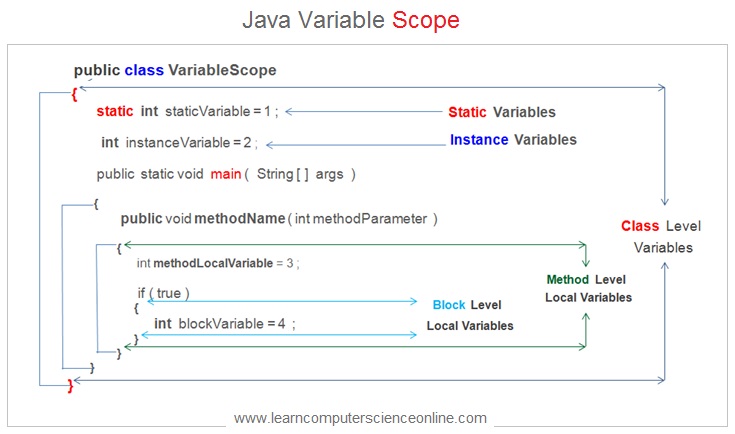
Java Variable Scope
The variables scope defines the visibility of the java variable within the program code . The scope of the variable defines the area within which the variable value can be accessed .
The Java variable is said to be in scope if the variable value can be accessed and operated upon within the segment of the program code .
The java variable scope depends upon the location where the variable is declared and the access modifier that precedes the variable name in the variable declaration statement.
The java programmer can control the scope ( visibility ) of the program variables by using the access modifiers ( Public , Private , Protected And Default ) and the location where the variable is declared .
Java Programming Basics
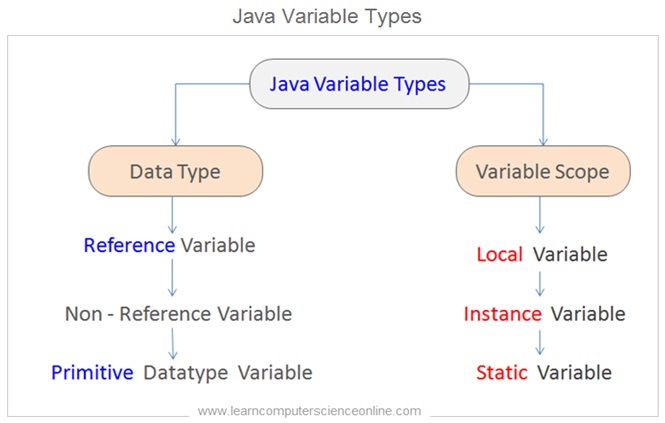
Java Variable Types
The java programming language makes use of different types of variables . The java variable types can be broadly grouped into two categories based on the type of the value stored into the variable and the scope of the variable.
The first category of the java variable type is based on the type of the data stored in a variable . As per this criterion , the java variable can either be of reference type or it can be of non-reference ( primitive ) type .
The second category of variable type is based on the scope and the life span of the variable . As per this criterion , the java variables can be categorized into three types which includes local variable , instance variable and static variable .
Types Of Java Variables
Java Programming Basics
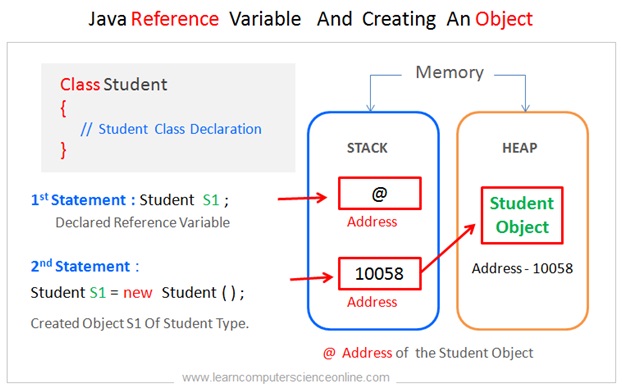
Reference Variable
The java programming language is said to be extensible because you can create a class and declare a variable of that class type . Then we can use the java new keyword and invoke the constructor to create an object .
Once the class is declared , we can create a variable of that class type and such variables are called reference variable. The reference variable can be assigned the address of an object . And therefore , a reference variable points to an object.
Let us consider one example of a Student class . We can create class Student using java keyword class . After creating the Student class, now we can create a reference variable Student class ( S1 ) which holds the address of an object and this reference variable ( S1 ) points to the actual object.
Java Programming Basics
Non-Reference ( Primitive ) Variable
The java despite being an object oriented language , the java supports primitive datatype and the programmer is allowed to use the primitive data types in the java program code .
The primitive datatype values ( such as int , float , double , String , char , boolean ) can be assigned to the non-reference variable type .
Local Variable
A local variable is said to be a block level variable .The local variables are declared and created within a block . A block is a group of java statements enclosed within a curly braces. For example variable declaration inside a methods , constructor and blocks.
A local variable in Java is a variable that is declared within the body of a method or within a instance block or in a constructor body. The local variable once declared can exist only within the method or constructor body or inside a instance block .
The local variables are not initialized and are not given the initial default values . These variables are created only during the method execution or when the constructor is invoked.
int addNumbers ( int x , int y )
{
int a = x
int b = y ;
return ( a+ b ) ;
}
Java Programming Basics
Local Variable Declaration And Initialization
The local variables are not given the initial default values and therefore local variables must be first initialized and assigned a value before it is used in any program statement.
The memory is allocated to the local variable when a method is invoked ( called ) since the local variables are declared inside the method body . The memory to the local variable is taken away and the local variables come to an end when the method execution is over .
The local variables cannot use any of the access modifiers as they exist only inside the method body. But the local variable can be declared as Final using non-access modifier.
The local variables are not given a default value and therefore the local variables must be first initialized before they can be used.
The scope of the local variables is only within a method body and the local variables cannot be accessed and used outside the method , constructor or block body .
int x = 100 , y = 200 ;
String firstName = “ Bill ” ;
float a = 4.56 , b = 3456.534 ;
Instance Variable
The instance variables are variables that are declared inside a class but outside the body of a method , constructor or a block without using static keyword. The instance variables belongs to the an object.
The instance variables are said to be an object level variable .The instance variables belongs to an instance ( object ) of a class . Each object will have its own copy of the instance variable .
The instance variables for an object defines the state of an object and stores values pertaining to the state of an object . For example if we crate a class Employee then we can create instance variables such as int employeeNumber , String department and so on .
public class Employee
{
int employeeNo ; // Instance Variable
String department ; // Instance Variable
void firstMethod ( ) { // Method 1 body }
void secondMethod ( ) { // Method 2 body }
}
The instance variables are created when the object is created and destroyed when object is destroyed. The object is created when a class is instantiated by using a java new keyword and by invoking the constructor . This is then assigned to a reference variable of that class type.
Creating An Object
Employee E1 = new Employee ( ) ;
The instance variables can be declared using any one of the four access modifiers ( public , private , protected and default ).
The instance variable initialization is not compulsory . However , if the instance variable is not initialized then its default value is zero ( 0 ) . The instance variables can be accessed by creating an object and by using the dot operator with reference to an object created .
How To Access Instance variable ?
E1.employeeNumber = 2010 ;
Static Variable
The static keyword is a non-access modifier in java that can be used while declaring a method or a variable . The java keyword static indicates that the method or variable belongs to the class and can be accessed without creating an object of the class.
The static members of the class ( methods and variables ) directly belongs to the class and does not belong to any object of the class.
The static variables are variables that are declared inside the class but outside the body of a method , constructor or a block using the java static keyword. The Static variables belong to the class.
public class StaticDemo
{
// Static Variable Declaration
public static int cityPinCode = 561001;
// Instance Variable Declaration
String firstName , LastName ;
// Local Variable Declaration
public myMethod ( int x , int y )
{
int a, b ; // Local Variables
a = x ; b= y ;
}
}
The static variables are said to be a class variable .The static variables belongs to a class and all the objects share a common copy of the static variable regardless of the number of objects.
The memory allocation to the static variables happens only once when class is loaded into the memory .It is the JVM which loads the class ( bytecode ) into the memory.
The static variables are created when the JVM loads the java program dot class ( bytecode ) file into the memory for the execution. The static variables are destroyed when the byte code execution is over.
The static variables belong to the class and can be accessed anywhere within the class. And therefore, the static variable cannot be declared inside a method in java.
Java Programming Basics
Data Types In Java
What are Java Data Types ?
The variables are created and declared in the java program to temporarily store the values during the program execution . The programmer also needs to specify the data type of variables in the variable declaration statements.
Based on the data type of a variable, the operating system allocates the required memory . The data type of the variable decides what kind of values that can be stored into this named memory location.
For example the integer type variables can store integer values ( such as 4 , 7, 23 , 1004 ) , float type variables can store floating point type values ( such as 3.14 , 245.009 , 0.7 ) similarly, the String type variables can store String Type values ( such as “Color” , “Red” , “Blue” ) . The class type reference variables can store object references .
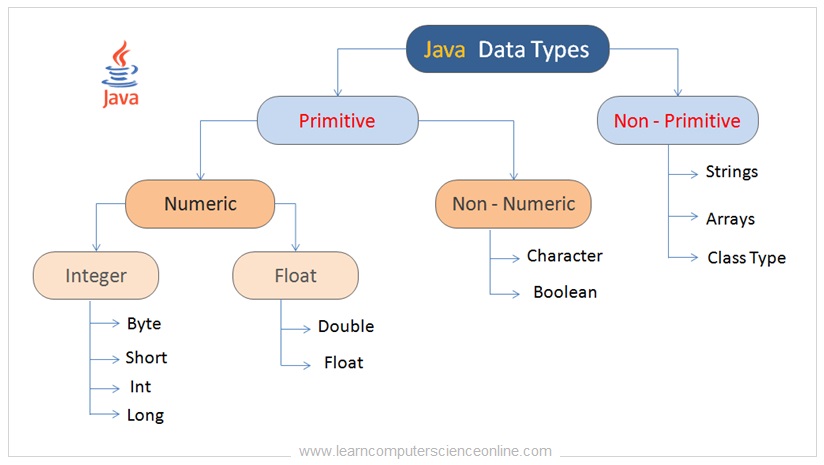
The data types in java can be broadly grouped into two types primitive type and non-primitive type . The primitive data type can be further grouped into two types that is numeric and non-numeric . The non-numeric data type include character and Boolean type. The non-primitive datatype include string , array and class type .
Primitive Data Types In Java
There are eight primitive data types supported by Java . The primitive data types are predefined by the java language and each data type is named by a keyword .
The primitive data types are the most commonly used and a special group of data types that is used extensively in the java programming . Although java is object oriented but supports the primitive data types with the help of wrapper classes.
The sizes of the primitive data types is the same for all the operating system. This is one of the key features of the java language that makes Java so portable .
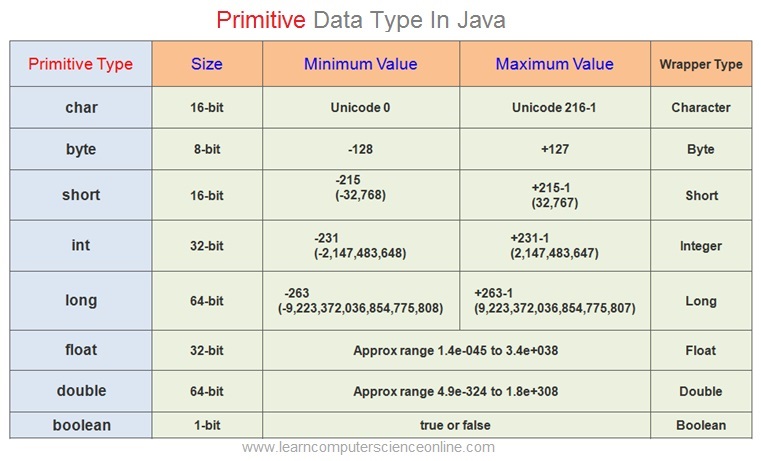
Primitive Data Types
int age = 10 ; // Integer Whole Number
float distance = 83.7 ; // Floating Point Number
char charDemo = J ; // Character Data Type
boolean booleanDemo = true ; // Boolean Data Type
String stringDemo = “Java” ; // String Data Type
Non-Primitive Data Types In Java
The non primitive data type in java include String Data type , Arrays and class types also referred to as reference data types.
The java programming language is extensible because the programmer can create classes and then define a reference variable of that class type . The reference data type do not store the values rather they store the address which points to an object .
The non-primitive data types are created by programmers as per the need of the program. The non-primitive data types are not predefined in the Java language like primitive data types.
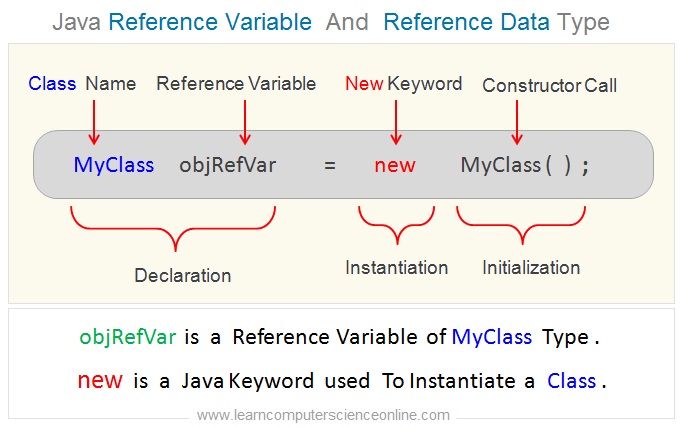
When we define a reference variable of non-primitive data types, it points to a memory location where data is actually stored in the heap memory where an object is actually stored.
Similarly , we can use arrays when we need to create a large number of variables of the same data type. An array is a single object that contains multiple values of the same data type that can be referred to with the same array name.
Java Programming Basics
Identifiers In Java
What are Java Identifiers ?
An identifier are the names given to the various program elements such as a package , class, method , interface or variable. An identifier allows the programmer to refer to that program element from other places in the program with specific name .
The main purpose of the identifiers is to easily identify the various program elements to improve the readability and maintainability of the code .
And therefore , the programmer must give meaningful names to the various program elements to improve the readability of the program code . The programmer should also follow the standard Java naming conventions for various identifiers used in the program.
Java Identifier Rules
- Java keywords are reserved words and its meaning is already predefined to the compiler . And therefore , the java keywords cannot be used for an identifier names .
- Identifiers must start with letter and cannot start with a digit . However the digits can be used after the first character ( For example name1, name2 are valid identifers ) .
- The only symbols you can use in identifiers are the underscore ( “_“ ) and dollar sign ( “ $ “ ) .
- Java Identifiers are case sensitive .
Java Programming Basics
Literals In Java
What are Java Literals ?
The java literals refers to a fixed value that does not change during the program execution . The literals in Java are a sequence of characters such as digits, letters and other characters that represent constant values to be stored in variables .
The java language supports five major types of literals. The literals in java can be any number, text, or other elements that represents a constant value.
- Integer literals.
- Floating literals.
- Character literals.
- String literals.
- Boolean literals.
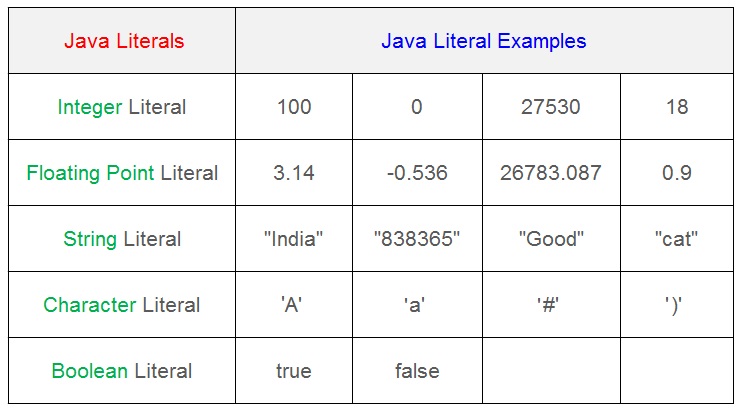
Java Programming Basics
Tokens In Java
What are Java Tokens ?
The java tokens are the smallest building block used in the java program . The java program is a collection of five basic program elements . These include classes, methods, constructors , instance blocks and static blocks .
Each of these element further consist of number of program statements and expressions . The java tokens are the smallest unit of code used to construct these program statements .
The java programming language support five types of tokens which include the java keywords, variables, constants, special characters and operators.
- Keywords.
- Identifiers.
- literals.
- Operators.
- Special Symbols.
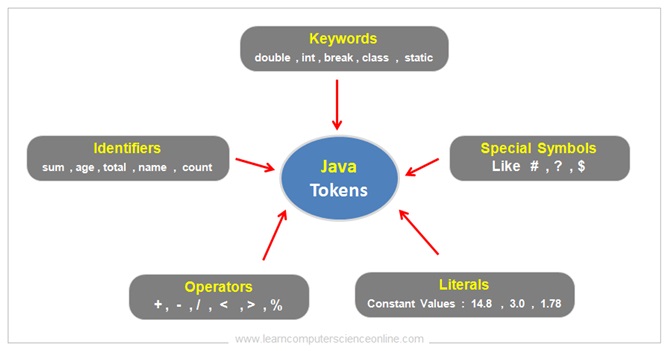
The tokens in java language are the various Java program elements which are identified by the java compiler. A token is the smallest individual block or element or unit of a java program that is meaningful to the java compiler.
Java Programming Basics
Operators In Java
What are Java Operators ?
The operator in java is a symbol that is used to perform specific operation as defined in the java language syntax .
The java program statement or expression can contain number of operators . An operator in Java is a special symbol that directs the compiler to perform some specific mathematical or non-mathematical operations on one or more operands.
The java language provides different types of operators to perform various operations . For example unary operator, arithmetic operator, relational operator, shift operator, bitwise operator, ternary operator and assignment operator .
The Java language supports eight different types of operators.
- Arithmetic.
- Uniry.
- Assignment.
- Relational.
5. Logical.
6. Ternary.
7. Bitwise.
8. Shift.
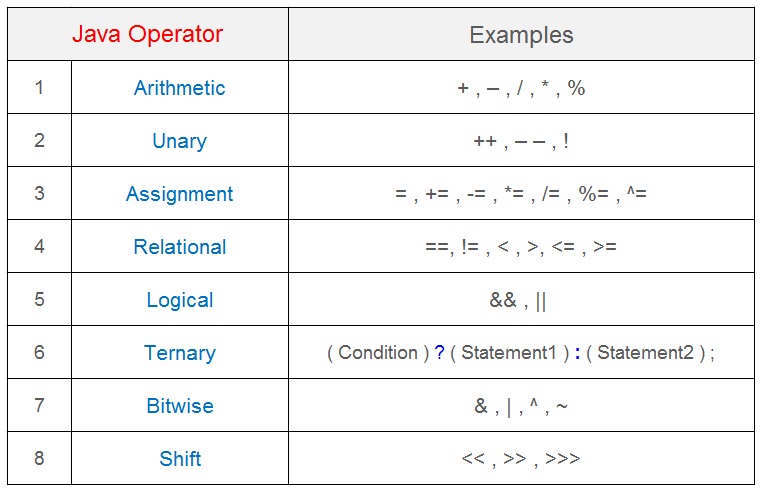
The operator precedence decides execution sequence. The operators with higher precedence are evaluated first before the operators with relatively lower precedence.
Java Programming Basics
Access Modifiers In Java
What are Access Modifiers In Java ?
One of the most important aspect of the object oriented programming is the ability to control the access various program elements such as classes , methods and variables .
By restricting the access permissions , the programmer can protect the critical data from unintentional modification. And therefore , the access modifiers are an integral part of object-oriented programming.
The Java Access modifiers are also known as visibility modifiers . The access modifiers are used to regulate the visibility ( access ) of the classes , variable and methods in the java program .
The access modifiers determine which variable or method in a class, can be called ( invoked ) from which part of the program by another method in another class or sub-class.
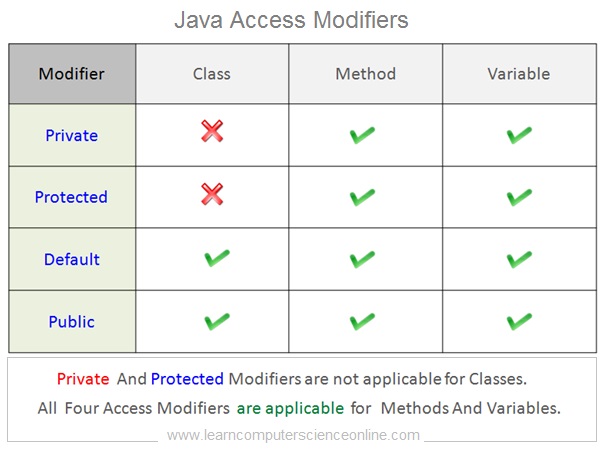
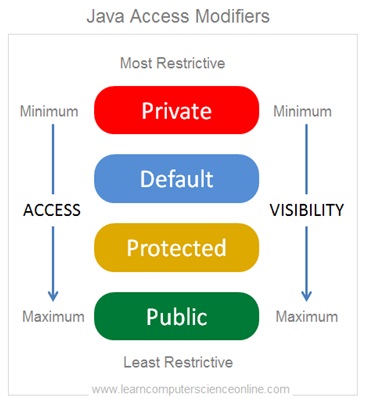
The Java language provides four access levels and three access modifiers. The four access levels are as follows .
- Private Access Modifier.
- Default Access Modifier..
- Protected Access Modifier.
- Public Access Modifier.
Private Access Modifiers
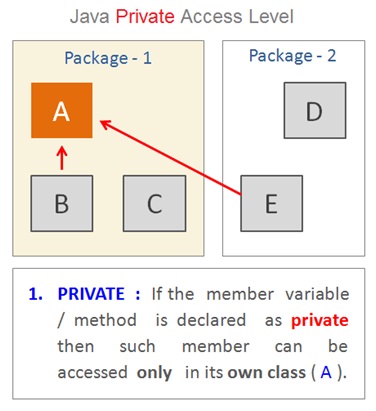
The private access modifier is the most restrictive modifier which allows access only within the class .
Which means the members of sub classes , other classes in the same package and also the members of from other packages do not get access to the private member.
If the class member method or a variable is declared as private then such member will be accessible only within its own class ( A ). A class ( outer class ) cannot be declared as private .
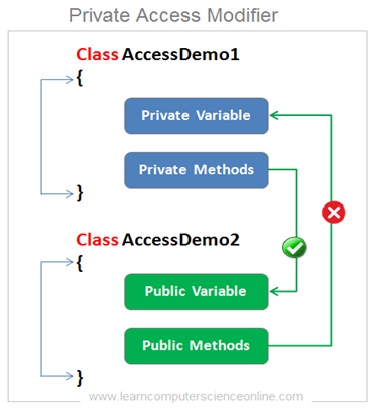
However , an inner class ( a class within class ) can be declared as private .The class members such as methods and variables can be declared as private.
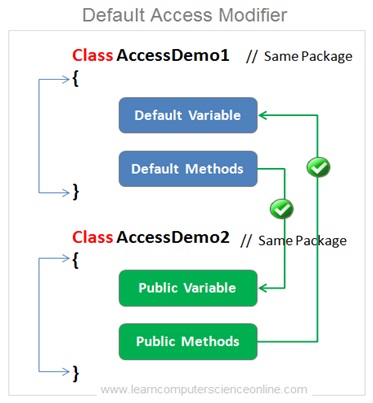
Default Access Modifiers
The default access modifier will be applicable when we do not specify any access modifier while declaring a class , method or variable then the access level is said to be the default .
The default access modifier is the second most restrictive modifier which allows access only within the package .
Which means the members of the same class as well as other classes in the same package can only have access to the default members . But the members of other packages and also the sub classes does not get access to the default member.
In other words , If the member is declared as default then it can be accessed by any one within the same package.
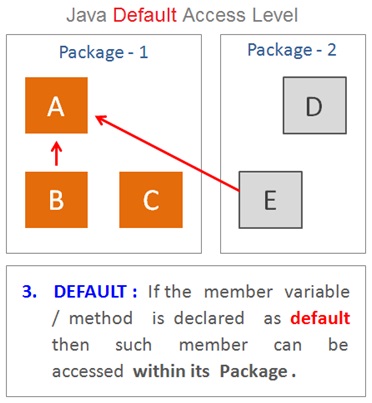
As explained in this example the class A , class B and class C belongs to the same package ( package 1 ) . And hence , the members of class B and class C can get access to the default members of class A .
Whereas the class D and class E belong to the different package ( package 2 ) and hence cannot get access to the default members of class A .
Java Programming Basics
Protected Access Modifiers
The protected access modifier will be applicable when we specify protected access modifier while declaring a method or variable
The protected access modifier is the third most restrictive modifier which allows access within the package and also to the members of the sub classes in other packages .
Which means the members of the same class as well as other classes in the same package and sub classes in other packages can have access to the protected members . But the members of the classes in other packages ( except sub classes ) do not get access to the protected member.
In other words , If the member is declared as protected then it can be accessed by anyone within the same package and also by the sub classes outside the package.
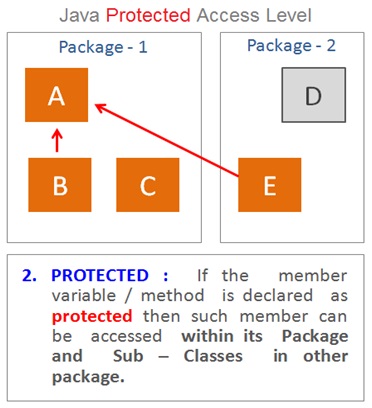
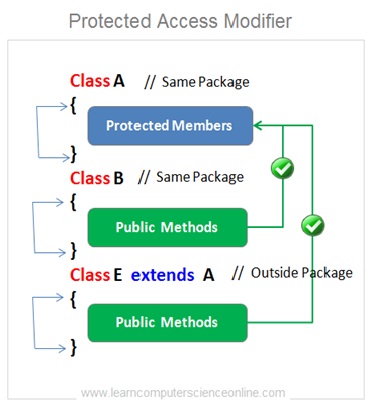
As explained in this example the class A , class B and class C belongs to the same package ( package 1 ) . And hence , the members of class B and class C can get access to the protected members of class A .
The class E extends class A which is a sub class of class A and therefore will get access to the protected members of class A . Whereas the class D belong to the different package ( package 2 ) and hence cannot get access to the protected members of class A .
Public Access Modifiers
The public access modifier will be applicable when we specify public access modifier by using public keyword while declaring a class , method or variable.
The public access modifier is the least restrictive modifier which allows access within the package and also to the members of the sub classes and other classes in other packages .
The public access is the most liberal access and provides maximum visibility under which a public member can be accessed anywhere in the java project.
In other words , If the member is declared as public then it can be accessed by anyone from all the packages within the java project.
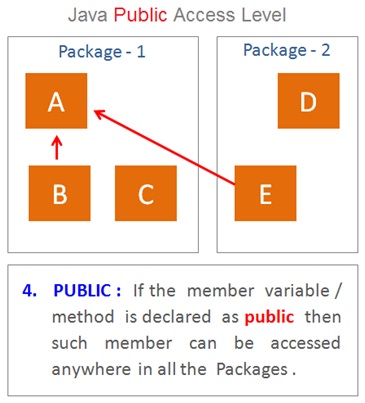
As explained in this example the class A public members can be accessed from all the classes and sub classes from all the packages .
Java Programming Basics
Java Keywords
What are keywords In Java ?
In the Java programming language, a keyword is a special reserved word that has a predefined meaning for the java compiler . The programmer can only use these keywords in the program code as per the java language syntax rules .
The java keyword meaning is already known to the compiler and therefore , the java keywords cannot be used as names for variables, methods, classes, or for any other identifier.
If you are using an IDE ( Integrated Development Environment ) then these reserved keywords are highlighted with different colors to facilitate the code syntax and improves the code readability.
Java Programming Basics
Java Control Statements
What are Control Statements In Java ?
The java program is a collection of program statements. In many situations , the programmer has to repeat statements either certain number of times or repeat the statements till the loop condition is evaluated to true .
As the name suggests , the control statements allows the programmer to control the logical flow of the program as per the program logic . The loop statements are the integral part of most of the program logic and also improves the program code readability .
The java control statement allows the programmer to repeat some program statements enclosed within the body of the loop .
The loop statements are also a type of program statement used in all programming languages to repeat ( reiteration ) some program statements for required number of times . The loop will reiterate the statement block till the time the looping condition is evaluated to either true or false .
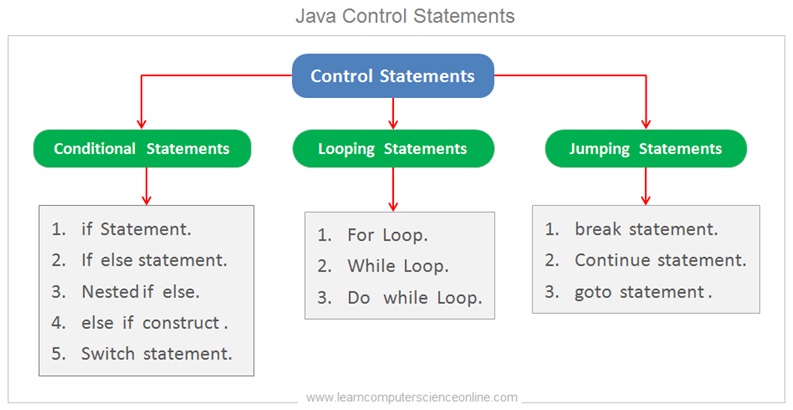
- Conditional Control Statements.
- Looping Control Statements.
- Jumping Control Statements.
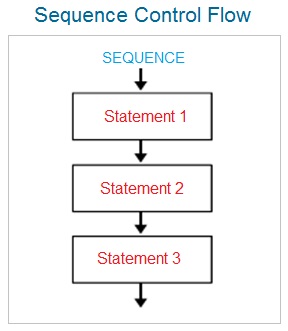
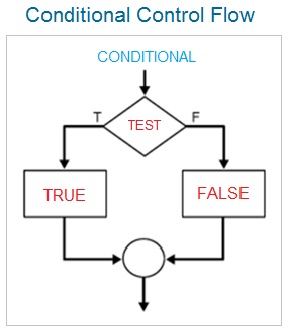
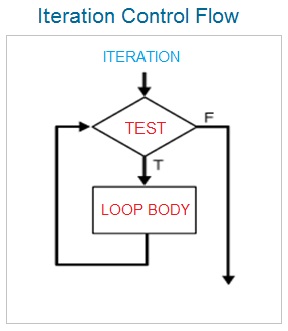
Java Programming Basics
Java Conditional Statements
The control statements are used to control the flow of the program . The conditional control statements allow to first test the condition ( usually an mathematical expression ) and then execute the statement block depending upon the outcome of the condition ( either true or false ) .
The control flow statements allow the java program execution either sequentially , or conditionally ( with the help of if-else, and switch ) or iteratively ( with the help of loops ) or by using the combination of various control statements depending upon the program logic.
Types Of Java Conditional Statements
The java language makes use of following conditional statements .
- if Statement.
- if else Statement.
- Nested if else Statement.
- else if Construct.
- switch Statement.
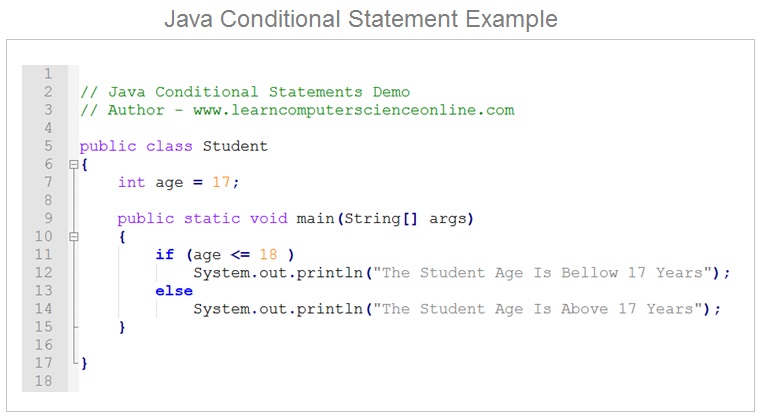
Java Programming Basics
Java Looping Statements
The java looping statements are used to repeat the program statement or a block of statements code either certain number of times or till the time the looping condition is evaluated to either true or false .
The java programming language provides three types of looping constructs which can be used by the programmer whenever a block of statements is required to be executed number of times . The java looping control statements include :
Types Of Java Looping Statements
- while Loop Statement.
- do while Loop Statement.
- for Loop Statement.
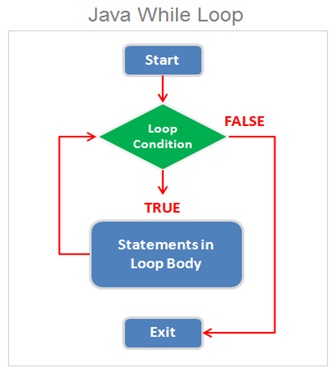
Java While Loop
A while loop is a control flow statement that allows the block of statements to be executed repetitively based on a given Boolean condition is evaluated to either true or false.
A while Loop provides a exit mechanism such as loop counter variable which will keep the track of the number of iterations after being incremented or decremented and the loop will be terminated once condition is evaluated to false.
The while loop will always evaluate the looping condition first and then execute the code if the Boolean condition is evaluated to true .
Example :
Java While Loop
int i = 0 ;
while ( i <= 10 )
{
Syetem.out.println ( i ) ;
i ++ ;
}
Java Do While Loop
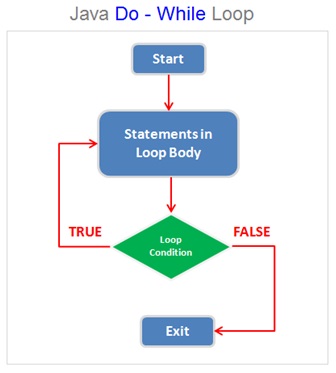
A do while loop is a control flow statement that allows the block of statements to be executed repetitively based on a given Boolean condition is evaluated to either true or false.
The do while loop will always first execute the statements in the loop body and then it will test the looping condition. The do while execute the code at least once .
The do while loop will continue the repeated execution till Boolean condition is evaluated to true . The loop will exit when the Boolean condition is evaluated to false.
Example :
Java Do-While Loop
int i = 0 ;
do
{
Syetem.out.println ( i ) ;
i ++ ;
} while ( i <= 10 ) ;
A do while loop must provide a exit mechanism such as loop counter variable which will keep the track of the number of iterations after being incremented or decremented .
The main difference between while loop and do while loop is the order of execution of the loop condition. The while loop always first test the loop condition whereas the do while loop will always first execute the statements in the loop body and then test the loop condition.
Java Programming Basics
Java For Loop
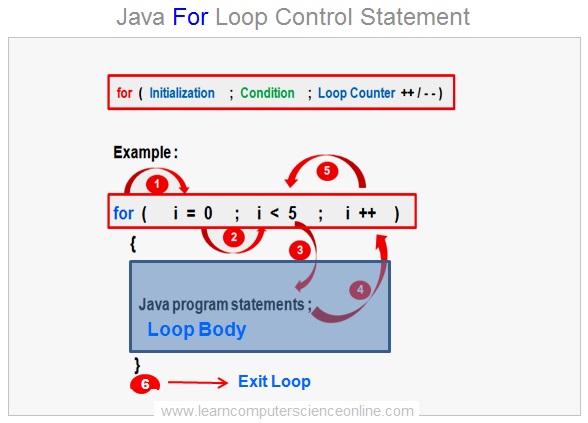
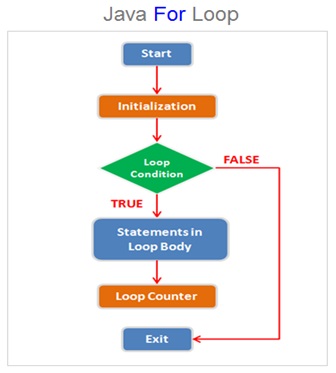
The for loop will keep executing the code within its body for the specified number of times as defined in the looping condition expression and will continue till the condition expression is evaluated to true .
The control will exit the for loop either when the looping condition expression is evaluated to false or the code executes a break ( keyword ) statement which terminates the for loop .
The for loop is mainly used in the program code where the number of loop iterations are known before the loop starts and the loop counter is defined in the condition expression to track the current number of the iteration completed by the for loop .
How Java For Loop Works ?
- The for loop starts with first initialization of the loop counter variable which is executed only once in the beginning of the loop .
- The loop condition expression is then evaluated with current value of the loop counter .
- The statements within loop body are executed if the loop condition Boolean expression result to true .
- The control is sent to the loop counter increment / decrement section where the counter is modified .
- The control then again checks the loop condition with reference to the current value of the loop counter variable .
- The loop will exit if condition loop expression is evaluated to false .
Example :
Java For Loop
for ( i = 0 ; i < 5 ; i ++ )
{
Syetem.out.println ( i ) ;
}
Java For Loop Example
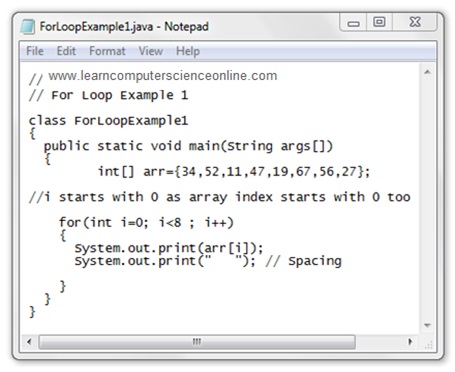
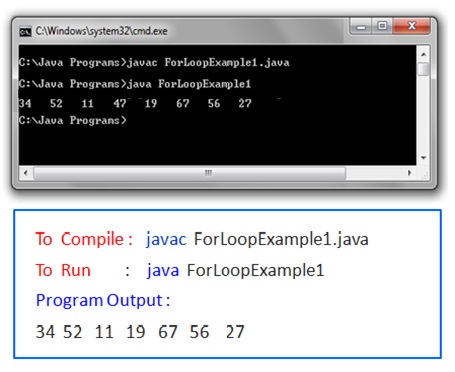
Java OOP Concepts
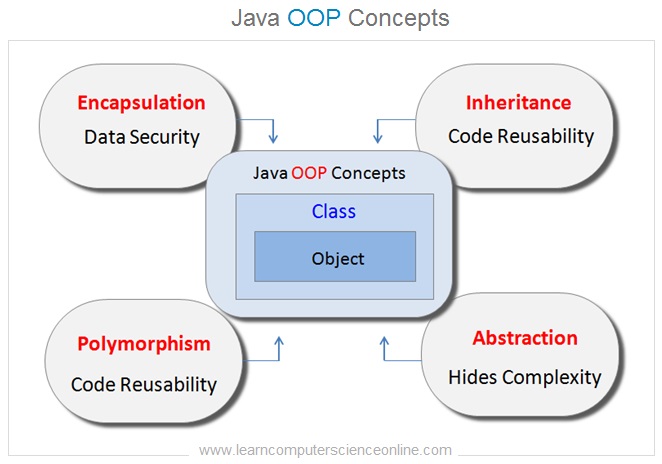
Java Principles Of Object Oriented Programming
The OOP ( Object Oriented Programming ) concepts are also referred as principles of OOP in Java . Java is an object oriented programming language which is governed by six basic fundamental core concepts .
The OOP is a programming paradigm ( approach ) which is based on the fundamental OOP design concepts which includes concept of class and object , inheritance , encapsulation , abstraction and polymorphism .
The object oriented programming is a methodology ( paradigm ) that is designed to simplify the software development and maintenance by implementing some fundamental design principles and concepts. These OOP design concepts are :
- Concept Of Class.
- Concept Of Object.
- Inheritance.
- Encapsulation.
- Abstraction.
- Polymorphism.
Java Programming Basics
Java Programming Basics
Java Concept Of Class
Let us first start defining the concept of class in java. A class in java represents a blueprint or template for creating the objects. The concept of class can be best understood from the analogy of building a house .
If we want to build a house then we need to first create an architectural drawing ( map ) which defines the house in terms of its plan , elevation and specifications .
Similarly , in order to create an object , the programmer has to first define class which defines an object in terms of its properties ( data ) and behavior ( methods ).
The java programmer is essentially a collection of classes when we write the java program code . So , a class is said to be a design time entity.

Java Concept Of Object
The concept of class and object is closely related . Let us now understand the concept of an object in java . As stated earlier , a class in java represents a blueprint or template for creating the objects.
In the java program , all the program entities must be represented as an object . These objects represents a real world entities . Each object has its own state , properties ( data ) and behavior ( methods ).
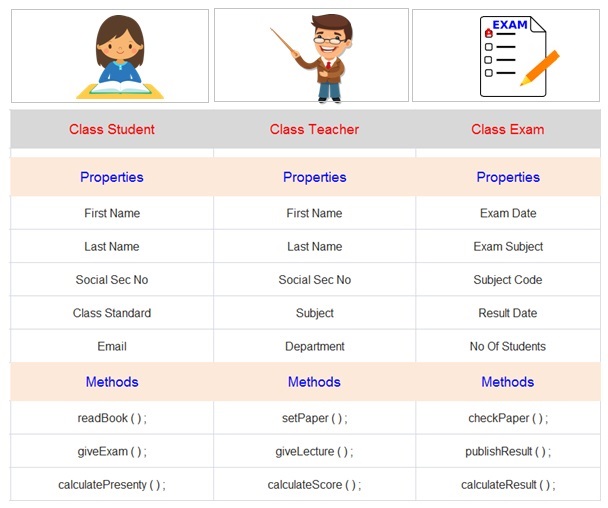
For example if we are designing a software for a college then entities that needs to be represented in the program includes student , teacher , exam and department .
The next step for the programmer is to first define these classes such as student class , teacher class and exam class and department class. Each of these class will have its own data and the methods which operates on the data.
The programmer can create number of objects from each of these classes during the program execution and perform various operations as per the program logic.
Java Programming Basics
Java OOP Concept - Encapsulation
The data security was one of the major limitations of the procedural programming. The object oriented programming provides a effective solution for data protection.
The encapsulation is one of the four fundamental OOP concepts. The other three fundamental OOP design principles are inheritance , polymorphism and abstraction.
The encapsulation in Java is a mechanism which binding together the data ( variables ) and the methods which acts on that data. The encapsulation is used to protect the data since only authorized methods can operate on the data .
Java Encapsulation Example
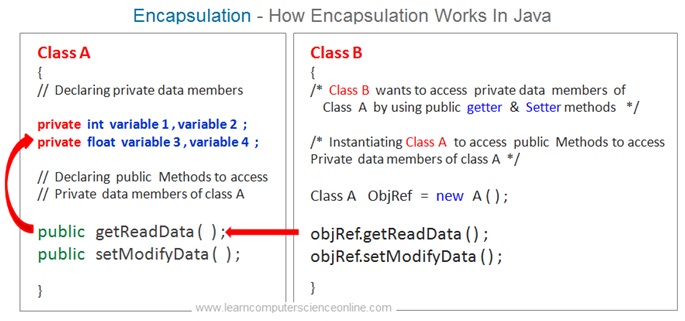
The encapsulation in java provides the programmer a mechanism to hide the data ( variables ) that needs to be protected from any unwarranted changes . This is also referred to as data hiding.
The programmer can hide the variables and restrict its visibility in the program code with the help of access modifiers. The programmer can also decide which methods can be given access to the program variables ( data ).
Java Programming Basics
Java OOP Concept - Inheritance
In case of large software development project the code reusability is an important consideration . The code reusability allows the programmer to simply reuse the code that has already been developed and tested.
The inheritance is mechanism in java which allows the java classes to inherit the properties ( data ,variables ) and behavior ( methods ) of the parent classes. The java language provides different ways to implement the inheritance concept in the program code .
A subclass is created using the java keyword extends to derive from the super class and extends keyword must be written in the header of the subclass definition.
The subclass inherits the members ( Variables And Methods ) of the super class and hence promotes the code reuse.

The subclass itself can add its own new behavior ( methods ) and properties ( Data ). The java.lang.Object class is always at the top of any Class inheritance hierarchy .
The inheritance allows the programmers to create a hierarchical order, relationship within the classes which makes the program code more manageable.
The class which acquires the properties of other class is known as subclass ( Derived Class or Child Class ). Whereas the class whose properties are acquired is known as super class ( Base class or Parent class ).
Inheritance Terminology
Before we start the discussion on the different types of inheritance in java , let us first understand the important terminology used in the implementation of the inheritance concept in the java programming.
Super Class , Parent Class , Base Class
A class is said to be a super class when its members ( variables and methods ) are inherited by another class . A super class is also alternately referred to as parent class or base class .
Sub Class , Child Class , Derived Class
A class is said to be a sub class when it inherits the members ( variables and methods ) of another class . A sub class is also alternately referred to as child class or derived class .
Inheritance Types
Inheritance Types In Java
There are different types of inheritance relationships used in different programming languages . However , the java language does not supports all inheritance .
Let us first understand the different types of inheritance that exists and then we will discuss the types that are supported by java. Different types of inheritance includes :
- Single inheritance
- Multi-level inheritance
- Multiple inheritance
- Hierarchical Inheritance
- Hybrid Inheritance
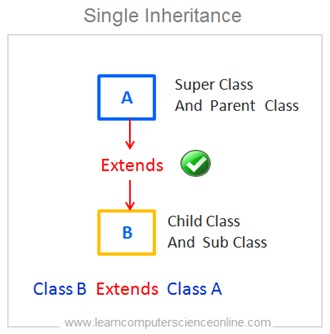
Single Inheritance
In single inheritance one derived class ( sub class / child class ) inherits the members of one base class ( parent class / superior class ) .
Let us consider one example of single inheritance . In this example the sub class B is a derived from base class A . ( Class B Extends Class A ).
Java supports single inheritance and it is allowed in Java .
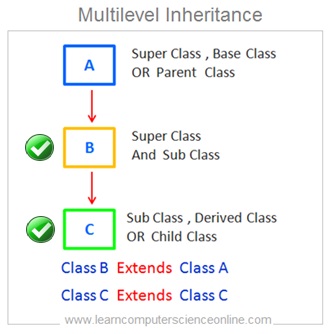
Multilevel Inheritance
In multilevel inheritance , the multilevel hierarchy includes more than two levels of classes . The top level class functions as only base class . The middle level class effectively functions as derived class as well as base class. The bottom level class functions as only derived class .
Let us consider one example of single inheritance . In this example the sub class B is a derived from base class A and sub class C is a derived from base class B.
Java supports multilevel inheritance and it is allowed in Java .
Multiple Inheritance
In multiple inheritance one derived class ( sub class / child class ) inherits the members of more than one base class ( parent class / superior class ) .
Let us consider one example of multiple inheritance . In this example the sub class C is a derived from two base class A and class B. ( Class C Extends Class A , B ).
Java does not supports multiple inheritance for classes and it is not allowed in Java . However , the multiple inheritance is allowed for interfaces .
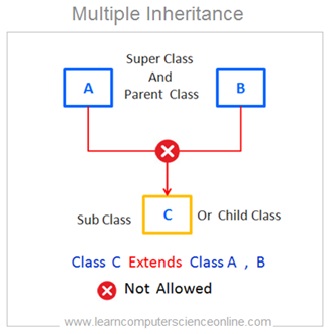
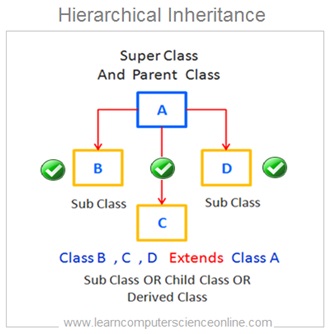
Hierarchical Inheritance
In hierarchical inheritance more than one derived class ( sub class / child class ) share the same parent class and inherits the members of the same base class ( parent class / superior class ) .
Let us consider one example of hierarchical inheritance . In this example the sub classes B , C , D are derived from the same base class A. ( Class B , C , D Extends Class A ).
Java supports hierarchical inheritance and it is allowed in Java .
Hybrid Inheritance
The hybrid inheritance is basically a combination of two or more inheritance as discussed earlier . Since the java does not support multiple inheritance for classes , the hybrid inheritance is not possible in Java using classes .
Let us consider one example of hybrid inheritance . In this example the sub classes B , C are derived from the same base class A. ( Class B , C Extends Class A AND Class D Extends Class B , C ).
Although the hybrid inheritance is not allowed in java for the classes but it can be implemented only using interfaces.

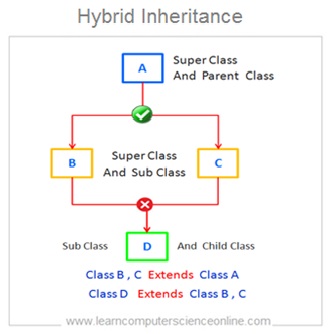
Java Programming Basics
Java OOP Concept - Polymorphism
Polymorphism In Java
The word polymorphism simply means many forms . The polymorphism is one the four fundamental OOP principle design concepts used extensively in the object oriented programming ( OOP ).
The word polymorphism consist of two Greek words poly and morph . The word poly means many and the word morph means forms . So , polymorphism simply means many forms .
We can also define polymorphism as single object with multiple different behavior when used in different context . The most common use of polymorphism in OOP occurs when a parent class reference is used to refer to a child class object.
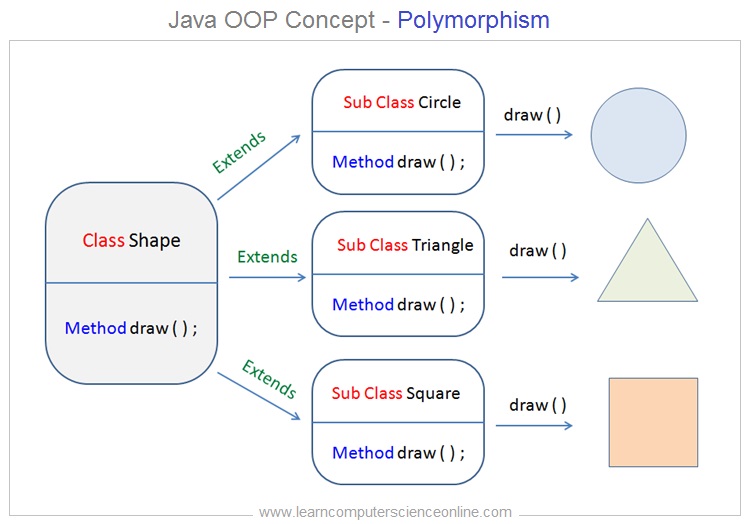
The most common and simple application polymorphism in java program is using the same method name but that method can perform multiple functions depending upon the contest of the object which invokes that method.
For example , when we define number of methods with the same method name but with different implementation. However , the correct method would be invoked either depending upon the manner in which the method is called or the arguments used while invoking the method.
The decision to invoke the appropriate method can either happen at compile time Or it can happen during the run time . This depends on the manner in which such methods are differentiated.
In this example , all the sub classes inherits method draw ( ) from the parent class Shape . However , each draw method in the sub class Circle , Triangle and Square will have different implementation and will draw the correct shape when invoked.
Java Programming Basics
Types Of Polymorphism In Java
The java language supports different types of polymorphism . The polymorphism types can be grouped into two types . The first type is compile time polymorphism ( Static Binding ) and the second type is runtime polymorphism ( Dynamic Binding ) .
Compile Time Polymorphism ( Static Binding ).
Runtime Polymorphism ( Dynamic Binding ) .
The process of connecting a method call to the method body ( also known as method implementation ) is known as binding . A binding could be either Static Binding Or Dynamic Binding and java supports both these bindings .
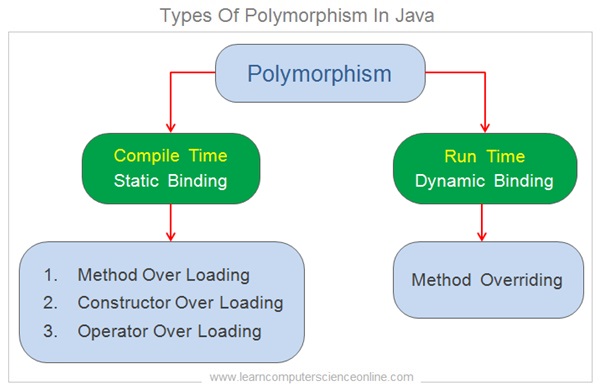
Java Programming Basics
Compile Time Polymorphism In Java
Static Binding In Java
The polymorphism that is resolved during compiler time by the compiler is known as static polymorphism. The method overloading , constructor overloading and operator overloading are examples of compile time polymorphism.
The concept of overloading is an example of compile time polymorphism . This allows the java programmer to define methods with the same name but with different parameters.
The correct method is invoked during the compile time depending upon the sequence , datatype or number of arguments.
The overloading can be achieved by declaring different method parameters in terms of parameter numbers , sequence and the data types of the parameters.
The compile time polymorphism is also referred as static binding Or early binding . The java language supports three types of compile time polymorphism which includes :
- Method Overloading.
- Constructor Overloading.
- Operator Overloading.
Method Overloading In Java
The method overloading allows the java programmer to define number of methods with the same name but with different parameters. The correct method is invoked during compile time depending upon the sequence , datatype and number of arguments.
In this example the calculator class contains two methods with same name addValues ( ) . The first overloaded method can be invoked by passing two arguments in the method call . Whereas the second method can be invoked by passing three arguments in the method call.
Method Overloading Example
Static Binding
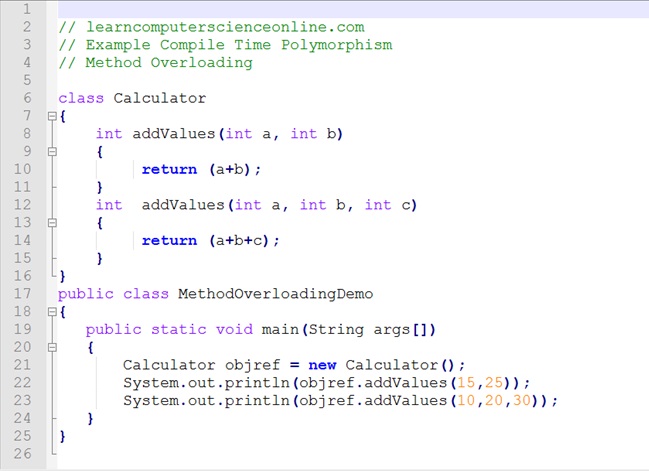
Java Programming Basics
Runtime Polymorphism In Java
Dynamic Binding In Java
The polymorphism is said to be runtime when a call to an overridden method is resolved at runtime and not during the compile time . And therefore , such polymorphism is also referred as dynamic binding or runtime polymorphism.
The runtime polymorphism is also referred as dynamic binding or late binding . The java language supports runtime polymorphism in the form of method overriding .
Method Overriding Example
Dynamic Binding
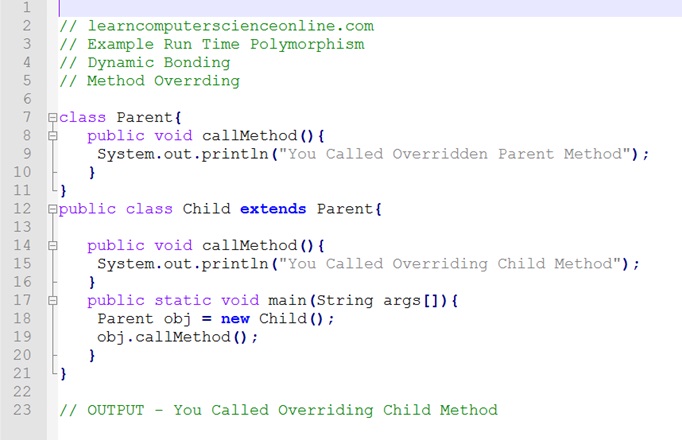
In case of dynamic binding when an overridden method is called through a reference of the parent class, then the object reference type determines which method is to be called .
Thus the dynamic binding happens during program execution. This call is taken dynamically by the JVM during the program execution.
Java Programming Basics
Method Overriding Example
How Dynamic Binding Is Resolved By JVM
Parent ObjRef = new Child ( ) ;
The Parent Class Object reference points to the Child Class object . Hence , a child class method will be called by the JVM . In this case Child class constructor has been used to instantiate the object .
Child ObjRef = new Child ( ) ;
The Child Class Object reference points to the Child Class object . Hence , a child class method will be called by the JVM . In this case Child class constructor has been used to instantiate the object .
Parent ObjRef = new Parent ( ) ;
The Parent Class Object reference points to the Parent Class object . Hence , a Parent class method will be called by the JVM . In this case Parent class constructor has been used to instantiate the object.
Java Programming Basics
Java OOP Concept - Abstraction
Abstraction In Java
Abstraction is a very common method used to create a simplified view of an object by removing the irrelevant details.
Abstraction is frequently used in many areas including programming to convey ideas. For example we can use an abstract image of some real world object such as vehicle , man , cat , dog without specifically pointing to any specific object of that type .
Abstraction is one of the key principle in Object oriented programming – OOP along with inheritance , encapsulation and polymorphism .

Abstraction involves hiding some irrelevant details of a process or system in order to highlight clearly other relevant aspects , details of an object . In other word , abstraction is effectively used to allows the user focus on other relevant details.
Let us consider example of a car . A driver of a car is presented a very simplified and relevant view of the car in terms of dashboard , steering wheel and other controls necessary to drive the car.
Whereas the mechanical gear , other parts and complicated electrical wiring behind the dashboard is hidden from the driver in order to let the driver focus on driving the car rather than showing him how it works.
Abstraction In Java
In java , the abstraction is achieved by using abstract class and interface.
- Abstract Class : 0% to 100 % Abstract.
- Interface : 100 % Abstract .
Abstract Class
Abstract class is a class which is declared with using abstract keyword and can have one or more abstract methods.
Abstract Method
Abstract method is a method defined without any implementation details ( that is method without any method body ).
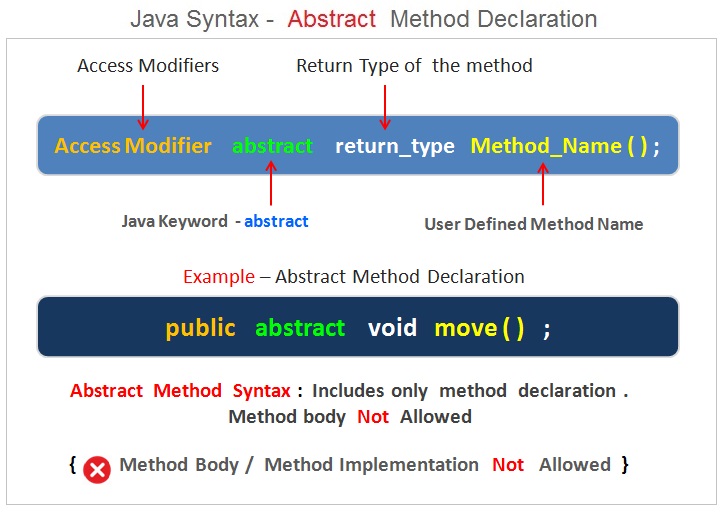
Concrete Method
A method is said to be a concrete method when it is defined with proper implementation details ( with proper method body { Method Body } ) .

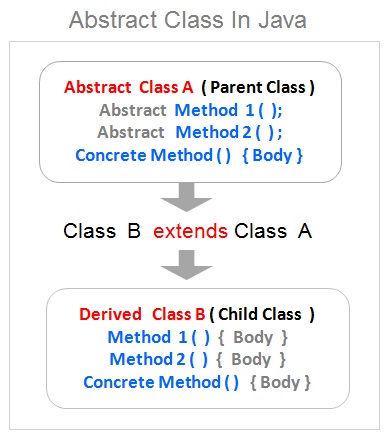
Java Abstract classes are used to declare the common characteristics ( functionality ) for the sub-classes.
An abstract class cannot be instantiated because it has abstract methods ( Incomplete methods ) . It can only be used as a super class for other sub classes that extend ( Inherit ) the abstract class.
Abstract classes are declared with the abstract keyword. Abstract classes are used to work as a template or design for the concrete sub classes in which the inherited abstract methods are defined with concrete methods with method body.
Virtual Method
In object-oriented programming, a method is said to be a virtual method if that method is inheritable and can be overridden by the sub classes .
All non static methods are virtual by default in java unless their ability to inheritance and overridability is constrained by using a java keywords final and private.
Java language does not have a virtual keyword because all non-static methods use dynamic binding and therefore by default they are virtual .
Abstraction
Interface In Java
An Interface is a 100% pure abstract class. That means all the methods declared inside an interface must be abstract methods.
A method is said to be an abstract method when it is declared without defining any implementation details ( That is without method body { Method Body } ) .
All the methods declared within an interface are implicitly treated as public and abstract even if such methods are not explicitly declared as public and abstract. The java compiler adds public and abstract keywords before the interface methods .
Java Programming Basics
Learn Computer Science And Programming Fundamentals
Online Course - Udemy
This is the most comprehensive and unique Computer Science And Programming Fundamentals course Online which will give you in depth understanding of most important fundamental concepts in computer science And Programming .

