Central Processing Unit
CPU Components | CPU Registers | CPU Functions
CPU Architecture | CPU Comparison
The Central Processing Unit ( CPU ) is the brain of the Computer System. The CPU is also alternately referred as a Computer Processor Or Microprocessor or simply a processor. The microprocessor is one the most crucial component that provides the processing power to the computer system.
The CPU initiates the program execution by fetching the program instructions and the data to be operated from the main memory RAM.
The Central Processing Unit (CPU) is a fundamental component of a computer system and is often referred to as the “brain” of the computer. It performs most of the processing operations inside a computer, executing instructions and managing data manipulation. The CPU interprets and executes instructions from the computer’s memory, coordinating the activities of all the hardware components to perform various tasks.
Different types of CPUs exist, including those designed for personal computers, servers, mobile devices, and specialized applications like graphics processing units (GPUs). The performance of a CPU is influenced by many factors like architecture, clock speed, cache size, and the number of cores. As technology advances, CPUs continue to evolve, becoming faster, more efficient, and capable of handling increasingly complex tasks.
Central Processing Unit (CPU), often referred to as the “brain” or main workhorse of a computer. It is a crucial component that performs the majority of processing tasks and executes instructions in a computer system.
It is the central hub where calculations, logical operations, and data manipulation take place. In this introduction to CPU, we’ll explore its functions, architecture, significance and how CPU works in the realm of computer science.
In this article, we will learn what is a processor , functions Of the CPU , How CPU executes the computer program instructions ( machine instructions ) , machine cycle , instruction cycle and other related important topics.
Microprocessor , Processor , CPU
Table Of Contents
FAQ
- What Is Central Processing Unit ( CPU )?
- What Are Functions Of Central Processing Unit ?
- Explain Central Processing Unit Architecture ?
- How Central Processing Unit Works ?
- What Is Central Processing Unit Instruction Cycle ?
- How To Measure Central Processing Unit Performance?
What Is Central Processing Unit ?
The CPU stands for Central Processing Unit of the Computer System. The CPU is also alternately referred to as a processor, central processor , or a microprocessor.

The CPU, or Central Processing Unit, is the primary component of a computer responsible for executing program instructions and performing calculations. Often referred to as the “brain” of the computer. The CPU interprets instructions fetched from the primary memory (RAM), processes data according to those instructions, and produces output.
It contains the arithmetic logic unit (ALU) for performing arithmetic and logical operations, as well as control units (CU) to manage other hardware components for execution of instructions. The CPU’s speed and efficiency significantly impact a computer’s performance, making it a most crucial component in computing devices.

The processor ( CPU ) controls all the activities of the computer system. And therefore, it is referred as brain of the computer system.
There are two main computer processor manufacturers Intel and Advanced Micro Devices ( AMD ). These two companies produce most of the processors used in desktop, laptops and notebooks.
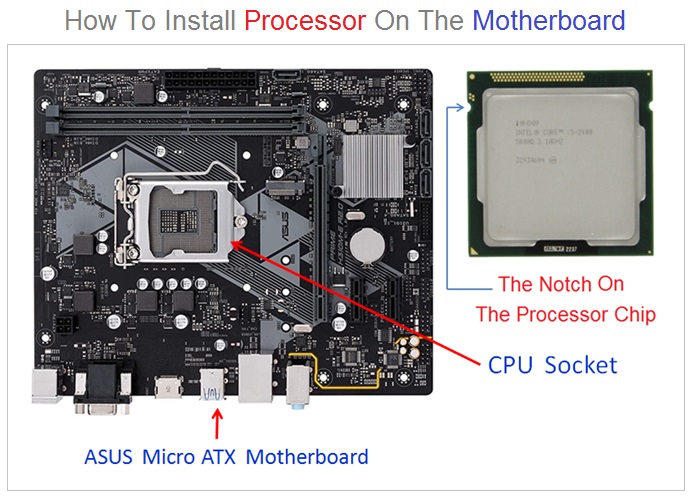
A CPU is placed on the motherboard in a processor socket with locking liver mechanism in order to fix the processor chip properly into the processor socket . The processor socket contains a IC socket in which the processor chip is firmly mounted .
A heat-sink is mounted on the top of the processor chip which protects the processor chip from the excessive heat generated.

The Central Processing Unit (CPU) is the primary component of a computer responsible for executing instructions and performing calculations. It serves as the “brain” of the computer, processing data and controlling the operation of other hardware components.
The CPU consists of arithmetic and logic units (ALU), control unit, and registers. It fetches instructions from memory, decodes them, and executes them to perform tasks such as arithmetic operations, logical comparisons, and data manipulation.
The CPU’s speed, measured in gigahertz (GHz), determines how quickly it can process instructions, influencing the overall performance of the computer system.
The Computer System consist of four major units and that includes :
- Input Unit 2. Output Unit 3. Memory Unit 4. Central Processing Unit ( CPU ).
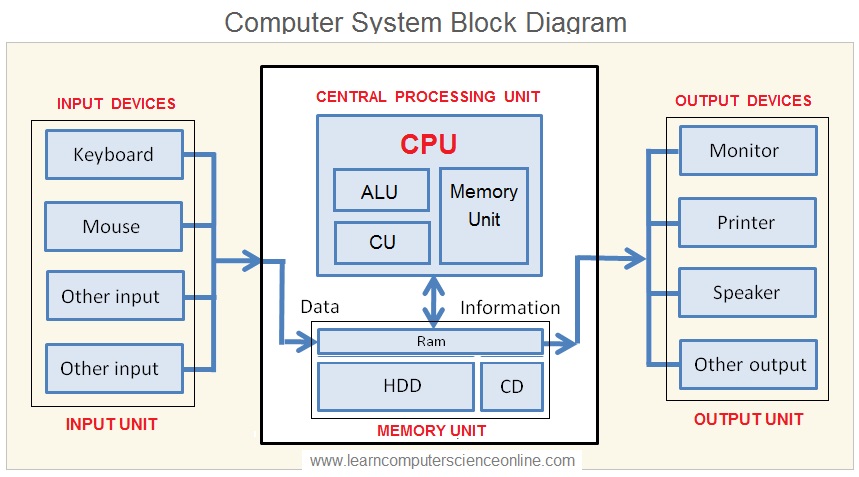
A CPU block diagram is a schematic representation of the components and architecture of a Central Processing Unit (CPU). It illustrates the internal structure of the CPU, including its various functional units and how they interact with each other to execute instructions.
The CPU block diagram provides a visual representation of how these components are interconnected and work together to process instructions and data, facilitating a deeper understanding of CPU architecture and operation.
The main function of the input unit is to allow the system user to input the data that needs to be processed with the help of application software . It is also alternately referred to as the program data.
Some of the standard user input devices ( peripheral devices ) include a keyboard , mouse , scanner , camera and other such input devices.


The main function of the output unit is to present the information ( processed data ) to the system user in the desired format. The data after being processed by the CPU is sent to the main memory RAM . The operating system then sends this data to a specific output device as per the program instruction.
The data after CPU operation is also alternately referred to as the processed data. The user might want to either display the program output or store the data in any permanent storage device such as disk memory.
Some of the standard user output devices ( peripheral devices ) include a display monitor , printer , projector, speaker , storage disk and other such output devices.
Functions Of Central Processing Unit
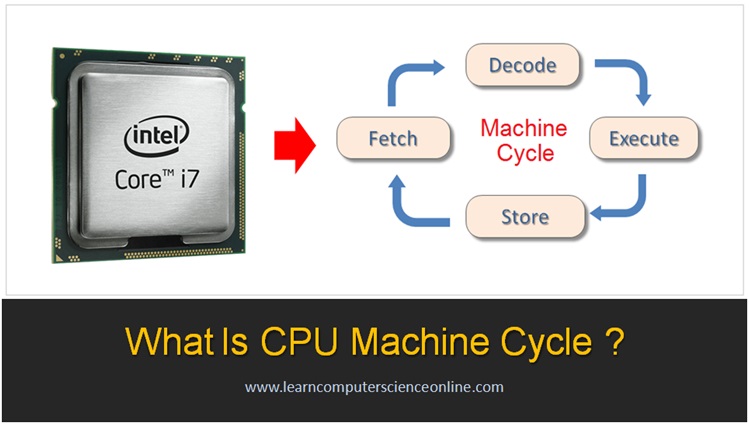
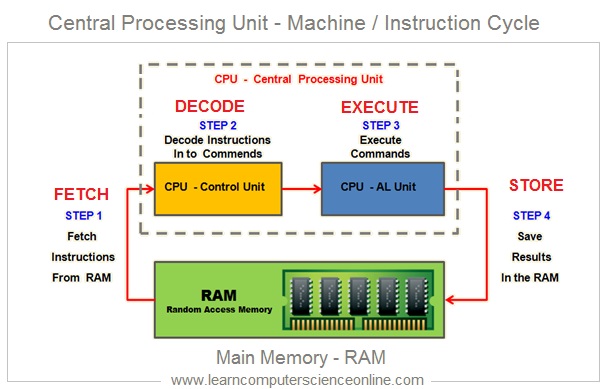
The CPU performs some of the most important functions in a computer System . The most important function for the CPU is to continuously perform Instruction Cycle. The CPU executes a program by repetitively performing the instruction cycle.
The Instruction cycle basically consist of four operations . These four operations include 1. Fetch 2. Decode 3. Execute 4. Store .These four operations are sequentially and continuously performed by the CPU during the program execution.
CPU Functions
- To perform Arithmetic calculation operations.
- To perform logical operations.
- To control functions of other hardware components..
- To fetch the data and program instructions from main memory RAM.
- To decode the program instructions.
- To operate on the data as per program instructions.
- To store the processed data into the RAM.
- To continuously execute instruction / machine cycle.
Microprocessor Functions
- Instruction Execution: The CPU fetches instructions from memory, decodes them to understand their meaning, and then executes them by performing calculations, data manipulations, or controlling other hardware components.
- Arithmetic and Logic Operations: The CPU performs arithmetic calculations (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division) and logic operations (AND, OR, NOT) to process data and make decisions.
- Control Unit: This part of the CPU manages the order of operations and controls the flow of data between different parts of the computer system. It coordinates the execution of instructions and ensures they are executed in the correct sequence.
- Registers: These are small, high-speed storage locations within the CPU that hold data temporarily during processing. Registers store data that is being actively worked on, helping to speed up calculations and operations.
- Clock Speed: The CPU operates at a specific clock speed, measured in Hertz (Hz), which determines how many instructions it can execute per second. Higher clock speeds generally result in faster processing, although other factors like architecture and efficiency also play a role.
- Cores: Many modern CPUs have multiple processing cores, allowing them to execute multiple tasks simultaneously. These cores can work independently or in coordination, improving multitasking and overall system performance.
- Cache Memory: The CPU often includes different levels of cache memory that store frequently used data and instructions. Cache memory is faster to access than main memory (RAM), which helps reduce the time the CPU spends waiting for data.
- Pipeline Processing: CPUs often use pipelines to process multiple instructions simultaneously. Each instruction goes through stages of fetching, decoding, executing, and storing results, allowing the CPU to work on different parts of multiple instructions at the same time.
- Floating-Point Unit (FPU): The FPU is responsible for handling floating-point arithmetic operations, which are used in complex calculations involving decimal numbers and real numbers.
Central Processing Unit
CPU Functions
The CPU provides the processing power to the computer. The main function of the CPU is to execute the program. For program execution, the CPU repetitively performs Instruction Cycle also referred as Fetch-Decode-Execute cycle.
It performs some of the most important functions within a computer system. These functions include :
- Fetching the program instructions from main system memory RAM one by one and starts its execution.
- To control the functioning of other hardware components by sending and receiving control signals on the control buses.
- To decode and operate on the program data as per program instructions and perform arithmetic and logical operations.
- To send the processed data back to the main memory RAM that can be stored in permanent memory ( disk memory ) .
- To repetitively perform machine cycle during the program execution.
CPU Components
Components Of Central Processing Unit
The CPU is primarily responsible to do all the calculations , Logical Operations such as decision making and controlling by sending control signals to other hardware components and devices connected to the computer system.
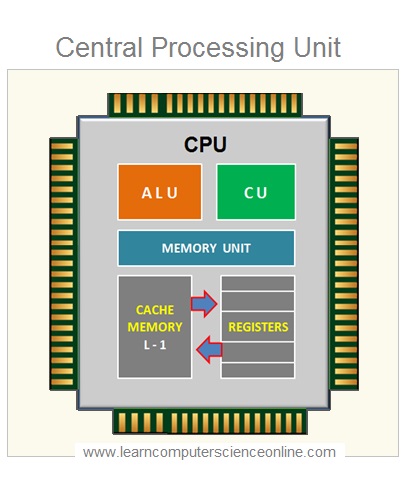
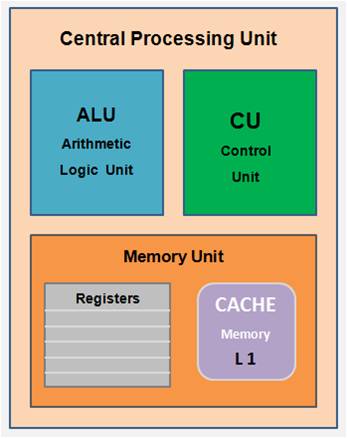
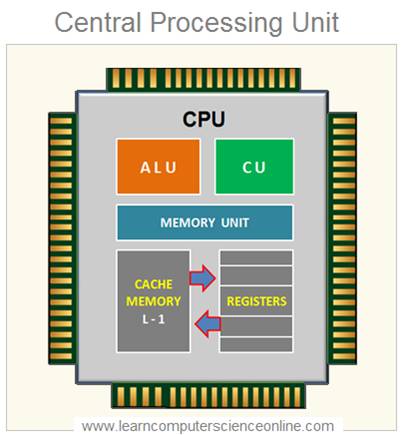
The CPU is a single microprocessor chip which performs all these functions. The CPU chip internally can be grouped into three major functional units as per their operations. The main internal CPU components include 1. ALU – Arithmetic Logic Unit , 2. CU – Control Unit and 3. Memory Unit .
1. Control Unit ( CU ).
2. Arithmetic Logic Unit ( ALU ).
3. Memory Unit ( MU ) .
Control Unit
The control unit ( CU ) is one of the internal component of a computer’s central processing unit ( CPU ). The Control Unit directs all the operations of the processor . The control unit directs the computer’s memory , arithmetic and logic unit , input and output devices. It is the control unit that decides on how to respond to the program’s instructions during the program execution.
How CPU Control Unit Works ?
The control unit ( CU ) directs the operation of the other units by providing timing and control signals to synchronize their operations .
The control unit is typically an internal part of the CPU with its overall role and operation unchanged since its introduction . Most of the computer resources are managed by the control unit .
The control unit also directs the flow of data between the CPU and the other devices especially the data flow between main memory RAM and the CPU.
The control unit decodes and translates the program machine code instructions during the program execution. The control unit then generates the necessary signals for Arithmetic Logic Unit ( ALU ) and for other units to perform the desired operation on the data.
All the operations of the computer system are synchronized by steam of clock pulses generated by the CPU clock . This timing signals generated by the CPU clock are generated by the control unit which synchronizes all the activities and different operations.
Read More
What Is ALU ?
Arithmetic Logic Unit ( ALU )
The ALU stands for Arithmetic Logic Unit . It is another complex digital circuit that is part of every processor and one of many components within a computer’s central processing unit .
The ALU performs both bit-wise logical and mathematical operations on the binary numbers. The ALU is the last component to perform the arithmetic calculations and logical operations in the processor.
The ALU operates on the data as per the program instruction decoded by the control unit of the CPU. And therefore , the data is actually processed by the ALU in terms of CPU operations.
The processed data is then sent to the main memory for further action. The operating system can either sent this data to the output unit such as monitor or it can sent to any permanent storage device for future use.
CPU Memory Unit
The Memory Unit ( MU ) inside the CPU consist of two components and that includes CPU Registers and Cache Memory ( L1 ) .
In order to optimize the CPU performance , the CPU needs high speed memory area to store the frequently used data during the program execution.
The CPU makes use of its very high speed memory registers during the various stages of the machine cycle. These registers are the fastest memory in the memory hierarchy.
CPU Registers
Each CPU contains number of high speed memory called registers. During the program execution, CPU makes use of its internal memory registers to optimize the CPU performance.
These registers are used by the processor as a high speed temporary storage memory area during the various stages of execution of the instruction cycle . The CPU can directly access these registers to perform the desired operation on the data.
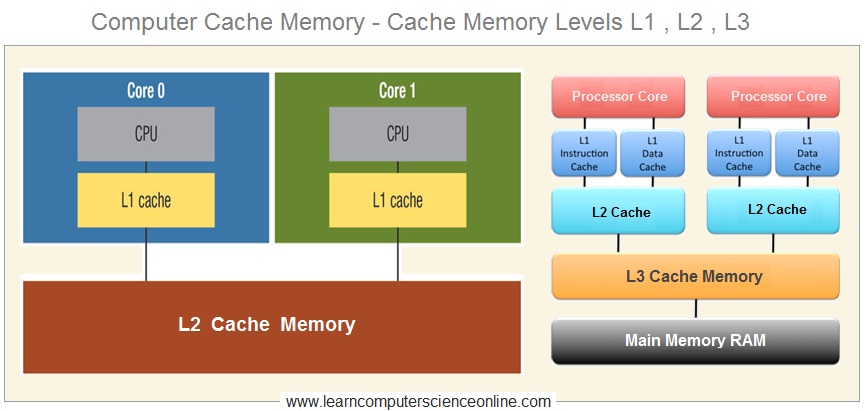
Cache Memory ( L1 )
In addition to CPU Registers , the CPU also contains Level 1 Cache memory . The L1 Cache is used by CPU to store the frequently used data and instruction during the program execution
Cache Memory Levels ( L1 , L2 , L3 )
Central Processing Unit
Machine Cycle
Instruction Cycle , Processor Cycle
The Computer programs are written to solve some specific problems. A computer program directs the computer CPU to perform specific operations on the data and produce the desired output that can be used for some meaningful work.
The computer programs are generally written in a human readable programming languages such as C , C++ , Java , Python.
The program written in any programming language needs to be first converted into machine readable program instructions in BINARY ( Machine Code ) that can be directly executed by the computers CPU – Central Processing Unit.
The process to convert program written in high level language into machine readable binary code is referred as program compilation.
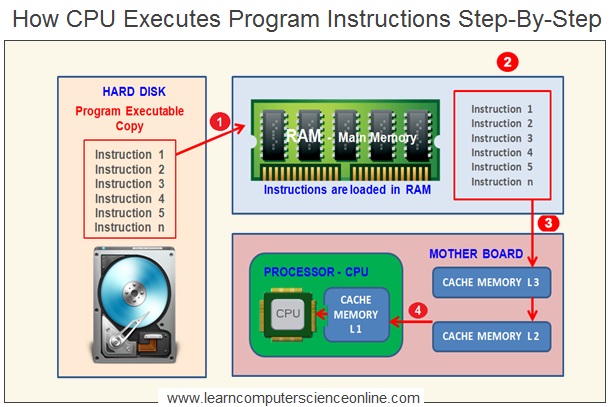
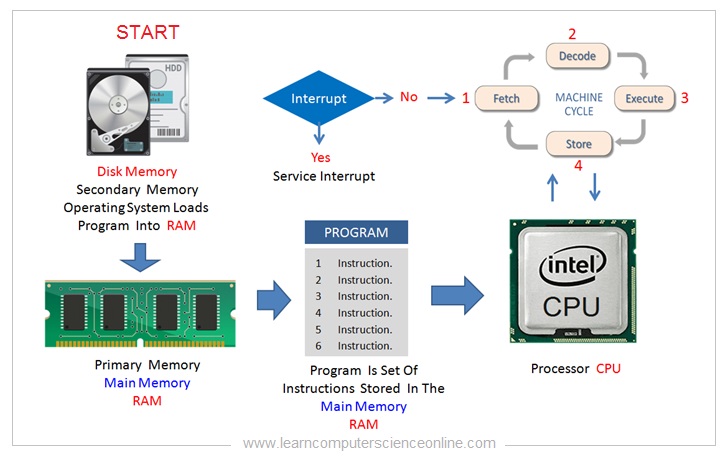
What Is Machine Cycle ?
The CPU is the main component in a computer system , which is responsible to interpret and execute the program instructions .
The CPU executes a program by repetitively performing a sequence of operations ( Fetch , Decode , Execute And Store ) which is collectively referred as Instruction Cycle.
The machine cycle refers to the one part of the instruction cycle.
A instruction Cycle ( Also referred as machine Cycle Or Processor Cycle ) is the basic operation performed by the CPU – Central Processing Unit to execute a program.
The CPU can execute the program instruction either in a single machine cycle or multiple machine cycles. Depending upon the complexity of the instruction , the CPU can take more than one machine cycles to execute one instruction. This is called instruction cycle.
What Is Instruction Cycle ?
Although a machine cycle is also referred as Instruction Cycle but there two CPU operations are a bit different.
The instruction cycle is the time taken by the CPU to execute one instruction which include fetch , decode and execute operation.
The processor can execute one single instruction either in a one machine cycle or CPU might need more than one machine cycles which depends upon the complexity of the instruction.
Learn More
How CPU Works ?
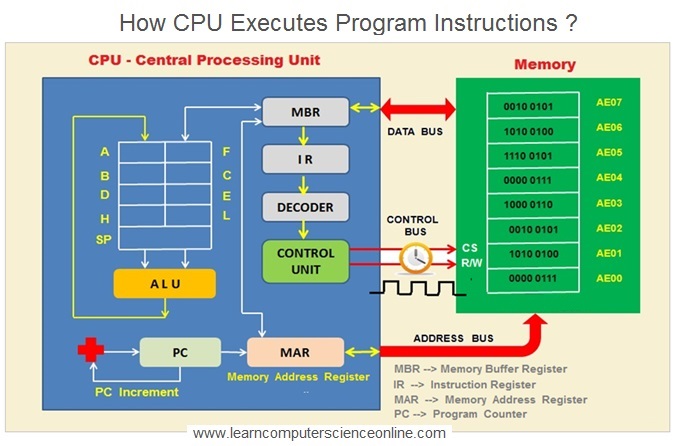
The CPU is responsible to execute the program . The Operating system allocates the necessary resources in terms of memory required and the processor time . The Operating system loads the program into the main memory RAM.
The CPU now starts the program execution . During the program execution , the CPU makes use of internal high speed memory of the CPU which includes L1 Cache memory and the CPU Registers .
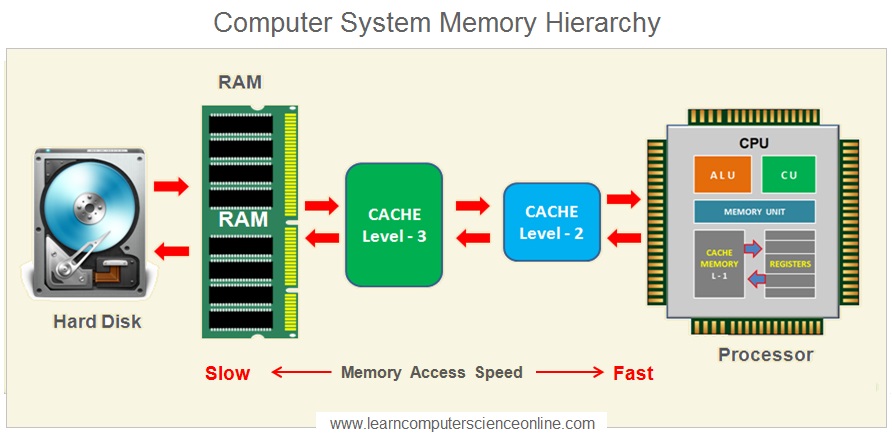
The CPU initiates the program execution by loading the address of the first instruction in to the PC register.
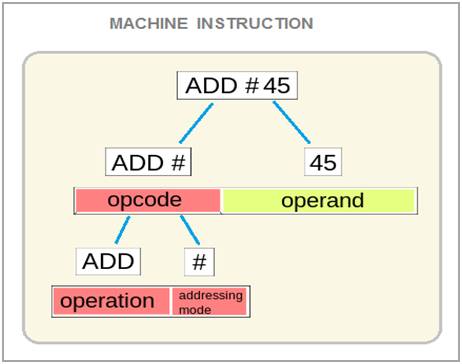
The program instruction consist of two parts that is OP Code ( Operation Code And the data ( operand ) on which needs to be processed . The This address is then transferred to MAR ( Memory Address Register ) and PC counter is simultaneously incremented .
How CPU Decodes Program Instructions ?
The CPU fetches the Data and program instruction from the main memory and transfer these to other internal registers ( MBR and IC ) for further processing.
The control unit of the CPU decodes the program instruction into OP Code ( Operation code ) and Operand ( Data ).
Machine Instruction Format
Machine Instruction Format
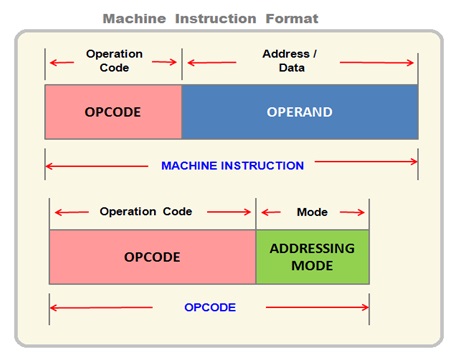
This data and the OP Code is then transferred to ALU ( Arithmetic Logic Unit ) of the CPU for operation . The ALU operates on the data as per the OP code and the corresponding operation as defined in the ISA ( Instruction Set Architecture ) Of the CPU .
Once the data is operated by the ALU , the processed data is than set to the main memory RAM . This data is then either sent to any output device Or stored on any secondary storage device ( Hard disk ) for future use .
How CPU Executes Program ?
Central Processing Unit
Machine Cycle
CPU Instruction Cycle Explained
Step-By-Step
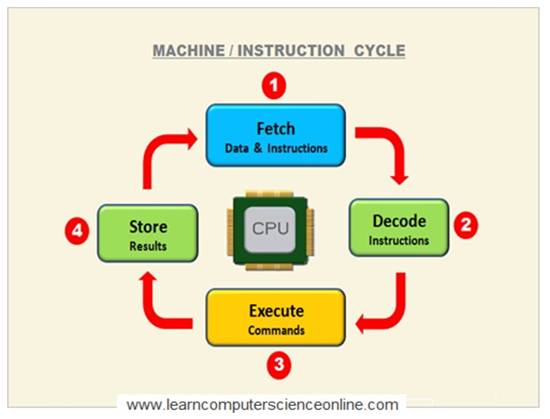
A machine cycle consists of a sequence of four steps that are performed continuously by the CPU . The CPU performs these steps millions of times per second during all the activities performed by the CPU and also during the program execution.
These steps are Fetch , Decode Execute And Store.
During the fourth step, store, in which the result of the processing done by the CPU is stored into the main memory ( RAM ).
This data is either sent output device or stored in secondary storage ( hard disk ) for later use. . However , no actual processing is performed during this step .
Instruction Cycle
Machine Cycle Steps
Instruction Cycle Steps
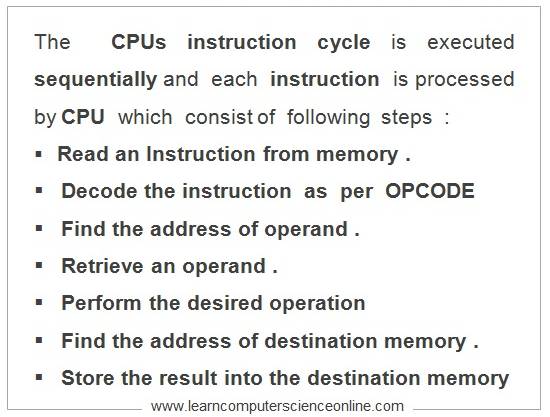
The machine cycle is the part of instruction cycle . And therefore , depending upon the type of the instruction , a single instruction might need one or more machine cycles to get executed by the CPU.
The minimum number of machine cycles requited is one and the maximum number of machine cycles is four to execute one instruction.
- The Operating System loads the data and program instructions to be executed into the main memory RAM.
- The CPU initiates the program execution by fetching the data and instruction one by one into the internal memory of the CPU ( Registers ).
- The control unit then decodes the OPCODE to perform the desired operation .
- The CPU then finds the memory address of the operand and retrieves the operand.
- The ALU performs the desired operation on the operand as per OPCODE.
- The CPU locates the address of the destination memory ( main memory RAM ).
- The CPU stores the processed data into the destination memory .
- The CPU repetitively performs the machine cycle during the program execution.
Central Processing Unit ( CPU )
Instruction Set Architecture
Microprocessor ( ISA )
The Microprocessor within a computer system is responsible to perform a predefined set of operations .
These CPU predefined set of operations include arithmetic operations , logical operations . data transfer operations and other operations that defines the computers response to various events ( User Or Program Instructions ) .
Each microprocessor design is based on the set of binary commands and the processor supports these predefined set of instructions .
This set of commands implemented ( embedded into the processor chip ) by the microprocessor into its micro-architecture is referred as “Instruction Set Architecture” ( ISA ) .
Instruction Set Architecture ?
What Is ISA In CPU ?
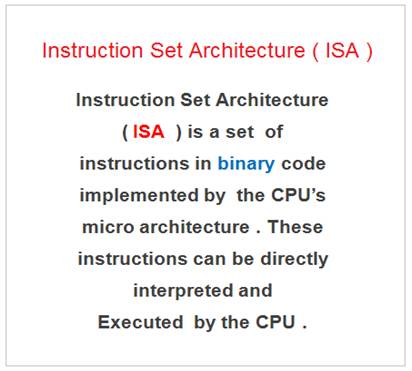
In other words , An instruction is a binary pattern defined inside a CPU ( Microprocessor ) to perform a specific operation .
The entire group of these binary machine code instructions that is implemented and supported by the microprocessor is called as “Instruction Set” . For Example ISA 8085 has 246 instructions.
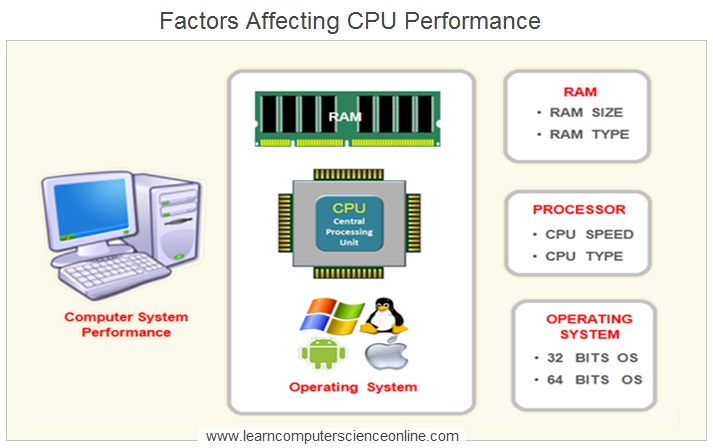
Central Processing Unit Performance
There are several factors that affect the CPU performance. Amongst the most important factors which directly affect the CPU performance are :
1. CPU Speed And Design.
2. RAM Size And Type.
3. Operating System Type.
CPU Speed
What Is Microprocessor Speed ?
The Microprocessor in a computer system is responsible to perform a predefined set of operations that includes arithmetic operations , logical operations , data transfer operations and other operations that defines the computers response to various events ( User Or Program Instructions ) .
What Is Gigahertz (GHz) ?
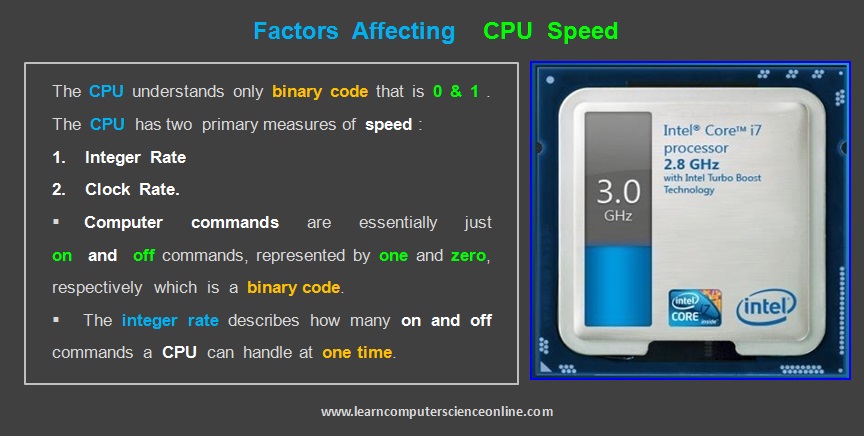
The CPU’s processing depends upon its speed. The CPU speed is measured in gigahertz (GHz). It determines how quickly processor can process instructions, influencing the overall performance of the computer system.
GHz stands for gigahertz, which is a unit of frequency equal to one billion cycles per second. In the context of a processor, GHz refers to the clock speed, or the number of cycles per second, at which the processor operates.
For each clock cycle CPU executes one instruction or part of the instruction. A higher GHz value generally indicates that the processor can perform more calculations per second, potentially leading to faster overall performance.
However, it’s important to note that GHz is just one factor affecting a processor’s performance, and other factors such as architecture and efficiency also play significant roles.
The clock speed is important measure of speed of a processor . The clock speed of a processor is how fast the processor can do the tasks while executing a program. The Clock speed is measured in Megahertz ( MHz ) or Gigahertz ( GHz ).
1 MHz = One million clock ticks every second.
1 GHz = One billion clock ticks every second.
This means that if one instruction was carried out per clock tick , a 3GHz processor could execute three billion instructions for three billion clock ticks every second.
CPU Clock Speed
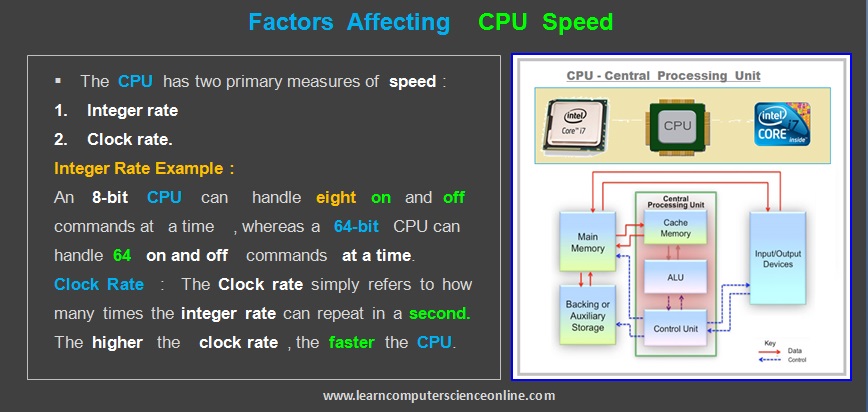
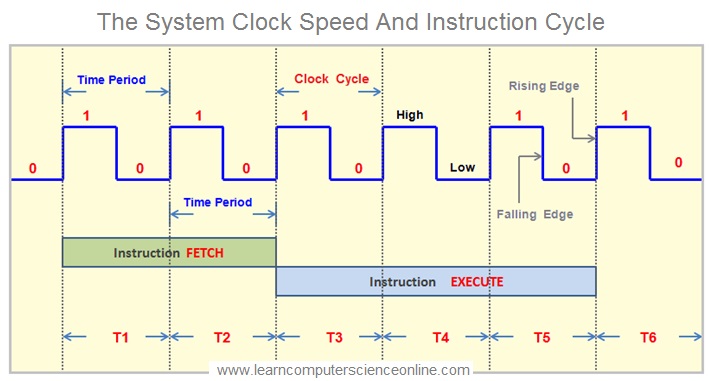
Every microprocessor requires a stream of clock pulses ( binary square pulse ) for its functioning . The CPU requires a fixed number of clock ticks ( called as Clock cycle / Clock Speed ) to execute each instruction.
A CPU is driven by an internal clock which generates a stream of square waves that regulates the rate at which instructions are executed by the CPU and synchronizes all other components in a computer system.
The faster the clock cycle , the CPU can execute more part instructions per second. And therefore, the number of clock cycles per second is known as processor speed . The processor speed is expressed in Megahertz ( MHz ) OR Gigahertz ( GHz ) .
The bit size of the CPU registers ( Register width 32 bits OR 64 Bits ) dictates the maximum permissible size of the RAM for a system .
For example, a 32 bit CPU and 32 bit OS the maximum RAM supported is 4 GB AND For a 64 bit CPU and 64 bit OS can technically support any size of the main memory RAM .
CPU Clock Speed And Instruction Cycle
CPU Bench Marking Tools
A CPU bench-marking tools are used to benchmark the CPU performance on various predefined parameters. A CPU bench-marking tool evaluates the CPU performance based on the outcome of a series of tests designed to measure the performance of a computer Central Processing Unit ( CPU ).
A CPU bench-marking tools make use of set of standards, or baseline measurements are used to compare the performance of different systems, using the same methods and under the same working conditions.
A standard CPU benchmark test will compare the test system performance on various parameters against the standards for the similar type of CPU used.
The important CPU performance parameters typically measured by a CPU bench-marking tool includes the CPU Clock speed, the number of instructions executed by the CPU, the registry calls per instruction cycle and the few more factors which indicates the overall architecture efficiency of the CPU and system.
The benchmark standards differ depending upon the generations of CPU and the most commonly used CPU brand like Intel and AMD .
The CPU benchmark Tool ( software ) also provides information about the other important devices which affect the overall system performance such as main memory RAM , Operating System , Motherboard , Graphics Card and Chipset.
Why Computer Use Binary ?
Why Computer Understands 0 And 1 ?
All of us know that computer understands the language of only two numbers that is Binary 0 and 1 . The binary number system is a base 2 number system that uses only two numbers 0 and 1 to represent any number.
You may be wondering , why computer use binary number system instead of using human friendly decimal number system which we are all familiar and use it in our daily life.
It is a legitimate question to ask why computer understands and execute programs only in binary machine code. It is also the most important and commonly asked questions in the technical interview.
Let us now discuss the reasons why computer use only binary number system. And the answer to this question lies in the computer system architecture.
READ MORE
Why Computer Use Binary ?
Central Processing Unit - FAQ
A processor ( CPU ) is an integrated circuit ( IC ). The processor consist of millions of IC chips and each IC chip consist of millions of tiny component called transistor. The Transistor is madeup of silicon which is a semiconductor material .
The processor ( CPU ) controls all the activities of the computer system. And therefore it is referred as brain of the computer system. There are two main computer processor manufacturers Intel and Advanced Micro Devices ( AMD ). These two companies produce most of the processors used in desktop, laptops and notebooks.
A Central Processing Unit ( CPU ) performs millions tasks per second to execute a computer program by performing the basic arithmetic, logical, control and input / output ( I / O ) operations as specified by the program instructions.
A CPU is placed on the motherboard in a processor socket with locking liver mechanism in order to fix the processor chip properly into the processor socket . The processor socket contains a IC socket in which the processor chip is firmly mounted . A heatsink is mounted on the top of the processor chip which protects the processor from excessive heat generated.
The CPU performs some of the most important functions in a computer System and these functions include :
- To Perform Arithmetic Calculation Operations.
- To Perform Logical Operations.
- To Control Functions Of Other Hardware Components.
- To Fetch the Data And Program Instructions From Main Memory.
- To Decode the Program Instructions.
- To Operate On Data As per Program Instructions.
- To Store Data After Processing.
- To Continuously Execute Instruction Cycle / Machine Cycle.
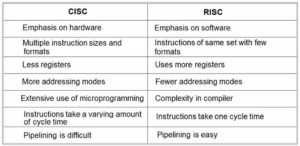
There are two main types of CPU based on the Instruction Set Architecture :
- CISC – Complex Instruction Set Computing .
- RISC. – Reduced Instruction Set Computing .
- Most desktop or laptop computers use CISC ( Complex Instruction Set Computing ) architecture made by Intel or AMD.
- Whereas Smartphones and tablets use RISC ( Reduced Instruction Set Computing ) by ARM architecture.
- Click On The Image To Expand.
Join The Best Seller
Computer Science Online Course
This is the most comprehensive and unique Computer Science And Programming Fundamentals course Online which will give you in depth understanding of most important fundamental concepts in computer science And Programming .