
Fundamentals Of Computer Science
Complete Beginners Guide To Fundamentals Of Computer Science.
Learning fundamentals of computer science is of paramount importance for students majoring in Computer Science (CS). The foundational knowledge and clarity of CS fundamentals is crucial for CS students since it facilitates the understanding the core principles, methodologies, and technologies that drive the field of Computer Science.
Let us find out why mastering these fundamentals is crucial for your success:
Introduction To Computer Science
In essence, mastering computer science fundamentals is not only essential for academic success but also for laying the groundwork for a successful and fulfilling career in the dynamic and rapidly advancing field of computer science.
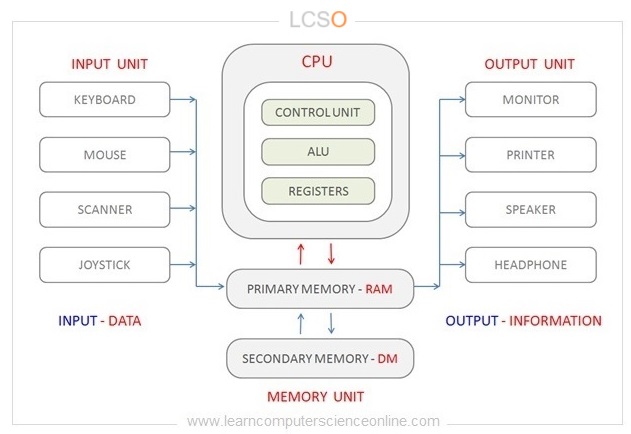
Computer Functions - Block Diagram
What is Computer Science ?
Before we dive into CS Fundamentals, let us get some clarity on what is computer science. Computer science is the study of data structures and algorithms, computation, computer software and hardware, computer architecture, and information processing, encompassing the theory, design, development, and applications of computer systems.
It involves analyzing and solving complex problems through algorithmic thinking, programming, and computational methods. Computer scientists explore topics such as data structures, algorithms, programming languages, artificial intelligence, data science, machine learning, cybersecurity, and computer networking.
They develop innovative software solutions, design efficient algorithms, and advance computing technologies to address real-world challenges in diverse domains. Computer science plays a crucial role in shaping the modern world, driving technological innovation, and revolutionizing industries across the globe.
Introduction To Computer System Video Tutorial
This article has been specially designed for absolute beginners to understand the basics of computer science, core principles, methodologies, and technologies.
Importance Of CS Fundamentals
Let us find out why mastering these fundamentals is crucial for your success:
1. Building a Strong Foundation
Computer science fundamentals provide students with a solid foundation in key concepts such as data structures, algorithms, programming languages, hardware, software, and computer architecture. This foundational knowledge serves as the basis for advanced coursework and specialized topics within the domain of CS.
2. Problem-Solving Skills
Computers and its applications are designed to address specific real-world problems. Therefore, mastery of fundamental concepts equips students with essential problem-solving skills, critical for handling complex challenges in software development, system design, and computational problem-solving.
3. Versatility And Adaptability
Understanding computer science fundamentals allows students to adapt to rapidly evolving technologies, scientific developments, and paradigms within the field. It enables them to learn new technologies, programming languages, applications, frameworks, and tools with greater ease and confidence.
4. Preparation For Advanced Study
Proficiency in fundamental areas of computer science is essential for pursuing advanced studies and research in specialized domains such as robotics, data science, artificial intelligence, quantum computing, machine learning, cognitive science, cybersecurity, and computer graphics.
5. Career Opportunities
Computer science is a rapidly evolving with the advent of latest hardware and software technologies. A strong grasp of computer science fundamentals enhances students’ employability across a wide range of industries, including software development, data analysis, cybersecurity, and research. Employers often prioritize candidates with a solid understanding of fundamental concepts in computer science.
Fundamentals Of Computer Science Subjects And Fields Of Study
Computer Science fundamentals cover a wide range of subjects, topics, each with its own set of sub-topics. Here’s a detailed list of important topics and their sub-topics:
- Introduction to Computer Science:
- Overview of computer science.
- History and Evolution of Computing.
- Basics of Digital Computing And Logic.
- How Computer Works ?.
- Binary Number System.
- Computer Organization And Architecture:
- Data Structures:
- Arrays.
- Linked lists.
- Stacks And Queues.
- Trees.
- Graphs.
- Hashing And Hash Tables.
- Heaps.
- Tries.
- Algorithms:
- Sorting Algorithms (e.g., bubble sort, merge sort, quick sort).
- Searching Algorithms (e.g., linear search, binary search).
- Graph Algorithms (e.g., Dijkstra’s algorithm, breadth-first search, depth-first search).
- Dynamic Programming.
- Greedy Algorithms.
- Programming Languages:
- Introduction to Computer Programming Languages.
- Programming Paradigms.
- Syntax, Semantics and Compilation.
- Data Types And Variables.
- Control Structures (e.g., loops, conditional statements).
- Functions And Procedures.
- Object-oriented Programming Concepts.
- Application Software.
- System Software.
- Operating Systems:
- Introduction to Operating Systems.
- Process Management.
- Memory Management.
- Virtual Memory.
- BIOS And UEFI.
- File Systems
- Input/output Management
- Scheduling Algorithms
- Computer Networks:
- Introduction to Computer Networks.
- OSI and TCP/IP Models.
- Network Protocols (e.g., HTTP, FTP, TCP, UDP).
- IP Addressing And Subnetting
- Routing And Switching.
- Wireless And Mobile Networks.
- Database Systems:
- Introduction to Databases.
- Database Management System (DBMS).
- Relational Database Management Systems (RDBMS).
- SQL (Structured Query Language).
- Database Design.
- Database Keys.
- Database Normalization.
- Indexing And Querying.
- Transactions And Concurrency Control.
- Software Engineering:
- Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC).
- Requirements Engineering And Elicitation.
- Software Design Principles.
- Testing And Quality Assurance
- Software Maintenance.
- Agile And Scrum Methodologies.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning:
- Introduction to AI and ML.
- Search Algorithms (e.g., depth-first search, breadth-first search).
- Machine Learning Algorithms (e.g., linear regression, logistic regression, decision trees)
- Neural Networks and Deep Learning
- Natural language Processing (NLP)
- Computer vision.
- Cybersecurity:
- Introduction to Cybersecurity.
- Cryptography.
- Authentication And Authorization.
- Network Security.
- Web Security.
- Security Protocols (e.g., SSL/TLS, SSH)
- Web Development:
- Introduction to web development.
- HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
- Frontend frameworks (e.g., React, Angular, Vue.js).
- Backend development (e.g., Node.js, Django, Flask).
- RESTful APIs.
- Web security and best practices.
- Computer Graphics:
- Introduction to computer graphics.
- 2D and 3D transformations.
- Rendering techniques (e.g., ray tracing, rasterization)
- Animation and simulation.
- Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR).
- Human-Computer Interaction (HCI):
- Introduction to HCI.
- User interface design principles.
- Usability testing.
- Interaction design.
- Accessibility.
- User experience (UX) design.
- Parallel and Distributed Computing:
- Introduction to parallel and distributed computing.
- Parallel programming paradigms (e.g., shared memory, message passing)
- Distributed systems architecture.
- Parallel algorithms.
- Cloud computing.
- Big data processing frameworks (e.g., Hadoop, Spark).
