DBMS
Database Management System
What Is DBMS ? | Types Of DBMS | RDBMS | MySQL
The Database Management System ( DBMS ) is a software application used to create , manage and administer the databases. The DBMS also provides the necessary tools required for the design and development of the databases.
A database management system (DBMS) is software that is used for the creation, organization, management, and manipulation of databases. It provides a systematic way to store, retrieve, update, and manage data efficiently and securely.
A DBMS serves as an intermediary between users and the physical database. It allows users to interact with the database by providing a set of tools and interfaces to perform various database operations such as querying, updating, and maintaining data. Therefore, all software that manipulate and store data need DBMS to perform these functions.
Database Management System ( DBMS ) is a vital component of most of the software applications . Whether you are working on a enterprise software development project or you may be developing a small website , the database design and development skills are needed in almost all software applications.
The business corporations are investing huge amount of money for the collection , analysis and management of large volumes data which is critically important to support the day-to-day business operations of the company .
And therefore , the database management professionals are in great demand having expertise in developing the software applications to handle the large volume of data , designing the database and for the database administration .

Characteristics of DBMS
The DBMS characteristics and properties includes:
- It provides controlled data access and data security.
- It does not allow duplication of data thus reduce data redundancy.
- It provides tools and systems to create and manage databases.
- It provides an interface between application programs and database.
- It supports multiple levels of data access and data views.
- It allows secure sharing of data and user permissions.
- It allows management of multiuser transaction processing.
- Database Management Software allows to define relationship between various database entities represented by tables.
- It enforces database integrity with ACID concept (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, and Durability).
- DBMS supports standard database communication language SQL.
- It facilitates import and export of data.
- DBMS supports database administration within a multi-user environment.
- It facilitates generation and presentation of various MIS reports.
Database Management System
Table Of Contents
Database Management System
What Is Data ?
Before we start discussion on the database , let us first understand the meaning of term data for a database design professional.
The data is the most important element of any DBMS. And therefore , It is important to understand what data means to the database user , database designers and to the computer system at the hardware level .
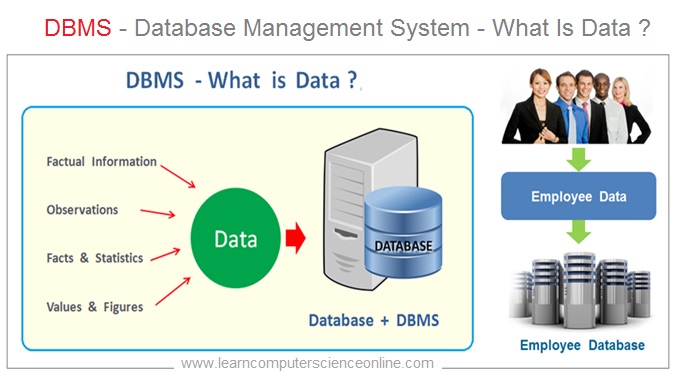
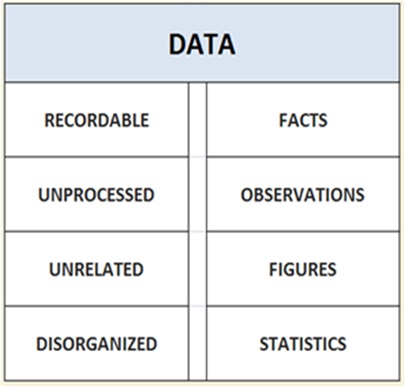
The term data simply means recordable facts , observations , factual information , set of values and figures that can be processed with the help of a computer system and DBMS software.
For example if we are designing a database to store the employee data then all the employee related information such as Name , Address , Designation , DOB , Salary can be stored as employee data.
Database Management System
What Is A Data Processing ?
The data generally means raw data that needs to be collected , processed and cannot be used directly for some meaningful work such as decision making .
However, once the data is processed into the information , then it can be used for some meaningful purpose such as MIS ( Management Information System ) used for decision making .
Therefore , It said that Information is a processed data .
The data processing essentially means manipulation of data with the help of computer system and a software application that defines the database operations to be performed .
The raw data is first converted into machine readable form so that it can be processed by the computer as per the program instructions .
Data Processing Example
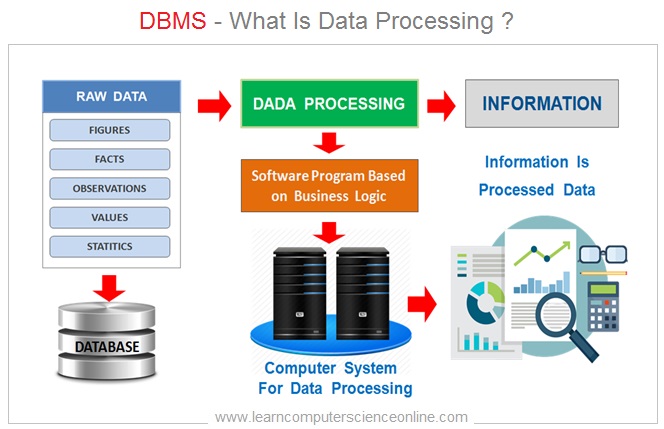
For example, employee attendance data is first recorded and then processed with the help of payroll processing software to calculate the employee salary details every month.
The data processing is extensively used for Business , Engineering , Scientific Research and practically in every industry.
Depending upon the volume of data , high speed computer systems and the software applications designed to process the data are used .
Some popular examples of database management systems (DBMS) include Oracle Database, MySQL, Microsoft SQL Server, PostgreSQL, and MongoDB. Each DBMS may have its own specific features, capabilities, and usage scenarios, but they all aim to efficiently manage and organize data in a structured and secure manner.
What Is A Database ?
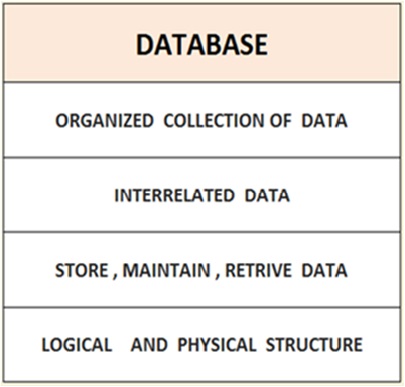
A database is a computer based record keeping system that is used to record , maintain and retrieve the data .
In other words , database is an organized collection of interrelated records such as employee database OR customer database.
The main purpose of the database is to operate and handle large amount of information ( data ) by efficiently storing , retrieving and managing the data in the database .
DBMS Video Tutorial
What Is Database ?
The database is a key component of most software applications which are designed to store the information about some real world business entities such as employee database , customer database , student database and so on.
The database is the well organized collection of interrelated data which makes it possible to easily access , retrieve and store the data for future use . The databases are created , administered and managed by using any DBMS software .
Database Management System
What Is DBMS ?
The DBMS stands for Database Management system.
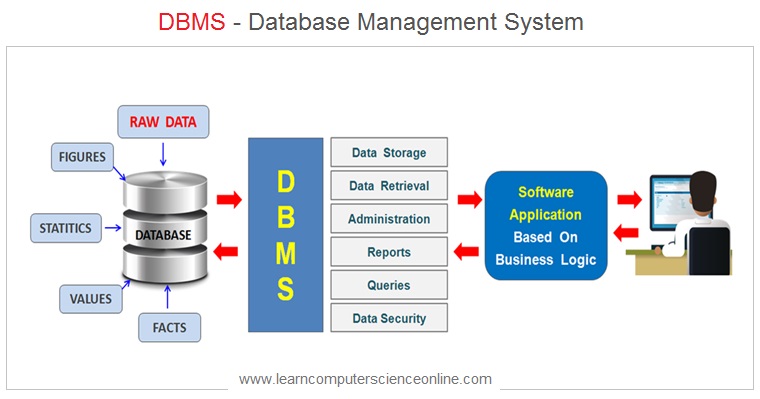
The DBMS is a software or a group of programs designed to perform the database operations such as creating new database , administering and managing the databases by performing various user specified database operations .
The DBMS allows the end users to perform various database operations such as creating a new records , save data , edit data , delete data , read and manipulate the data .
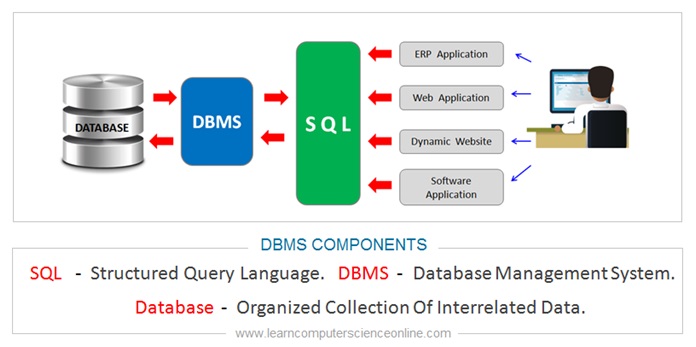
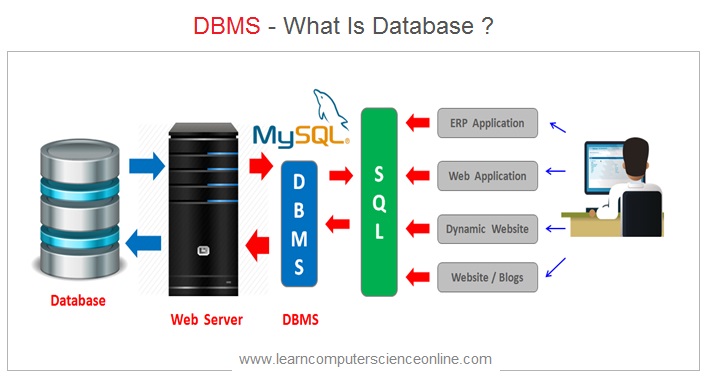
The database user interacts with the application program. The application programs communicates with the DBMS using SQL ( Structured Query Language ) commands. The DBMS effectively functions as an interface between the application program and the database. The DBMS operates on the database as per the SQL commands.
The DBMS also enforce certain constrains to ensure that the data stored is consistent and accurate.
What Is DBMS ?
The DBMS provides the centralized view of the data that can be accessed simultaneously by number of database users . The Database can be accessed by either actual end user , database programmer or by database administrator .
The DBMS gives complete control to the database administrator to decide which data can be viewed by the user and operations that user can perform on that data .
The database administrator can create different groups of database users and set the access permissions .
What Is DBMS ?
The DBMS also provides an abstracted view of the database thereby completely hiding the complexities involved in how the data is actually physically stored into the database .
However , the end user generally interacts with the database through application software interface.
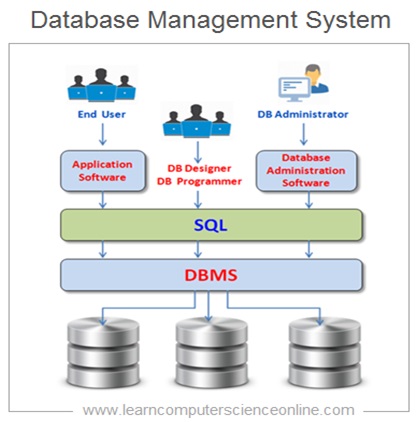

Some of the most commonly used DBMS includes MySQL , Oracle , MS SQL Server , Oracle , IBM DB2 , MS Access , Maria DB , Mango DB , Postgre SQL and there are many more.
These DBMS are based on the Relational Database Model hence referred as Relational Database Management System ( RDBMS ) .
Database Management System
Functions Of DBMS
DBMS interacts with the physical database , manipulates and operates on the data and performs some critical database operations. Some key functions of a typical DBMS include:
1. Data Definition
A DBMS allows users to define the structure of the database schema, including tables, relationships, constraints, and data types.
2. Data Manipulation
Users can insert, update, delete, and retrieve data from the database using query languages such as SQL (Structured Query Language). DBMS provides mechanisms to process these queries efficiently and optimize performance.
3. Data Integrity And Security
DBMS enforces data integrity constraints, such as enforcing unique values, primary key constraints, referential integrity, and data validation rules. It also provides security mechanisms to control access to the database and protect data from unauthorized access.
4. Concurrency Control
DBMS manages concurrent access to the database by multiple users or applications to ensure data consistency. It handles concurrent transactions, maintains isolation, and provides mechanisms like locks and transaction management to prevent conflicts and maintain data integrity.
5. Data Recovery And Backup
DBMS implements mechanisms to recover the database in case of failures, such as system crashes, disk failures, or other disasters. It allows for regular backups and provides restore and recovery options to minimize data loss.
6. Data Abstraction And Independence
DBMS provides data abstraction, which means it hides the complexity of the underlying data structures and operations from users. It allows users to work with high-level conceptual models such as tables and relationships without worrying about the physical implementation details.
7. Scalability And Performance Optimization
DBMS is designed to handle large volumes of data and optimize performance. It employs various techniques such as indexing, query optimization, caching, and data partitioning to improve query response time and scalability.
Database Management System
DBMS Advantages
A DBMS is integral and indispensible part of almost all modern organizations irrespective of the size and scale of the business operations. A DBMS offers many advantages as compared to any traditional computer based record keeping system.
- Minimum Data Redundancy.
- Ease Of Data Sharing.
- Data Security.
- Data Independence.
- Consistency Of Data.
- Improved Data Integrity.
- Data Backup And Recovery.
- Data Abstraction.
Database Management System
Most Popular DBMS
DBMS Examples
- MySQL
- Oracle
- MS SQL Server
- SQLite
- MariaDB
- MS Access
- IBM DB2
- PostgreSQL
- MangoDB
- NoSQL

Database Management System
MySQL
MySQL is the most popular and extensively used open source DBMS . MySQL is a Relational Database Management System ( RDBMS ) based on relational database model .
MySQL is extensively being used for providing database functionality to the web based applications and websites.
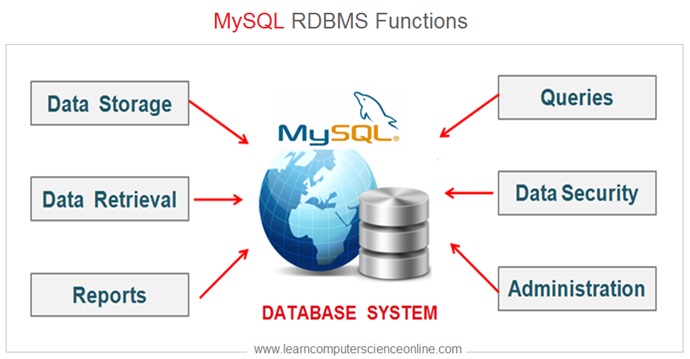
Another major advantage of MySQL database is open source , that means the user has access to the source code under license , which can be modified as per needs .
My SQL also offers a paid enterprise version , which offers some additional plug-ins , to augment the existing functionality .
MySQL with its proven track record of performance , reliability , scalability and ease-of-use has become default choice for some of the largest web applications such as Facebook , Twitter and YouTube.
Database Evolution
File System Databases Vs DBMS
The first generation of Databases were based on the collection of unrelated files . The file system based database was logical extension of manual record keeping , but it was a computer based record keeping .
In a file system database , the files were grouped and organized in folders . The file system databases had many limitations . Any change made in file structure , needed a corresponding change in the program code designed to operate on these files .
A File system database is a DBMS that allows access to single files or a single tables at a time. The File System organizes the either in a single file or group of files stored on a local hard disk.
These files are not interrelated and it is difficult to establish relationship between these files . The file is referred as flat file when the data is stored in a single file .
Database Management System
DBMS Characteristics
1. DBMS Can Handle Wide Range Of Data Types
The DBMS offers wide options for data types and therefore, it is easier to model any real world database entity in DBMS .
2. DBMS Is ACID Compliant
DBMS Is ACID ( Accuracy, Completeness, Isolation, and Durability ) Compliant . The DBMS can enforce the constrains on the user data and operations to ensure the accuracy and the consistency of the data in a database.
3. DBMS Allows Controlled Access
The DBMS allows to create different types of User groups and set different access permissions to these groups .
4. DBMS Allows To Define Relationships
The DBMS allows the database designers to define the logical schema of the database. The database designers can create logical entities such as table and establish relations between the tables .
5. DBMS Can Be Configured
The DBMS can be configured to support complex computer networks and system architecture such as multi-location distributed database operations without any technical issues with concurrent database operations.
6. DBMS Provides Database Safety
The DBMS offers many features to ensure the data security and the safety of the database such as back and recovery which makes the life much easier for database administrators .
Database Management System
Types Of DBMS
Types Of Database Models
The database design approach depends upon the database model being implemented.
It is important for database design professional , to understand the different types of database models and how these database models are fundamentally different in terms of their design approach.
A database model is a type of database structure that determines the logical structure of the database and fundamentally determines , the manner in which the data can be stored, organized and manipulated within a database .
- Graph Databases.
- ER Model Databases.
- Document Databases.
- NoSQL Databases.
Most database management systems are built with a particular database model in mind and require their users to adopt that model .
For example, MySQL DBMS supports only “Relational Database Model” although some DBMS do support multiple database models.
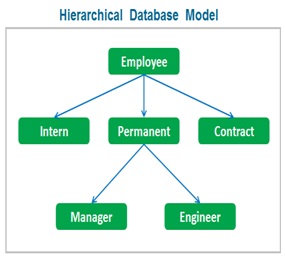
Hierarchical Database Model
The hierarchical database model is based on parent-child relationship . It is a database model in which , the data is organized into a tree-like structure. The data is stored as records which are connected to one another through links.
A record is a collection of fields , with each field containing only one value. The entity type of a record defines , which fields the record contains .
Network Database Model
The network database model was a progression from the hierarchical database model . The network database model was designed to solve some of the model’s problems such as the lack of flexibility.
The network database model allows each child to have multiple parents . The network database model can handle needs to model more complex relationships .
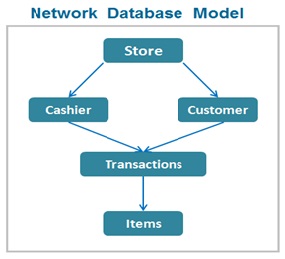
The main advantage of the network database model as compared with the hierarchical model is the ability to handle more complex relations such as many-to-many relations by allowing records to have more than one parent .
Database Management System
Relational Database Model
The ‘Relational Database Model is the most commonly used model in the industry today. Some of the most popular RDBMS ( Relational Database Management System ) being used are based on the relational model and that includes MySQL , Oracle , MS Access and MS SQL .
A relational database is based on the relational model proposed and developed by E.F. Codd who was an English computer scientist while he was working for IBM .
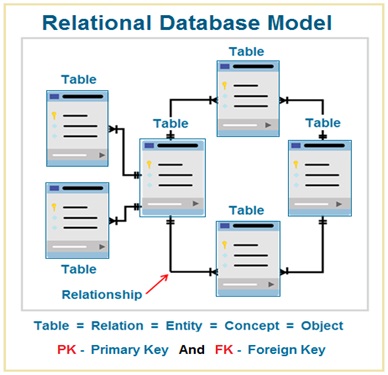
In a relational database model , the database is logically organized as group of related tables . Each table can have multiple rows and columns . A table is a collection of records related to an entity .
Each row in a table represents a record ( Tuple / Row ) which consist of number of data fields . A column in a table represents an attribute for a database entity .
READ MORE
Database Management System
Object Oriented Database Model
The Object Oriented programming ( OOP ) is a programming style that is associated with some fundamental design concepts , which govern the manner in which a program code is organized and written in OOP .
The Object Oriented Programming ( OOP ) is an approach to software application development in which all application components are treated as objects and the actions performed by these objects.
An object is a component of a program that binds data and methods together . The methods knows how to perform certain actions on the data and how to interact with other elements of the program. The Objects are the basic units of object Oriented programming .
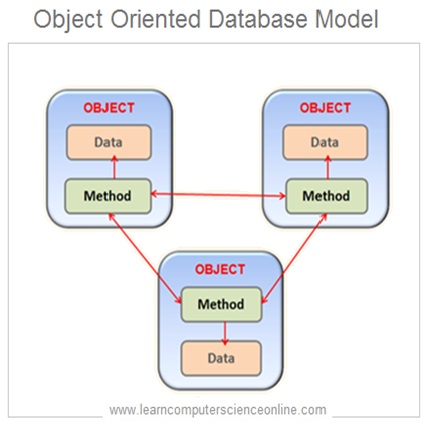
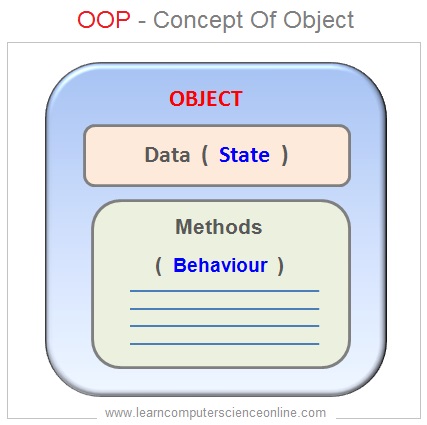
The Object Oriented Database Model ( OODM ) is based on the core concepts of Object Oriented programming and provides all the features of Object Oriented Programming ( OOP ) .
In OODMS , all the database objects are represented in the form of objects . This model allows the database designers , to easily model complex databases .
Database Management System
DBMS Architecture
The DBMS has become critical component of most business organizations , which helps the organizations to record and manage all business transactions .
The selection of the suitable DBMS depends upon several factors and the database system architecture is designed accordingly to meet the needs of an organization.
The database system architecture is generally based on the client server architecture and the computer networking technology to provide the suitable database system solution as per the needs of an organization.
The DBMS can be configured to meet the database system requirements and system architecture is designed to support such database system .
The client – Server Architecture can be categorized into three types depending upon the number of tiers ( Presentation , Business And Database Tier ) present on one computer . The most commonly used client server architecture include :
- Single Tier Architecture
- Two Tier Architecture
- Three Tier Architecture
Database Management System
DBMS Architecture
Single Tier Architecture
There are three components of DBMS architecture . Presentation tier , business tier and the database tier .
In Single tier DBMS architecture all the three tiers ( also referred as layers Or logic ) which includes Presentation tier ( GUI Interface ) , Business tier ( Application Software ) and Data tier ( Database ) resides on the same computer system .
DBMS Single Tier Architecture Diagram
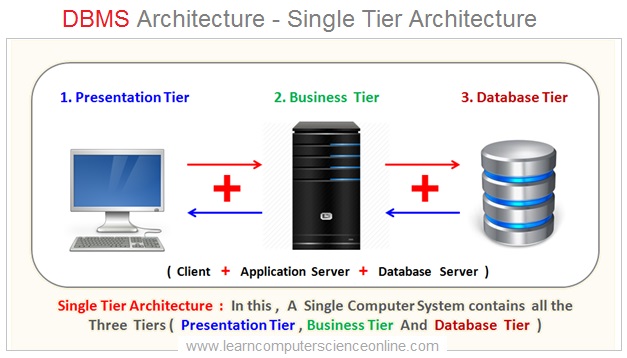
The presentation tier is a software application that end user interacts to communicate with the database . The business tier generally resides on the server and holds the business logic. The database tier again resides on the server where the data is actually stored into the database.
Database Management System
DBMS Architecture
Two Tier DBMS Architecture
In two tier client server architecture , the Presentation tier ( GUI Interface ) resides on the Client system whereas the remaining two tiers i.e Business tier ( Application Software ) and Data tier ( Database ) resides on the same computer system .
DBMS Two Tier Architecture Diagram
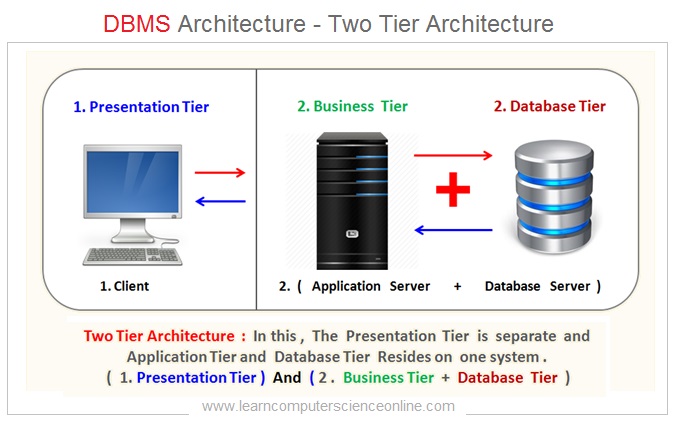
DBMS Architecture
Three Tier DBMS Architecture
In three tier client server architecture all three layers / logic / tiers resides on a separate system. The front end Presentation tier ( GUI Interface ) resides on the Client system , the Business tier ( Application Software ) and Data tier ( Database ) resides on the separate computer system .
Three Tier DBMS Architecture Diagram
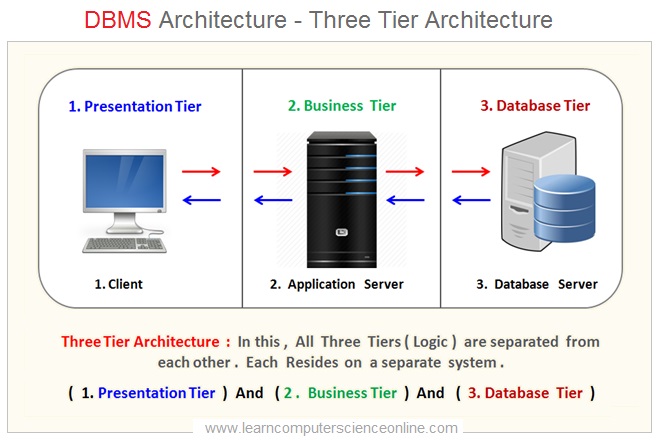
Database Management System
What Is Data Independence ?
Logical And Physical Data Independence
The database management system allows the database designers both logical and physical data independence. The database schema defines the view of the database at three levels that is external schema , logical schema and internal schema .
The data independence is the ability to modify a schema definition in one level ( either Internal , logical Or external schema ) without affecting a schema definition in the next higher level.
DBMS Three Schema Architecture
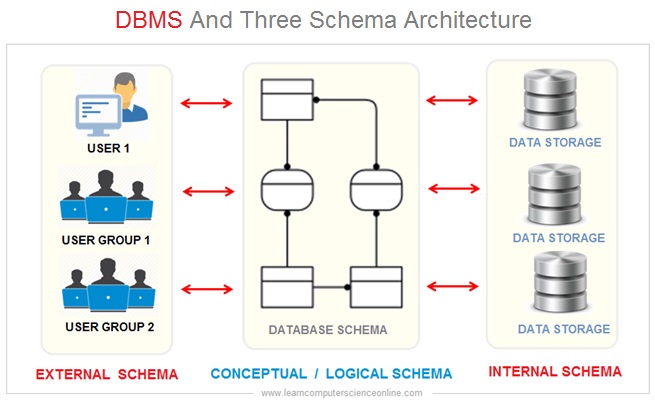
The logical data independence provides a simplified view of the database and the end user need not worry about complexities of how the data is physically being stored and any changes in the hardware ( Storage devices ) .
The end user interacts with the application program which acts as an interface between the user and DBMS. The application program makes use of the DBMS API ( Application Programming Interface ).
And therefore, the application program doesn’t require any modification due to changes in the database structure .
Database Management System
DBMS
Database System Environment
The database system environment refers to a set of components used within a database system that define and control the collection, storage, management and use of data . Each component performs a specific role within a database system environment.
A DBMS structure usually consist of number of components ( Also referred as modules ) depending upon DBMS architecture and the relationships between these components .
The DBMS software internally might consist of several modules. Each module or component is assigned to perform a specific database operation .
Database System Environment Components
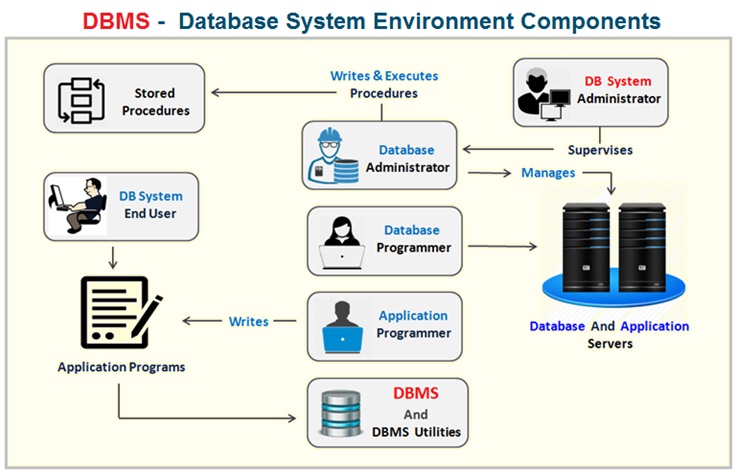
Some of the functions of the DBMS are supported by the operating system ( OS ) to provide basic services and DBMS is built on top of it . The physical data and system catalogue are stored on a physical storage disk.
Database Management System
RDBMS
Relational Database Management System
A relational database is a database that is based on the relational model . The Relational Database Model was proposed and developed by E.F. Codd who was an English computer scientist while working for IBM .
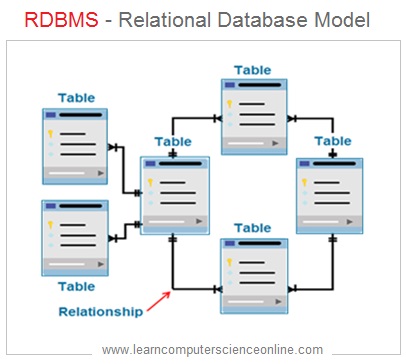
What Is RDBMS ?
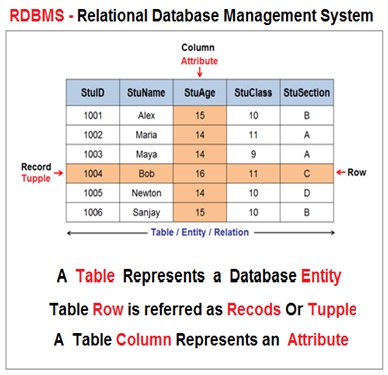
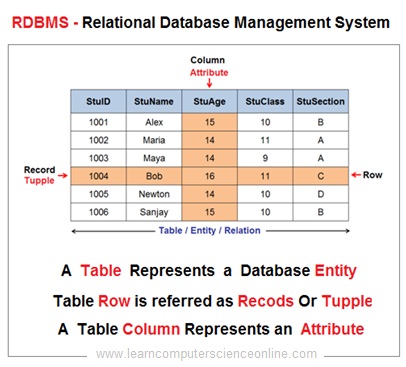
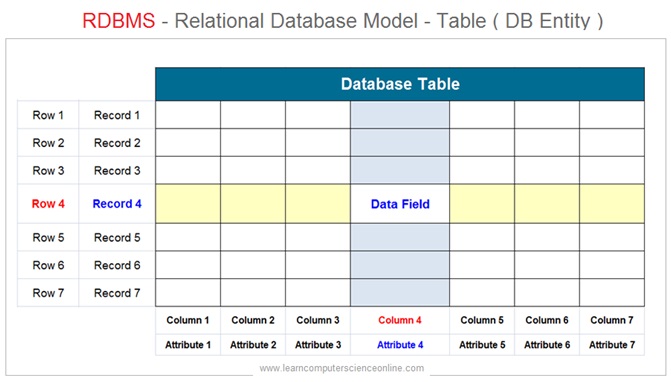
In a relational database model , the database is logically organized as group of inter related tables . Each table can have multiple rows and columns . A table is a collection of records and represents a database entity .
Each row in a table represents a record ( Tuple / Row ) which consist of number of data fields . The columns in a table represents an attribute for an entity .
The intersection of row and column is referred as field which actually holds the data. Each field can be accessed with reference to respective column and row.
READ MORE
What Is Table In RDBMS ?
DBMS FAQ
Database Management System FAQ
What Is Database ?
The Database is an organized collection of inter-related data permanently stored into the storage device. The database can be used for the efficient management of data.
The database allows the retrieval, insertion and deletion of data from the database. The data is organized into the database in the form of tables, views, schemas, reports etc.
For Example, a business organization can store the data related to the customer, employees, inventory and accounts.
Similarly, the university database can organize the data related to students, exam records, time tables, staff, faculty, and accounts.
What Is Data ?
Since the database contains the data , and therefore it is important to understand the meaning of term in the context of DBMS.
The term data is defined as recordable facts , observations , factual information , set of values and figures related to some specific entity.
The entity can be either an object that has physical existence or simply a conceptual entity such as courses offer by an university.
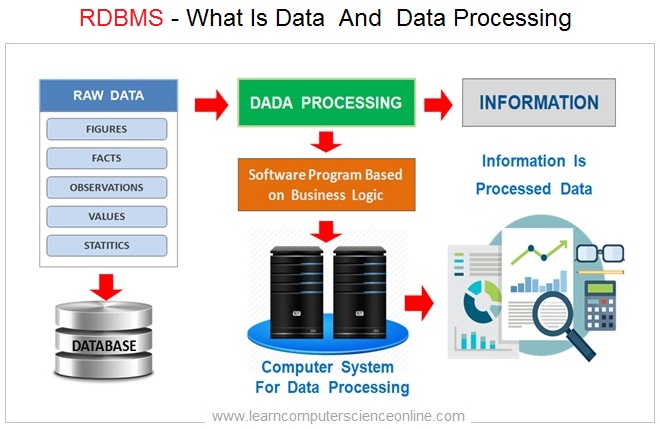
The objects can be either students , employees , customers , house, car and other such entities. The data must be collected and stored that can be digitally processed.
For example the employee related data could be the information such as employee Name , address , designation , DOB , Salary and other such information stored into the employee database.
What Is Database Management System ( DBMS ) ?
The term Database Management System ( DBMS ) is an application software specially designed and used for the creation and management of the databases.
Some of the most common examples of the Database Management System ( DBMS ) include MySQL , Oracle, MangoDB, Vector Database and MS SQL Server.
The DBMS works as an interface between the application program and the database to perform various database operations.

What Is SQL?
The SQL is a standard database communication language used by the application software to communicate with the DBMS to perform various database operations.
The SQL stands for structured Query Language is a standard database programming language and considered as industry standard. The SQL is widely supported by many database management systems.
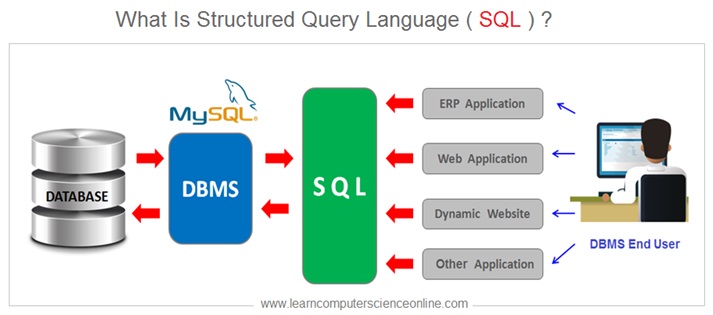
What are database operations ?
The database are managed by using DBMS software. The DBMS performs various database operations such as creating database and tables, data retrieval, data insertion, data deletion and report generation.
The database user communicates with the application software for DB operation to be performed.
The application software communicates with DBMS and translates the into necessary SQL commands. The DBMS performs the desired DB operation as per the SQL command.
Join Best Seller
Database Design Online Course
Learn database design and development step by step. This is the most comprehensive and unique Database Design course Online.
This course will give you in depth understanding of most important fundamental concepts in database design with MySQL project .
Join The Best Seller
Computer Science Online Course
This is the most comprehensive and unique Computer Science And Programming Fundamentals course Online which will give you in depth understanding of most important fundamental concepts in computer science And Programming .