Computer Memory
How Computer Memory Works ? | Memory Hierarchy
What Is Computer Memory ?
The computer memory is one the most vital component of the computer system. The computer memory is an important resource which is managed by the operating system.
In this article you will learn, what is computer Memory ? , Functions Of system Memory , System Memory Hierarchy , What is Primary And Secondary Memory.
The computer memory unit consist of different types memories organized in a hierarchical order in order to optimize the processor performance.
In computer architecture , the computer memory unit closely works with the processor. The system makes use of different types of memories during the program execution.
The operating system loads the executable copy of the program into the main system memory ( RAM ). The CPU then initiates the program execution with its internal process called the instruction cycle.
In this article . we are going to discuss all these topics in detail in order to understand the functioning of the computer memory unit.
We will also discuss other important topics related to the Computer Memory and how memory unit functions in a computer system.
What Is Computer Memory ?
Table Of Contents
What Is Computer Memory ?
Interview Questions Answered
- What Is Computer Memory ?
- What are different types of computer memory ?
- Why Computer System needs memory hierarchy ?
- What is Primary And Secondary Memory ?
- What is Temporary And Permanent Memory ?
- What Is Cache Memory ?
- What Is Virtual Memory ?
- What Computer Data Storage Devices ?
- How CPU Executes Program Instructions ?
- How Computer Memory Is Organized ?
What Is Computer Memory ?
Human brain is super intelligent and amazing organ of our body . It helps us do all the calculations , make decisions , control all other organs of the body , store and retrieve information .
The human brain can store the information in the brain cells in the different parts of our brain. We can also retrieve this information depending upon how that information is stored in our brain .
Human brain can store information in the brain cells in different parts of our brain and we can also retrieve this information depending upon how that information is stored in our brain .

The human brain can store the information in temporary and permanent memory in the brain cells in different parts of our brain .
And we can also retrieve this information depending upon how that information is stored in our brain .
Similarly , the computer system also makes use of both temporary and permanent memory . Depending upon the type of data and the program instruction , the information is stored or discarded after its use.
What Is Computer Memory ?
Computer System Memory
A Memory Unit is an essential feature of all computer system . The Computer memory can store information ( Data ) and instructions ( Computer Program ). A computer memory is the storage space in the computer system where both data and the program instructions are first stored .
The computer system needs a program to perform a specific operation on the computer system . The operating system allocates the necessary resources to execute the program in terms of memory space and the CPU processing time .
The CPU initiates the program execution by fetching the program instructions and data from the main system memory RAM ( Random Access Memory ).
Computer Block Diagram
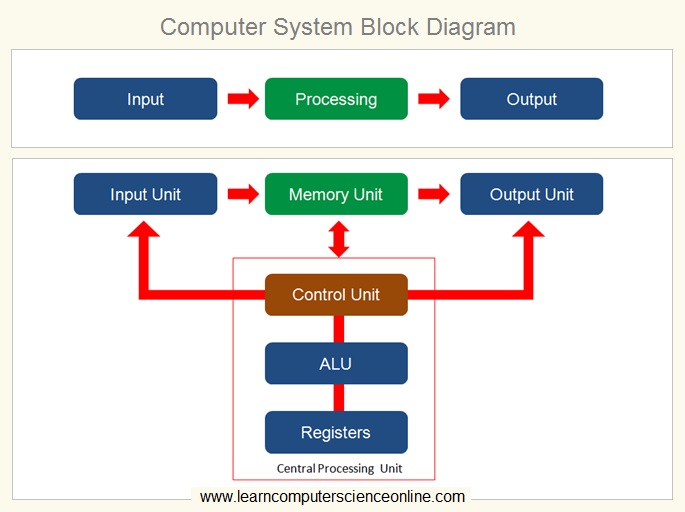
During the program execution , the computer CPU ( Central Processing Unit ) fetches the data and program instructions into the processor’s internal memory and then operates on the data as per program instructions.
The Processed data then either sent to the output devises or stored in to the computer system permanent memory ( Storage Device ) for future use.
Types Of Computer Memory
The computer system makes use of different types memory depending upon the functional requirements .The system memory is mainly divided in to two basic types based on the data retention by the system memory when the electric power is switched off to the computer system.
Primary Memory OR Volatile Memory
The primary memory is also known as Temporary Memory OR Volatile Memory OR Main System Memory.
The primary memory retains the data till the time the computer system is switched on . Once the computer system is switched Off the data will be lost . And therefore, this memory is referred as volatile memory OR temporary memory .
( Example – RAM , CACHE Memory ).
Secondary Memory OR Non-Volatile Memory
The Secondary memory is also known as Permanent Memory OR Non-Volatile Memory OR Storage Memory.
The Secondary memory is mainly used to permanently store the data . The secondary memory retains the data even after the computer system is switched off and electric power is disconnected . And therefore ,this memory is referred as Non-volatile memory OR Permanent memory .
( Example : Hard Disks , CD ROM Disks , Pen Drives ).
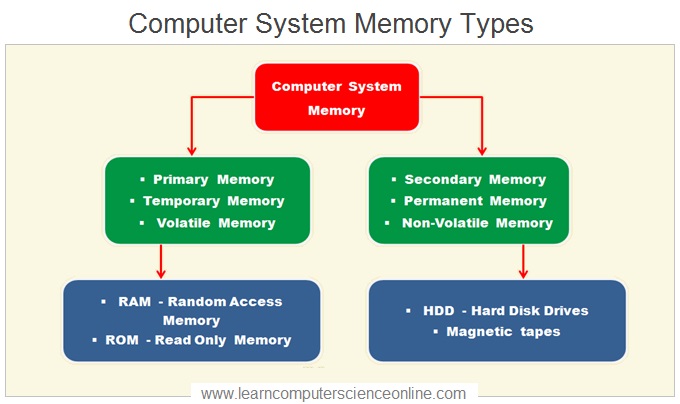
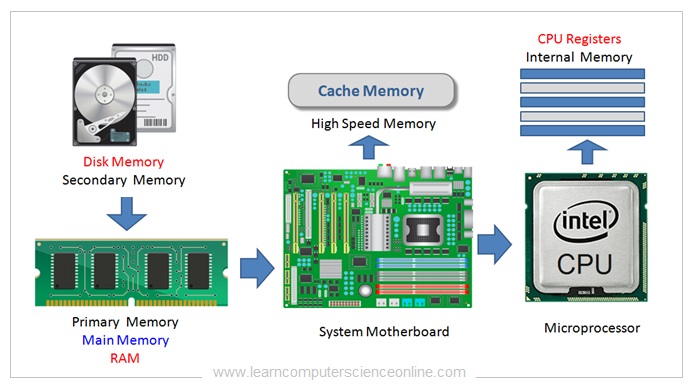
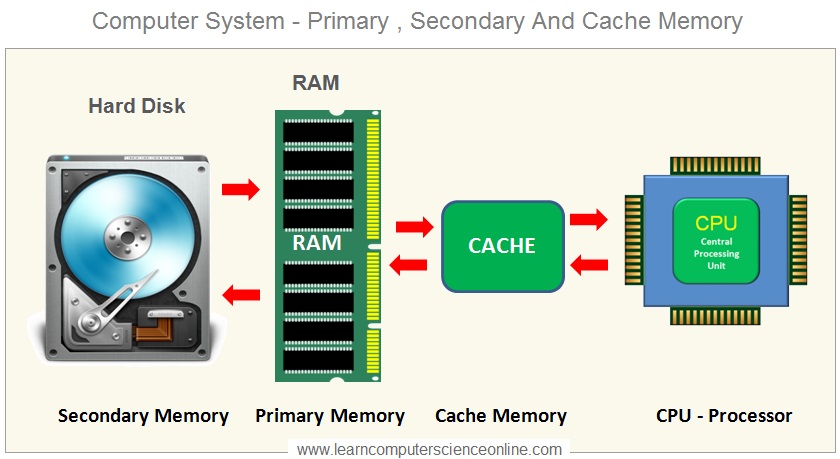
In a computer system , different types of memories are used which are part of the overall system memory unit . These different types of memories are organized in hierarchical order to optimize the CPU performance.
This hierarchical arrangement of different types memory storage used in computer architecture is called the memory hierarchy.
The memory hierarchy in a computer system is designed in such a manner that CPU can quickly access the data and the program instructions . This hierarchical memory arrangement significantly improves CPU performance .
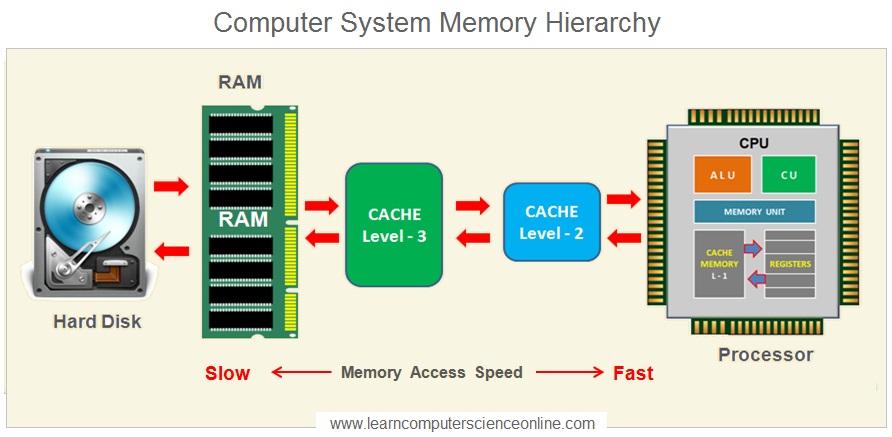
The CPU can process the data and instructions at a very high speed as compared to the speed of the data that can be accessed by the CPU from the disk ( permanent / secondary ) memory which limits the CPU performance .
And therefore , an intermediate high speed memories ( Cache Memories L1 , L2 , L3 ) are placed in between the CPU and the disk memory to enhance the CPU performance by providing quick data access .
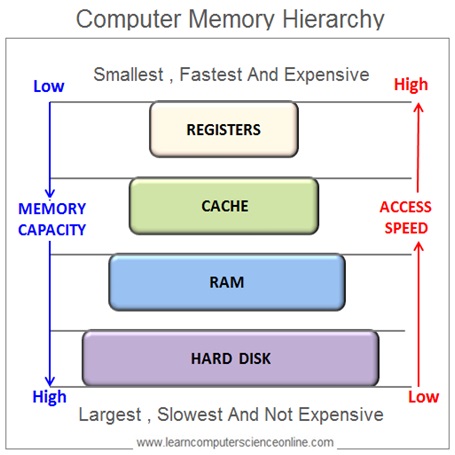
As shown in the memory hierarchy diagram , the computer system memory unit consist of different types of memories arranged in hierarchical order . The CPU registers are the fastest , smallest and closest to the CPU .
Whereas the the secondary memory ( disk memory ) is the slowest in data access speed , largest in memory capacity and farthest from the CPU in a typical system memory hierarchy.
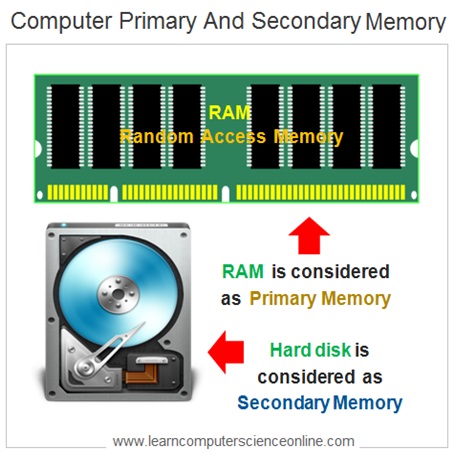
Computer Primary Memory
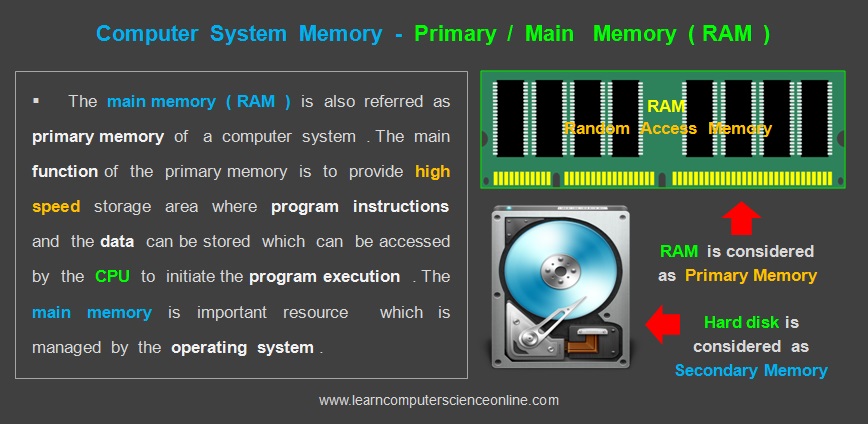
The primary memory in a computer system is also called as main system memory . The main memory stores the data in RAM – Random Access Memory of the computer system which is a volatile memory
In order to execute any program , the computer program and the data must be first loaded into the RAM . The memory resource is managed by the operating system . The computer CPU starts fetching data and program instructions from the RAM during the program execution.
The RAM ( Random Access Memory ) is the main memory of any computer system .The RAM is directly readable by the Central Processing Unit ( CPU ) of a computer system. Every computer system must have a RAM .
The RAM modules are installed into the motherboard slots of a computer system. Additional RAM modules can be added to the system to increase the size of the main memory available to the computer system.
Read More
Computer Secondary Memory
The secondary memory is also alternately referred as permanent memory Or Non volatile memory Or disk memory and used to store the programs and data on a long-term basis. The commonly used secondary storage devices are the hard disk and optical disks
The secondary memory is also alternately referred as permanent memory Or Non volatile memory Or disk memory and used to store the programs and data on a long-term basis. The commonly used secondary storage devices are the hard disk and optical disks .
The storage capacity of the hard disk is very high as compared to the RAM . The common size of the RAM is generally 4 GB to 16 GB whereas the common hard disk size is 250 GB to 1 TB ( 1024 GB ) , 5 TB .
However , the data access speed of the secondary ( disk memory ) is very slow as compared to the data access speed .of the main memory RAM.
What Is Cache Memory ?
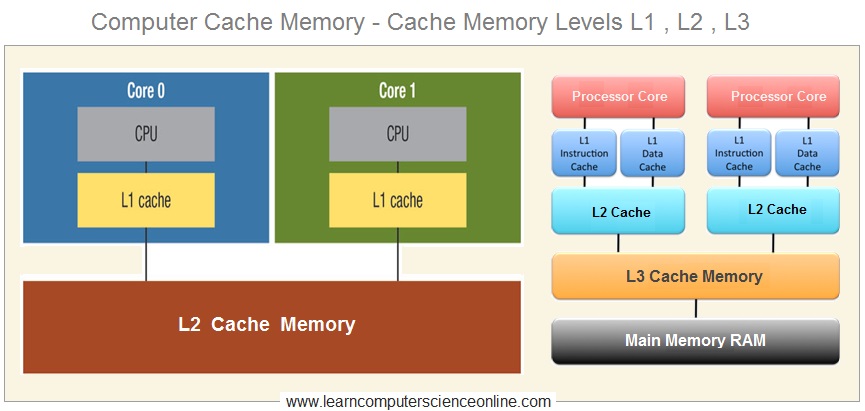
The Cache memory is a small-sized high speed volatile system memory that provides high-speed data access to a processor . The cache memory stores the frequently used computer programs, applications and the program data.
The cache memory is the fastest memory in a computer and can be used in three levels ( L1, L2 And L3 ) depending upon system architecture.
The L2 cache is generally integrated onto the motherboard and L1 cache is directly embedded in the processor chip . The L3 cache memory is placed into the main memory module RAM ( Random Access Memory ).
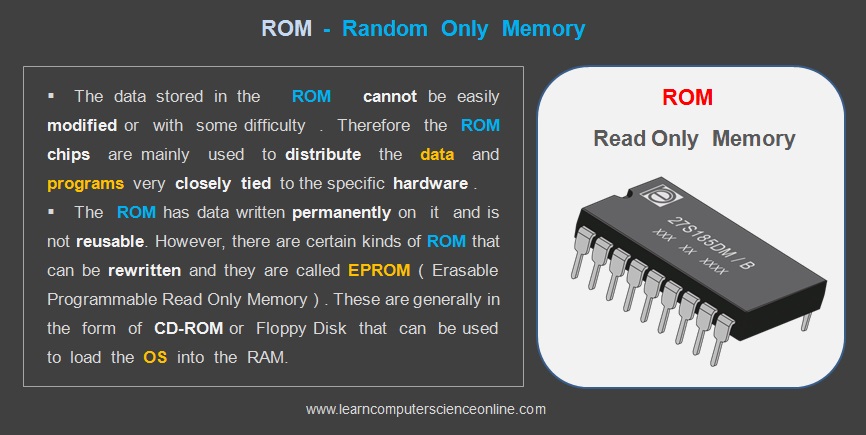
Read Only Memory ( ROM )
In computer architecture, a computer system makes the use of different types of memories arranged in a hierarchical order . These memories can be classified as Volatile and Non-Volatile memory depending upon the ability of the memory to retain the data when system power supply is switched off .
The ROM stands for Read Only Memory which is a non-volatile memory that means the contents of the ROM will not be lost even if the computer system supply is switched off .
The ROM chip is type of IC ( Integrated Circuit ) chip in which the data and program is embedded by the chip manufacturing company . Example : A BIOS chip which BIOS routines used in booting process.
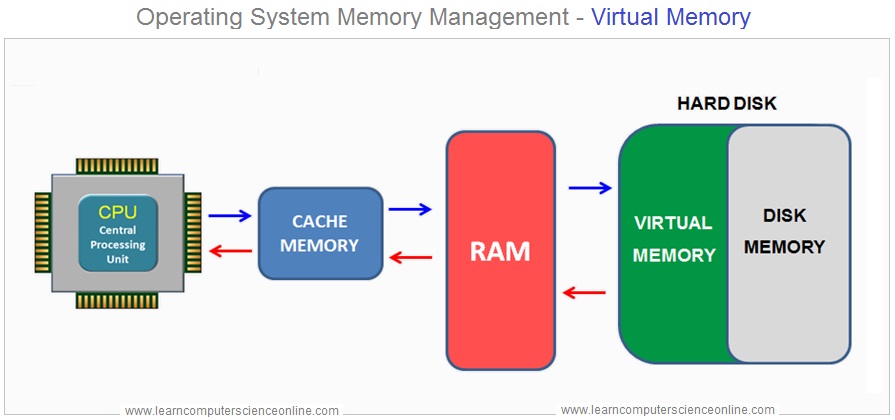
What Is Virtual Memory ?
The virtual memory is a mechanism used by the operating system to run processes that exceeds the available RAM size. Operating System Memory Management.
The virtual memory is a mechanism ( software ) used by the operating system to efficiently execute the multiple programs or processes simultaneously running on the system .
Computer Memory Units
The computer system memory is a crucial resource within a computer system . The computer operating system is responsible to manage this crucial resource.
The operating system allocates the required memory to the various processes running on a computer system .The computer system memory is measured using different types of standardized measurement units .
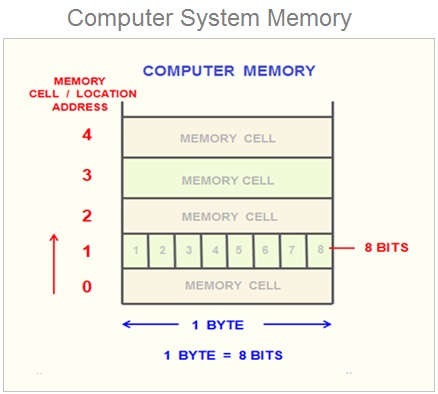
In computing world , a bit represents a 1 memory cell which stores either Binary 1 ( One ) Or 0 ( zero ) .
The Byte is the least measure unit of memory which consist of 8 Bits . The most commonly used data storage units are expressed in terms of multiple of Bytes .
Computer Memory Units

Memory Organization
The Computer system makes use Of main system memory ( RAM ) to hold the programs being executed and the data associated with these programs on which CPU operates.
The memory is divided into large number of small parts called cells ( 1 Cell = 8 Bits = 1 Byte ) . Each memory location or cell has a unique address which starts from zero to memory size minus one.
For example if computer has 64 kb words, then this memory unit has 64 * 1024 = 65536 Bytes cells / memory locations. The address of these locations varies from 0 to 65535.

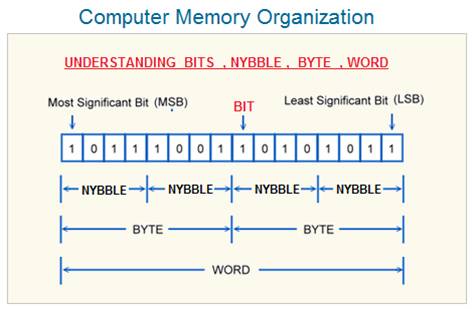
In computing , with reference to memory organization, a word is defined as specific number of bits which can be processed together ( i.e. in one attempt ) by the processor .
Alternatively , we can say that a Word defines the amount of data in terms of number of bits that can be transferred between the CPU and main memory RAM in a single operation.
In this example , the memory word size is 16 Bits . That means the 16 Bits of data can be transferred between CPU and main memory RAM in single operation.
Computer Memory Organization
The memory is generally organized as array of bytes ( 1 Byte = 8 Bits ) and each byte represents a memory location with its unique memory address .
The memory can also be organized as word addressable and each word with unique memory address . However the memory address numbers for each word will be decided depending upon the word size ( 32 Bit word OR 64 Bit word ) as shown in this example.
The program execution starts when it is loaded in to the RAM by the operating system . The Operating system allocates the required memory for the program execution .
The program loaded into the RAM is a set of machine code instructions in binary consisting of only 0 and 1 .
Computer Memory Organization
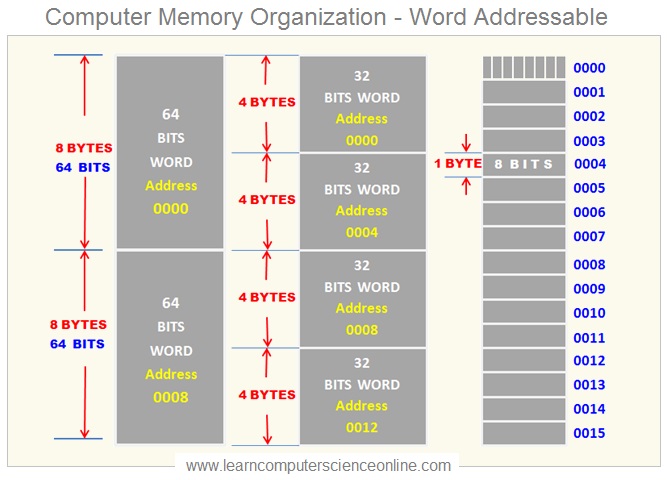
The Memory ( RAM ) is composed of bits, groups of 8 bits which form a 1 byte . Each byte can be addressed with unique memory address number and hence byte is a smallest addressable memory unit
Computer Data Storage
Computer data storage is an essential feature of every computer system . In computer architecture , the computer system makes use of both temporary and permanent computer data storage devises . Computer data storage devises are the memory of the computer system.
Computer data storage is the name for number of data storage components and devises used to store the data within a computer system .
During the program execution , the operating system loads the executable copy of the program and its data into the main system memory RAM which is a temporary or volatile data storage device .

The CPU is responsible to run the program . The computer program consist of number of program instructions in machine code ( Binary ) . The CPU initiates the program execution by fetching these instructions from the main memory RAM .
The computer data storage makes use of Cache memory and memory registers another intermediate data storage components placed between the CPU and the main primary storage RAM .
The CPU can access data from these computer data storage devises ( Registers , Cache And RAM ) at mush faster rate which significantly improves the CPU processing speed.
Computer Memory And Program Execution
How CPU Executes Program Instructions ?
The Operating System initiates the program execution by loading the program instructions and associated data into the main system memory ( RAM ) .
The CPU ( Central Processing Unit ) fetches these program instructions and data from main memory RAM into first intermediate Cache memory and finally into the CPU Registers which is a internal memory of the processor.
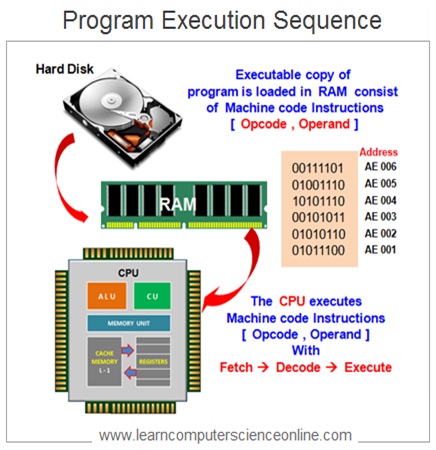
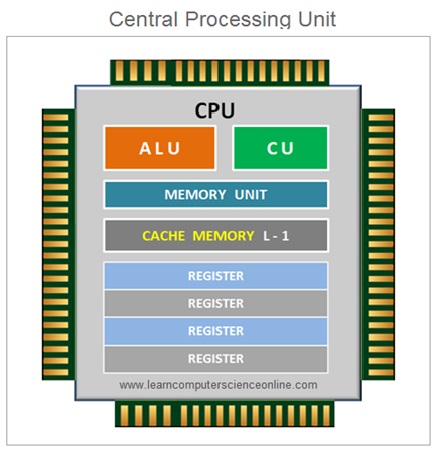
The CPU performs the operation on the data as per the program instructions . Once the data is operated , the processed data is sent back to the main memory RAM for further action .
At this stage the processed data can be either transferred into the permanent storage device ( disk memory ) or sent to the output device such as printer or system monitor for the user .
Computer Memory And Microprocessor
Learn Computer Science And Programming Fundamentals
Online Course - Udemy
This is the most comprehensive and unique Computer Science And Programming Fundamentals course Online which will give you in depth understanding of most important fundamental concepts in computer science And Programming .
Join Best Seller
Database Design Online Course
Learn database design and development step by step. This is the most comprehensive and unique Database Design course Online.
This course will give you in depth understanding of most important fundamental concepts in database design with MySQL project.