Virtual Memory
What Is Virtual Memory ?
How Virtual Memory Works ?
The virtual memory is a mechanism ( software ) used by the operating system to efficiently execute the multiple programs or processes simultaneously running on the computer system .
The system memory management is one of the important function managed by the operating system . The virtual memory allows the operating system to execute the programs that are larger than the available main memory ( RAM ) size in a computer system.
The system memory unit consist of number of components such as main memory RAM , disk memory , cache memory and ROM which are present in the system as hardware components. Whereas the virtual memory is just a logical extension of the main memory.
The virtual memory ( VM ) is crucial for the functioning of the computer system and it is created and managed by the operating system .
In order to understand the concept of virtual memory and how it works , we need to first understand the related topics such as process management and memory management functions performed by the operating system.
In this article , we will discuss in detail what is virtual memory , why system needs it , how VM is created and managed by the operating system , process management and how it is linked to the virtual memory.
Virtual Memory
Table Of Contents
Memory Unit
What Is Computer Memory ?
The system memory in an important component of the computer system . The memory is used by the system to store the data and programs that directs the computer system.
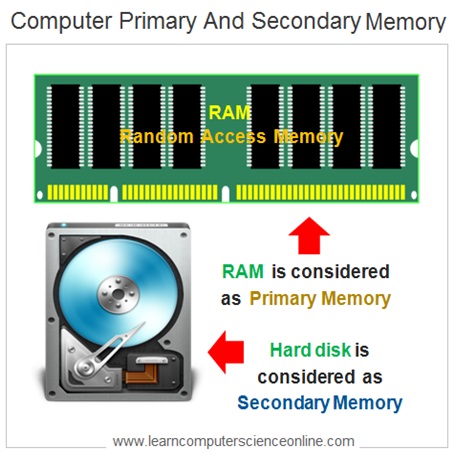
A computer memory unit consist of both permanent memory ( disk memory also known as secondary memory ) and the temporary memory ( main memory RAM also known as primary memory or volatile memory or temporary memory ) .
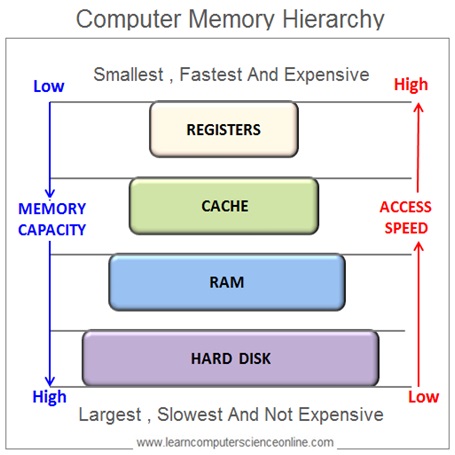
The computer system architecture makes use of different types of memory which differ in size and data access speed . These memories are placed in a hierarchical order in order to optimize the CPU ( Microprocessor ) performance.
And therefore , the Computer system memory unit consist of different types of memory arranged in hierarchical order . Each of these memory performs a specific function and optimally used by the OS during various stages of the program execution .
What Is Computer Memory ?
Virtual Memory
Operating System And Memory Management
The Operating System is a system software and an essential component of every computer system . The user can operate the computer system when the operating system is loaded into the memory and fully operational.
An operating system is the most important software component of a computer system which provides the necessary resources and the run-time environment to various software applications running on the computer .
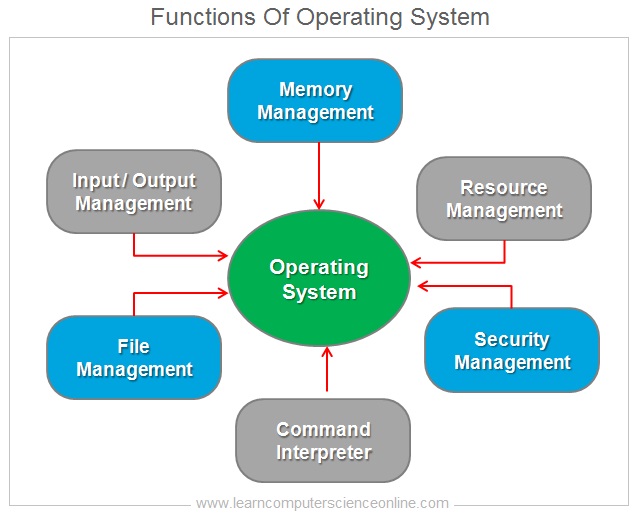
The operating system is the overall in charge of the computer system . The operating system also has the access to all the critical functions and the resources managed by the computer system.
The operating system handles some of the most crucial functions necessary to operate the computer system . These important functions managed by the operating system include resource management , file management , memory management and process management .
The memory management is one of the most crucial function managed by the operating system . The operating system allocates the resources to various programs ( processes ) running on the system . These resources include main memory RAM and the processing time of the processor.
Virtual Memory
Process Management And Virtual Memory
The computer user generally works with number of programs which is also referred as multi tasking environment.
For example the user might open two or more websites simultaneously using the internet browser. Each of these open web-page in the browser represents a process .
When the user initiates the program execution , the operating system loads the executable copy of the program into the main memory RAM. The CPU then starts the program execution by fetching the program instructions from the main memory ( RAM ).
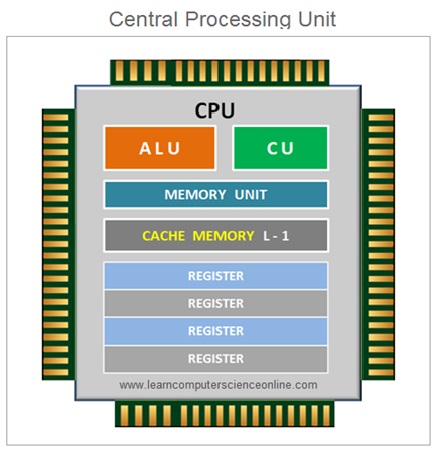
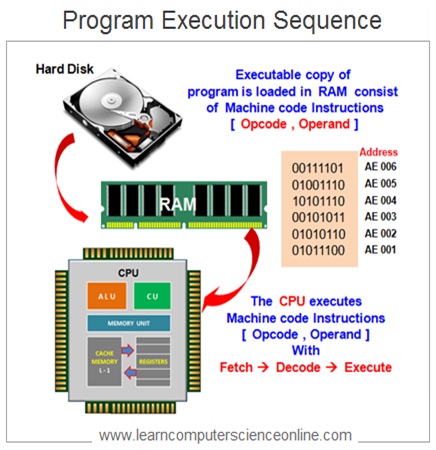
Virtual Memory
Process Management And Virtual Memory
A process is created by the operating system to execute the program . The process management and memory management are important functions managed by the operating system.
The memory management is an important function managed by the operating system . However , memory is a limited critical resource and the operating system is responsible to allocate the memory to different programs.
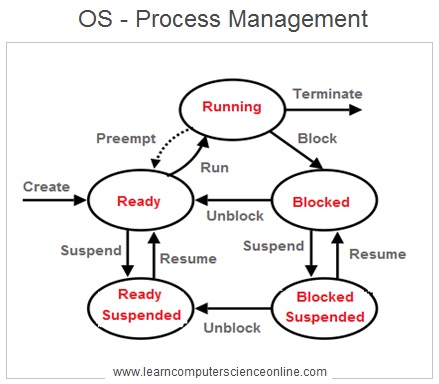
What Is A Process ?
How A Process Is Managed By The Operating System
In simple terms , a process is an instance ( copy ) of a computer program that is being independently executed by the CPU. Each open web-page in a browser represents an instance of a program .
A process is created by the operating system when the program is loaded into the memory for its execution. A process goes through different stages and these stages are managed by the operating system.
The operating system handles several processes running simultaneously on the system . These processes can either be associated with the same program or with different programs.
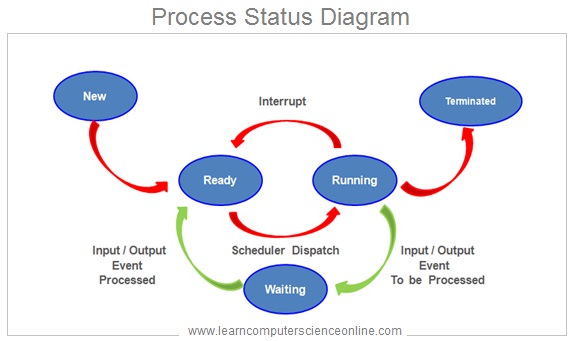
In order to initiate the program execution , the operating system loads an executable copy ( binary machine code / low level ) of the program into the main system memory RAM.
In other words , a process is the actual execution of these program instructions when operating system allocates the necessary resources ( in terms of memory and processor time ) and loads the program into the RAM.

What Is Virtual Memory ?
The main memory ( RAM ) size in a computer system is one the important performance parameter. The RAM size generally ranges from 4 GB to 16 GB depending upon the system configuration .
If the memory size required for the process exceeds the available main memory ( RAM ) then system will crash . However , the operating system efficiently handles this problem with the help of inbuilt mechanism called the virtual memory .
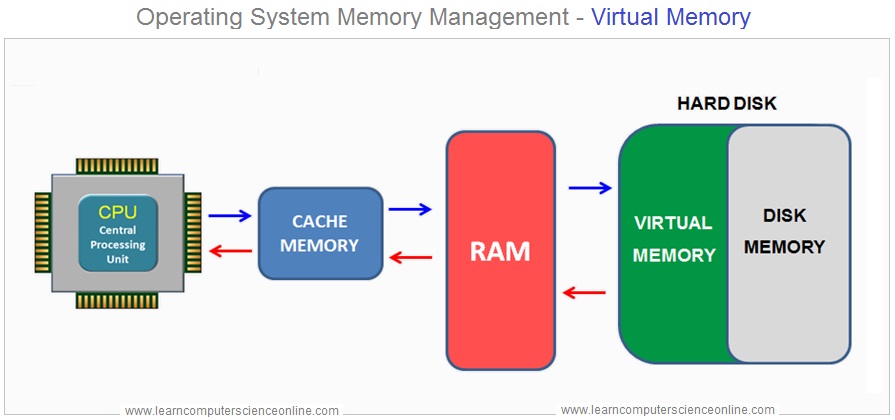
The virtual memory solves the problem of insufficient memory by converting a part of disk memory ( secondary memory ) into virtual addresses thereby creating a large size of RAM to accommodate the increased demand for memory requirement.
The OS also creates a process table to keep the track of mapping between RAM and virtual memory . The Operating system then translates these virtual addresses into physical addresses.
The virtual memory is a critical mechanism which allows the OS to use some portion of the disk memory ( Secondary Memory ) as logical extension of the main system memory RAM . Thereby allowing the execution of the programs that exceeds the available size of the main memory RAM .
How Virtual Memory Is Implemented By The Operating System ?
The virtual memory is an important mechanism provided within the operating system to use some portion of the secondary memory ( Hard Disk also referred as disk memory ) as an extended RAM.
The operating system makes use of this extended virtual RAM to efficiently manage the various processes simultaneously active in the main memory RAM.
The operating system implementation of the virtual memory function consist of number of steps . These steps includes implementation on both hardware and software side.
The hardware side of virtual memory deals with the physical RAM modules and the software side deals with the process management by the operating system .
The main memory RAM is physically present in the computer system installed on the motherboard as RAM modules. Whereas the virtual memory is the logical extension of the main memory RAM using some portion of the disk memory.
The operating system manages the virtual memory mechanism by splitting the main memory RAM into number of page frames and the process into number of blocks .
Virtual Memory Implementation
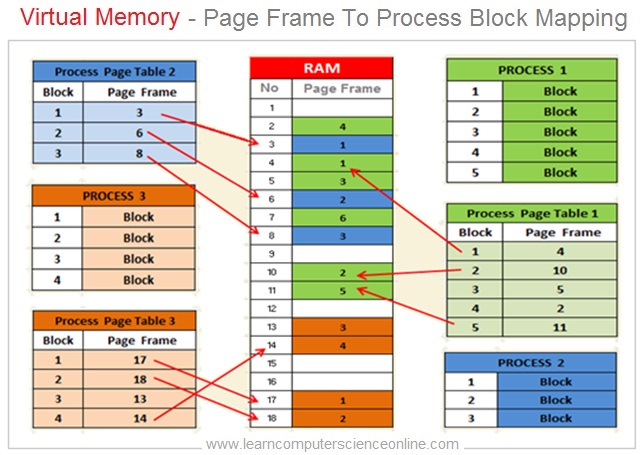
The operating system splits the RAM in to equal size partitions called page frames or simply pages . The general size of the page frame for Intel processors is 4 Kb which could vary on a higher side for some recent processors.
EACH PAGE FRAME SIZE = 4 KB
Similarly , The operating system also splits the process into equal size partitions called blocks . The operating system splits the process in such a manner that that the process block size is equal to the size of the RAM page frame.
PAGE FRAME SIZE = 4 KB = PROCESS BLOCK SIZE
Virtual Memory Implementation
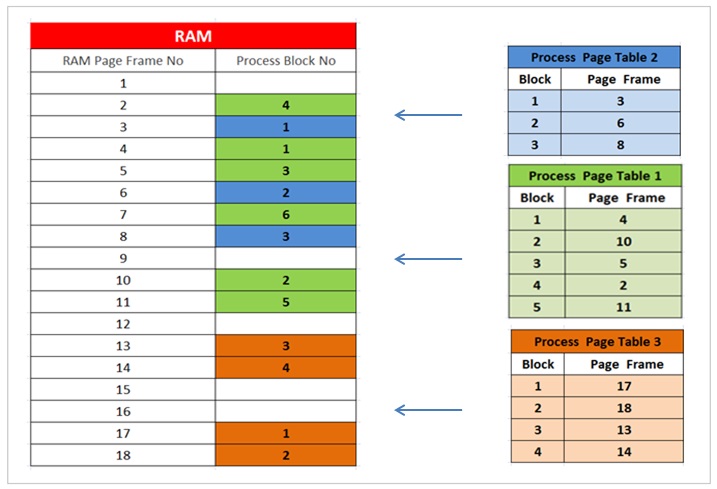
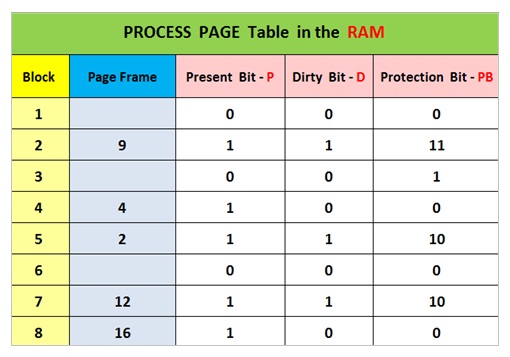
The operating system also maintains “Page Frame Table” for each process that is being executed by the CPU . The page frame table is also stored into the RAM .
The page frame table contains the details of the mapping for each process block and the corresponding page frame in the main memory RAM . The operating system creates this page frame table for each process loaded into the main memory RAM.
The CPU ( processor ) executes only one process at a time and during this period the associated page frame table will be a active table . The CPU will access the memory addresses only from the page frame table which is currently active .
The operating system does not load all the blocks associated with process but loads only those blocks which being used by the program.
Virtual Memory - On Demand Paging
The operating system allocates some portion of secondary storage ( Disk Memory ) as swap space . This swap space will have all the blocks / pages belonging to a process .
These pages from the swap area are loaded by the operating system on demand as required during the process execution by the CPU ( Central Processing Unit ).
The operating system also creates a process table ( a data structure ) in the RAM to keep the track of which pages are present and also not present into the main memory RAM.
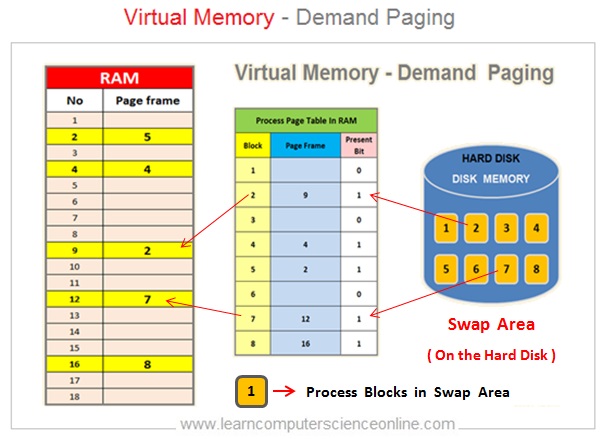
The present bit in the process page table indicates if that block is present in the RAM or not present in the RAM .
If the Present Bit = 1 Then the Block is present in the RAM.
If the Present Bit = 0 Then the Block is Not present in the RAM.
The CPU use page fault interrupt to load the blocks.
In demand paging the operating system loads only a part of the program ( blocks / pages ) into the main memory RAM . The remaining pages are stored into the virtual memory .
If the program access the page which not present in the RAM then processor issue a page fault interrupt which is a trigger for the operating system to load the page from swap space into the RAM and update the process page table present bit from 0 to 1 .
Virtual Memory
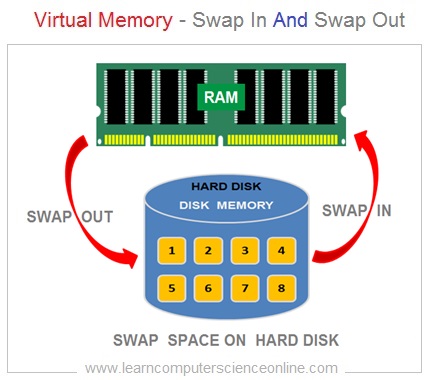
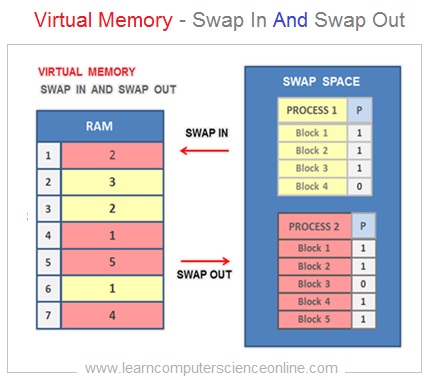
Demand Paging - Swap In And Swap Out
If there is no free page frame available in the RAM for new pages to be loaded then the OS has to remove some pages from the RAM . The OS takes this decision based on the replacement algorithm .
- First In First Out .
- Least Recently Used .
- Least Frequently Used .
SWAP OUT
The OS removes the pages from the RAM which are not in use by the process and copies back to the swap space on the secondary storage ( hard disk ) .
SWAP IN
The OS loads the required pages by the program from secondary storage ( hard disk ) swap space to the RAM . The present bit status is updated in process page table from 0 to 1 .
Virtual Memory
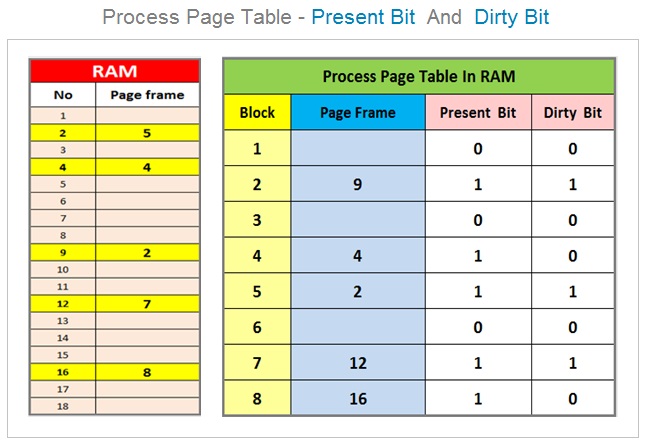
Process Page Table
Present Bit And Dirty Bit
PRESENT BIT
The present bit indicates the status of the process page / block presence in the main memory RAM.
DIRTY BIT
The pages already present in the RAM can be modified by the program and need to swapped out and copied back to the swap space so that the swap area on the secondary storage will have the updated copy . The process page table also need to be modified to track this change .
The process page or block modified by program inside RAM must be written back to the swap area . The operating system keeps the track of such pages with the help of dirty bit status inside the process page table .
Virtual Memory
Process Page Table
Protection Bit
PROTECTION BIT
The process page table has one additional column as protection bit in addition to P and D columns .
The PB column is used by the operating system to assign some additional attributes to the process page / block , such as executable code , read only and some other .
Learn Computer Science And Programming Fundamentals
Udemy Online Course
This is the most comprehensive and unique Computer Science And Programming Fundamentals course Online which will give you in depth understanding of most important fundamental concepts in computer science And Programming .