
Operating System
Introduction To Operating System
Basics Of Operating System
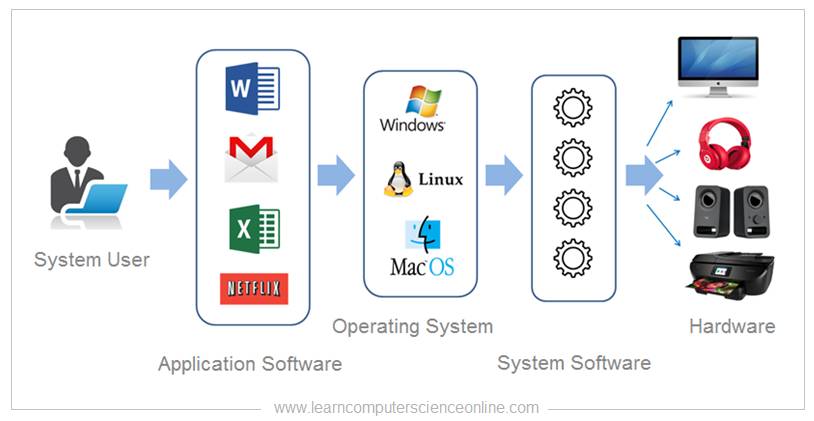
An Operating System is a type of system software and a crucial component of every computer system. The Operating system ( OS ) functions as an interface between application software and the computer hardware .
The OS provides an user friendly interface to the system user to perform various operations on the computer system.
Operating system performs some of the most crucial functions such as resource allocation management, system security, command interpreter, file management, communication with hardware components and, input and output management.
In this article , you will learn what is operating system , OS important functions, features, different types of OS and modes , components of OS and its architecture, OS booting process, program execution, processes management and other important topics related to the OS.
What is Operating System ?
Definition Of Operating System ?
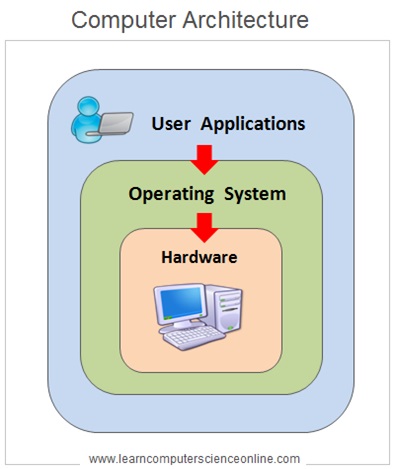
An operating system (OS) is a software program that acts as an intermediary between users and computer hardware. It manages hardware resources such as the CPU, memory, and storage devices, and provides services that allow applications to run smoothly.
The OS handles tasks such as managing files, running programs, and controlling input/output devices. It also provides a user interface, allowing users to interact with the computer system and perform tasks such as launching programs, managing files, and configuring settings.
Overall, the operating system is essential for the functioning of a computer, enabling users to use and control hardware resources effectively and providing a platform for running applications.
Fundamentals Of Operating System
Table Of Contents
What Is Operating System ?
The Operating System ( OS ) is an essential component of every computer system . The computer system cannot function without the operating system .
And therefore , when the computer system is powered on , the CPU’s first task is to load the operating system . The computer system becomes fully operational to the user only after the OS is loaded into the main system memory .
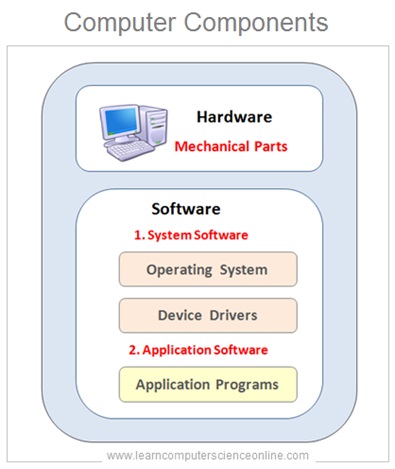
A Computer System consist of two main components :
- Hardware Components .
- Software Components .
The Software components consist of system software and application software . The application programs which provides an interface to the user cannot directly interact with the hardware components .
And therefore , the system needs a special system program called “Operating System” which can interact with the hardware components.
The OS internally use another system software called driver. The operating system interacts with hardware components through a set of drivers ( another system program ). The OS manages all application programs and system resources .
An operating system ( OS ) is the most important software component of a computer system which provides the necessary resources and the run-time environment to various other applications running on the computer .
An OS is system software that manages the computer hardware , software applications , system resources such as memory and provides common services to the computer programs .
The operating system is the overall in charge of the computer system . The OS also has access to all the critical functions and the resources managed by the computer system.
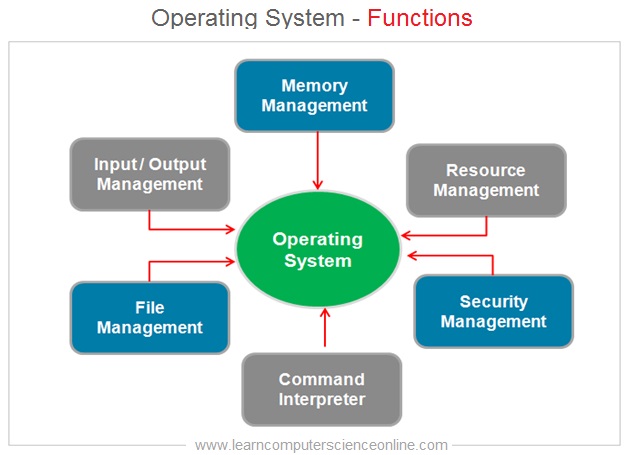
In order to effectively perform this role , the OS performs some of the most important functions for managing the software and hardware resources of the system .
Process Management
The computer user generally works in a multi tasking environment . For example the user might simultaneously open two or more ms word document or open multiple web pages in a browser .
Each of this open document represent a process . The OS initiates the program execution by loading an executable copy of the program into the main memory RAM .
In other words , In computing , a process is an instance of a computer program that is being currently executed . Each open MS word document active in the system memory represents an instance of program .
A typical computer program consist of number of program instructions . During the program execution , the OS allocates resources and the CPU starts executing these program instructions.
A process is the actual execution of these program instructions when Operating System allocates the resources ( Memory and processor time ) . The OS handles several processes running simultaneously and associated with the same program .
For Example : A user may working on number of MS word documents simultaneously .
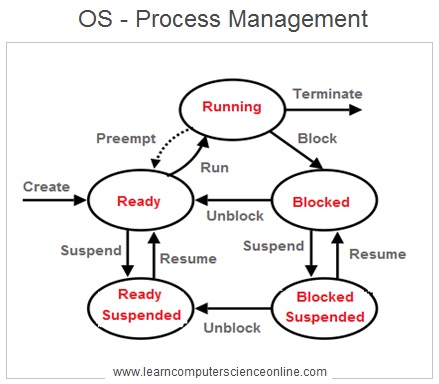

A process can be user application program Or system process . The OS is responsible to manage both these processes .
A multitasking operating system rapidly switches the CPU execution time between the different processes currently being executed .
Although , the CPU executes only one process at a time but due to rapid switching between the processes in queue , it creates an illusion that all programs ( processes ) are running simultaneously but actually CPU executes only one process at a time.
Process Management Diagram
The process management is an important function managed by the operating system . The CPU can execute only one process at a time . And therefore, The OS has to decide the schedule for the process execution .
This schedule includes the order of execution for different processes in pipeline at various stages of their execution and the CPU time to be allocated .
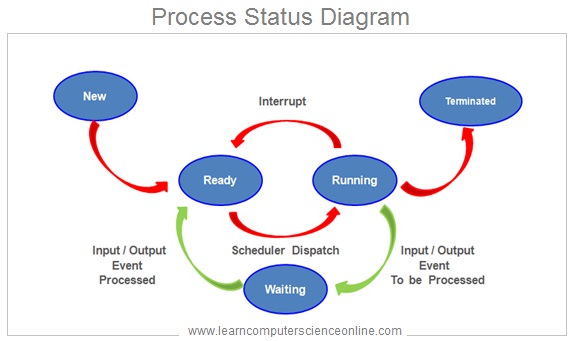
Process Status Diagram
Memory Management
The Operating System ( OS ) loads the program to be executed in to the main system memory RAM . The system memory is a limited resource that is managed by the OS . The program execution needs resources in terms of memory and the CPU’s processing time .
The operating system manages the memory of the computer system by allocating main memory to different process currently under execution at various stages .
The OS is also responsible main memory to reallocated the memory from the process that is already terminated . The system memory is an important resource and the OS manages this by allocation to new processes and by reallocating the memory from terminated processes.
Read More
Virtual Memory
Operating System Memory Management
For a computer system , the main memory RAM will always be a limited resource due to ever increasing size of the software and the number of programs simultaneously running on the system .
The OS solves this problem with the help of mechanism called the virtual memory . The virtual memory solves this problem by converting a part of secondary memory into virtual addresses thereby creating a large size of the RAM to accommodate the increased memory requirement.
The Operating system ( OS ) translates these virtual addresses into physical addresses.
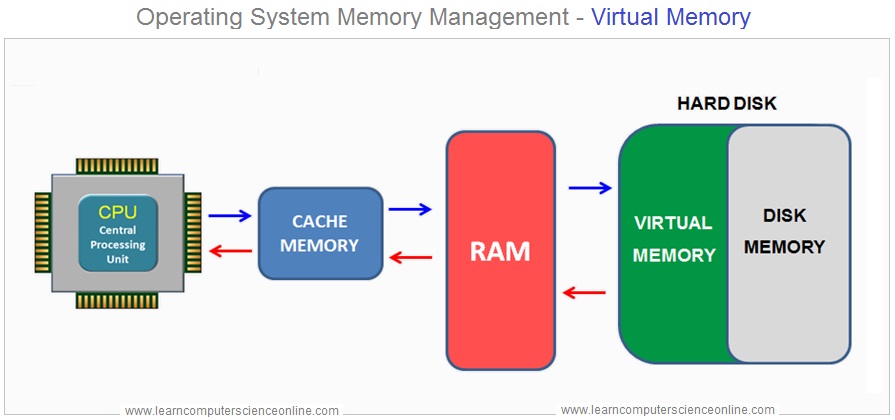
What Is Virtual Memory ?
The Computer system memory unit consist of different types of memory arranged in hierarchical order . Each memory performs specific function and optimally used by the OS during various stages of program execution .
The virtual memory is a critical mechanism which allows the OS to use some portion of the disk memory ( Secondary Memory ) as logical extension of the main system memory RAM . Thereby allowing execution of the programs that exceeds the available size of the available RAM .
READ MORE
System Resource Management
The resource management is one of the important function handled by the OS. The OS is the overall in-charge of the system resources . Some of the most important system resources include the main system memory RAM , Storage space and the processor cycle time .
The CPU starts the program execution when the operating system loads the executable copy of the program into the main system memory RAM .
The OS allocates the required memory to execute the program . The OS also allocates another important resource that is CPU’s processing time .
The computer system may be equipped with multi-core processor where each core functions as an independent processor . This complexity is more in a network environment where system resources are shared by many users.
The OS handles this complex operation of allocating and deallocation the resources amongst different processes running on the system and at different stages of execution.
Security Management
One of the important responsibility of the operating system is to provide secure and protected run-time environment to the various process ( both application process and system processes ) which are being executed on the computer system .
The System security is another important aspect which is handled by the OS . Protecting system against unauthorized access can be implemented by activating different security features of the OS .


Command Interpreter
A command interpreter is a crucial component of the OS and it is a program which reads the instructions given by the user. The command interpreter then translates these instructions into the context of the OS followed by its execution. The Command interpreter is also known as “shell’.
A command interpreter is the part of a computer operating system that interprets and executes commands that are entered interactively by the system user or from a application program. In some operating systems ( OS ), the command interpreter is commonly referred as “‘shell’.
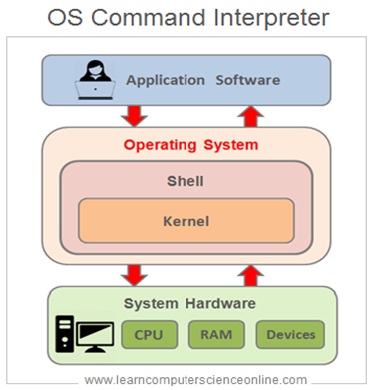
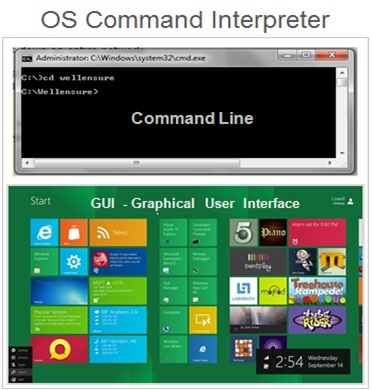
A command interpreter is an interface between system and the user. There are two types of user interface :
1. Command Line Interface.
2.Graphical User Interface ( GUI ).
Command Line : With a command line user interface the user interact with the Operating System by typing commands to perform specific tasks .
GUI Interface : With a graphical user interface ( GUI ) the user interacts with the Operating System by using a mouse to access windows icons and menus .
File Management
The file management is one of the basic and important features of the operating system ( OS ) .
The OS is responsible to manage the files in a computer system. All the files with different extensions are managed by the OS. The User interacts with the OS to perform various file operations.
A file is a collection of related information . A file can be a text file , image , audio , video and may contain data in any other form .
The OS presents the information to the user through GUI user friendly interface . However , the data is represented in a computer system only in a binary form ( 0 and 1 ) .
The data is stored permanently in a secondary storage device such as hard disk drives. This data is physically stored in hard disk in two states ( for magnetic tapes it is south and north poles ) which is represented in the binary form in a computer system .
The OS performs number of file operations that includes creating new file , modifying the and deleting the files . The OS also presents the user friendy logical view of the files which includes folders and different types of files .

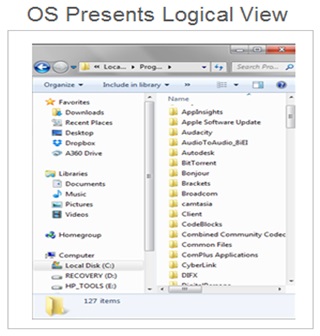
- Single User Single Tasking OS.
- Single User Multi Tasking OS.
- Multi User Multi Tasking OS.
- Multi Processor OS.
- Multi Programming OS.
- Multi Programming OS.
- Real Time OS ( RTOS ) .
- Batch And Parallel Processing OS.
- Distributed OS.
- Embedded OS.
A computer system can be designed to operate in different modes in terms of number of users working on the machine at the same time , number of processors used, data handling and the number of applications running simultaneously on the same computer system .
A computer system also needs to be configured accordingly and the system will also need the operating system which can support such operations . And therefore different types of operating system are used to support the different modes of operation .
What Are Modes Of Operating Systems ?
- Single User Single Tasking Mode.
- Single User Multi Tasking Mode.
- Multi User Multi Tasking Mode.
- Multi Processor Mode.
- Multi Programming Mode.
- Multi Programming Mode.
- Real Time Mode.
- Batch & Parallel Processing Mode.
- Distributed Mode.
- Embedded Mode.
Single User Single Tasking OS
A computer system can be designed to operate in different modes in terms of number of users working on the machine at the same time , number of processors used, data handling and the number of applications running simultaneously on the same computer system .
A computer system also needs to be configured accordingly and the system will also need the operating system which can support such operations . And therefore different types of operating system are used to support the different modes of operation .
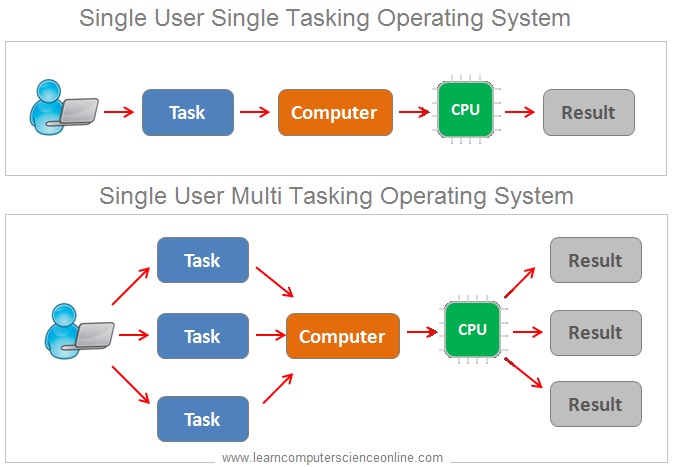
The single user single tasking OS supports only single process being executed by single user using single processor .
Whereas the single user multi tasking OS allows more than one program ( processes ) Or many instances of the same program to run concurrently.
For example with MS Windows OS , the user can open multiple MS word document files at the same time .
The single user multi tasking OS share common processing resources , such as a CPU time and main memory RAM . In multi tasking process , only one CPU is involved but it switches from one program to another so quickly that it gives an illusion of executing all the programs at the same time.
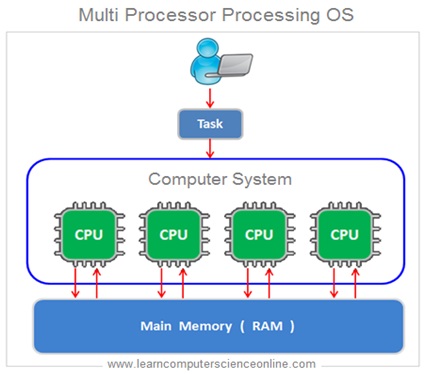
Multi Processor Processing OS
The Multi Processor processing makes use of more than one processor in a single system to enhance the system performance . Due to more number of processors, the system performance is significantly improved . However , all the processors share the same common main memory ( RAM ) .
A computer system with multi processor capability needs operating system which can support multiple programs execution simultaneously being processed by number of processors .
Real Time Operating System
A real-time operating system ( RTOS ) that is also commonly pronounced as “are-toss” is a multitasking operating system designed for real-time applications. A real-time computing guarantees response within specific time limits and thus suitable for quick reaction systems .
The Such applications include embedded systems, industrial robots, scientific research equipment and others. A real-time computing has extensive application especially in the field of military and space research .
The RTOS ensures a guaranteed response within specific time limits and thus suitable for quick reaction systems.
Common Operating Systems
Some of the most commonly used operating systems include :
- MS Windows.
- Android.
- Apple iOS.
- Linux.
- Unix.
- MS DOS.

Microsoft Windows
Windows is Microsoft’s flagship operating system , the de facto standard for home and business computers . Windows OS is GUI based operating system which provides a very user friendly interface . Even today MS windows has a leadership position
Google Android
Android is a mobile operating system developed by Google, based on the Linux kernel and designed primarily for touch screen mobile devices such as smart phones and tablets .
Apple iOS And Mac OS
The Apple iOS and mac OS are operating systems created and developed by Apple corporation exclusively for its own hardware that includes iPhone , iPad , Apple Laptops and desktops .
The latest version of iOS 12.3.1 And mac OS is 10.14.5 as on 2019 . Both iOS and mac OS are considered to be the most advanced mobile and desktop operating system respectively.
The Apple iOS and mac OS are also one of the most secured , powerful and user friendly OS with huge customer base across the world .
Linux
The Linux is a open source operating system. The Linux OS, is a freely distributed, cross-platform operating system
The Linux is based on Unix that can be installed on PCs, laptops, notebooks, mobiles , tablet devices, video game consoles , even as a server OS , Supercomputers and other computing devices.
Unix
The first version of Unix was not open source but subsequently many derivatives of Unix were developed including some open source . Mac OS is also Unix derivatives .
The Unix is a stable and powerful operating system that has been developed by many different vendors . There are many different derivatives of Unix systems that differ in terms of functionality , GUI look and feel , licensing terms and other non standard features , developed by these different vendors.

Microsoft DOS
The advent of the IBM PC in 1981 was accompanied by the emergence of IBM PC-DOS, which was provided by Microsoft and later marketed virtually unchanged as Microsoft MS-DOS.
The DOS ( Disk Operating System ) was a command-line operating system which borrowed many ideas from UNIX and other early operating systems, although it was essentially a single-user, single-tasking operating system without any GUI support .
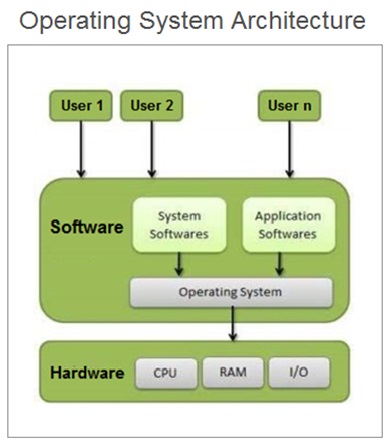
Operating System Architecture
Operating System Structure
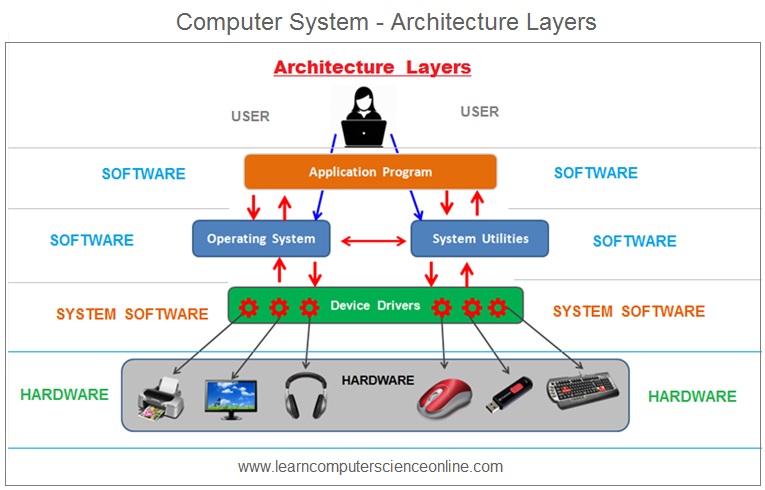
The OS is a complex piece of system software which is designed to handle some of the most crucial and complex operations performed by the computer system . The OS provides an interface between the system user and the computer hardware components .
The OS also allocate the required resources and the runtime environment to the application programs .The OS design is based on some structures which defines the internal architecture of the OS .
An operating system structure ( Also referred as OS Architecture ) is a term that specifies the overall internal structure of the operating system.
It includes the logical components and the logical interrelationships of various components and the functions of these structural components that constitute an operating system
Types Of Operating System Structures
Depending upon the internal structure , the Operating Systems can be grouped into of four major types as under :
OS Structure Types
- Simple Structure OS.
- Layered Approach OS.
- Monolithic Approach OS.
- Microkernel Approach OS.

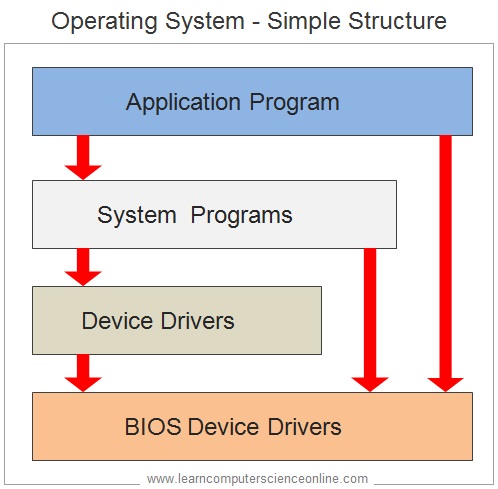
Simple Structure OS
As the name suggest , the simple structure OS has only four layers although it is not a layered OS . The MS DOS ( Disk Operating System ) was based on the simple structure . However , the simple structure OS had some major limitations .
In these OS , the application program had direct access to the BIOS drivers . If the application program fails due to some reason , which may cause system crash . The Simple Structure OS did not have a well defined structure which made these OS vulnerable for system crash .
Layered Structure OS
The lack of well defined layers and the modules was problem area for simple structure OS . To overcome these limitations, the next generation of operating systems adopted a layered Architecture approach of operating system developed in 1960’s.
In layered approach based OS , the operating system components are grouped in layers based on the functionality of these components . The bottom layer ( layer 0 ) is the hardware layer and the topmost layer ( layer n ).
In layered approach OS architecture , each top layer can use immediate bottom layer . And therefore , the functionality of the each layer needs to carefully designed and implemented in each layer .
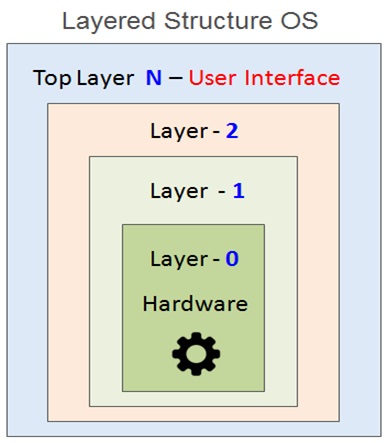
In case of layered OS structure , the OS is divided into number of layers depending upon the functionality of layers . It is relatively much easier to implement the layered architecture and that is the main advantage .
On the other hand , the layered structure OS are relatively less efficient .The MS Windows NT which is a network OS and OS2 were based on the layered approach OS .
Monolithic Kernel Operating Systems
What Is Kernel In OS ?
The OS consist of number of components and the core software components of an operating system are collectively called as the kernel .
The kernel components include system software components that manages file system , Inter process communication , Input and output , Device Management and process Management .
The kernel has unrestricted access and also responsible to manage all of the resources of the computer system.
Monolithic Operating Systems Architecture
In monolithic architecture operating systems , each layer of the operating system communicates only with the layer immediately placed above and below it .
In this architecture , the lower-level layers provide services to higher-level ones using an interface that hides their implementation.
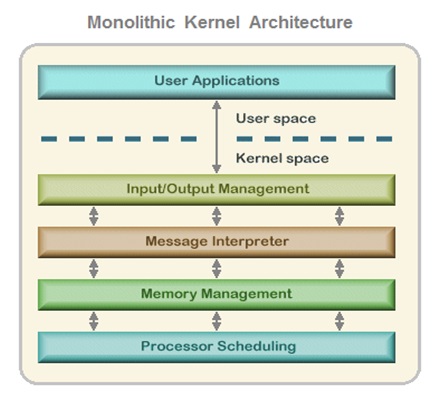
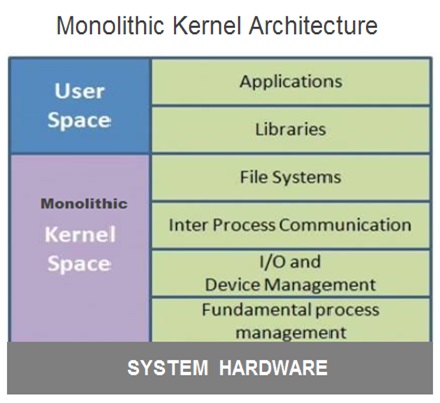
And therefore , the Applications had access and could communicate directly with any internal component of the operating system which gave unrestricted system access .
This kind of layered design was perceived to be very efficient but at the same time more vulnerable for system crash due to unrestricted system access.
Monolithic Kernel Operating Systems
What Is Micro-kernel In OS ?
In case of micro-kernel architecture , the kernel components includes only a very small number of bare minimum essential services within the kernel space in order to keep the kernel design small and scaleable.
The services within the micro-kernel area typically include low-level memory management, inter-process communication and basic process synchronization to enable processes to cooperate.
This kind of micro-kernel design was observed to be more stable and at the same time less vulnerable for system crash caused due to unrestricted system access.
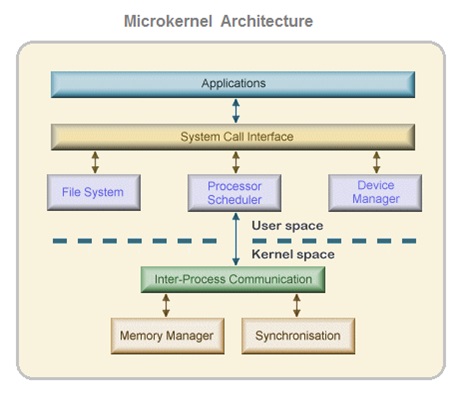
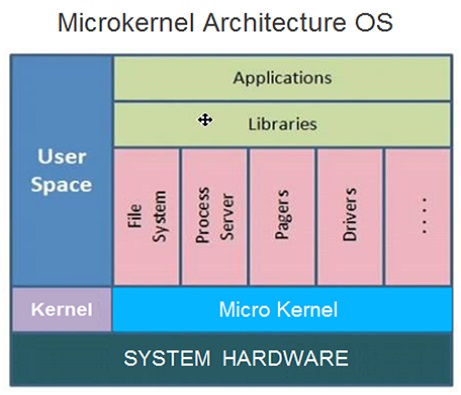
In micro-kernel architecture design based operating systems , only critical components are placed inside kernel area .
And other operating system components such as process management and device management are placed outside kernel area which execute outside the kernel within a user area with lower level of system access.
BIOS , UEFI And CMOS
Operating Systems Booting Process
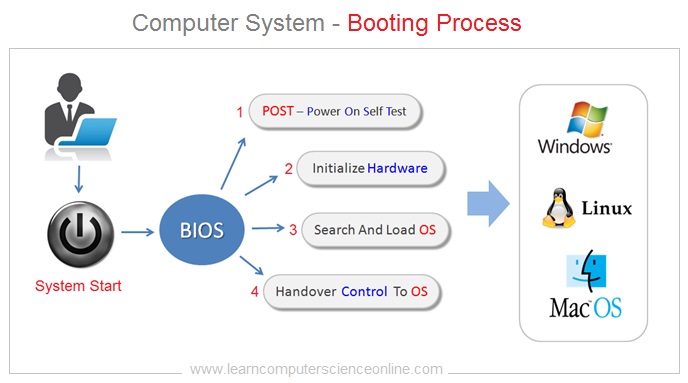
The process of loading the main operating system into the RAM ( Random Access Memory ) is referred as booting process.
The operating system is essential system software which effectively handles some of the most important functions.
The system user can start using the computer only after the OS is fully loaded into the RAM. And therefore , the CPU initiates the booting process by activating another system software ( firmware ) called the BIOS.
The BIOS is a start up routine present on the motherboard in the form of BIOS chip. The BIOS main job is to search and load the operating system.
What Is BIOS ?
Basic Input Output System
The BIOS ( Basic Input Output System ) is a start up system program that gets activated every time the system is powered on .
It is the BIOS that performs initial hardware check on some key components such as power supply unit ( PSU – SMPS ) , memory RAM , processor, display monitor and keyboard.
The BIOS initiates the system booting process by starting a self diagnostic test called POST. The POST stands for power on self test.
BIOS Chip On Motherboard

BIOS Start Up Screen
If the POST test is completed successfully , then the BIOS will proceed further and search for a capable operating system.
The BIOS loads the operating system into the main memory RAM and handover the control to the OS. The user can operate the system when OS is fully operational.
Read More
What Is CMOS ?
Complimentary Metal Oxide Semiconductor
During the computer system booting process the BIOS takes the hardware configuration data , settings from another source called CMOS memory.
The CMOS memory chip is a type of miniature volatile memory chip which stores the data required during the system booting process.
Since the CMOS is a type of volatile memory , it needs to be continuously powered so that it can retain this data. This power is provided by the CMOS battery.
CMOS Battery On Motherboard

CMOS Battery

Both BIOS and CMOS memory jointly participate into the system booting process to load the main operating system.
Read More
What Is UEFI ?
Unified Extensible Firmware Interface
The UEFI is a new replacement for the firmware BIOS. In simple words , the BIOS is a small piece of system software placed in a ROM chip on the motherboard.
The UEFI is latest new advanced version of the BIOS that will be doing the same job previously done by the BIOS. However , both BIOS and UEFI operate differently.
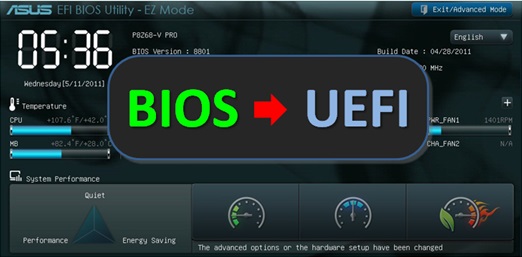
The UEFI has some major advantages as compared to the legacy BIOS. The UEFI offers a presentable GUI interface as compared to the text navigation menu of the BIOS.
The UEFI has also added number of security features and that has significantly improved the system security.
Read More
Join The Best Seller
Computer Science Online Course
This is the most comprehensive and unique Computer Science And Programming Fundamentals course Online which will give you in depth understanding of most important fundamental concepts in computer science And Programming .



