Computer Bus
Data Bus | Address Bus | Control Bus
Bus Architecture | Bus Width | Bus Speed
Introduction To Computer Bus
The Computer Bus is a communication link used in a computer system to send data, addresses , control signals, and power to various hardware components in a computer system.
The computer buses are used to connect the various hardware components that are part of the computer system. In simple terms, the computer buses are electrical wires that connect the various hardware components in a computer system . The computer bus carries the data , control signals , memory addresses, and power supply to these components.
The buses act as a shared communication channel, allowing various hardware components, such as the CPU (Central Processing Unit), main memory RAM modules, storage devices, input/output devices, and expansion cards, to interact and transfer data with each other.
The computer system makes use of different types of buses, such as data buses, address buses, and control buses.
What Is Computer Bus ?
The primary purpose of a computer bus is to provide a standardized method for components to communicate with each other. By using a bus, various devices can interact and transfer information without the need for custom connections or protocols for each individual component.
Different types of busses are used in the computer. Computer buses can vary in terms of their speed, width, and protocols depending on the specific requirements of the system. Advancements in technology have led to the development of faster and more efficient bus architectures, allowing for increased data transfer rates and improved overall system performance.
In summary, computer buses provide a crucial communication infrastructure within a computer system, enabling the exchange of data and signals between different hardware components. Bus architecture plays a vital role in ensuring the smooth operation and coordination of various components in a computer system.
In this article, we are going to study in detail what computer buses are, the computer system bus architecture , types of buses , technical features, and functions of computer buses.
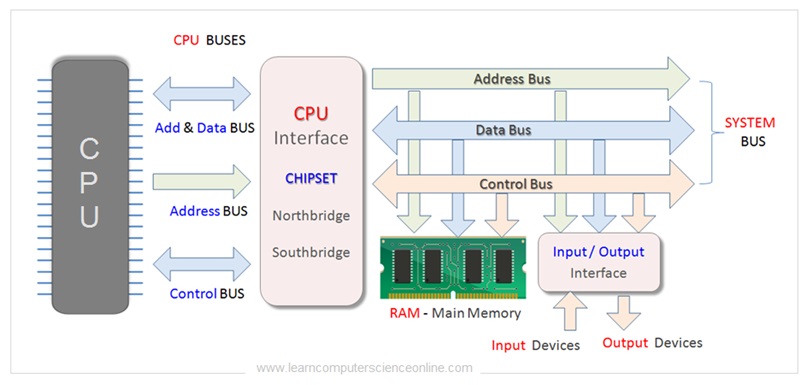
Computer Buses And Functions
Buses are typically categorized based on their functionality and the type of data they carry. Here are some common types of computer buses that are important part of computer architecture:
Computer Bus Type | Computer Bus Function | Bus Connects |
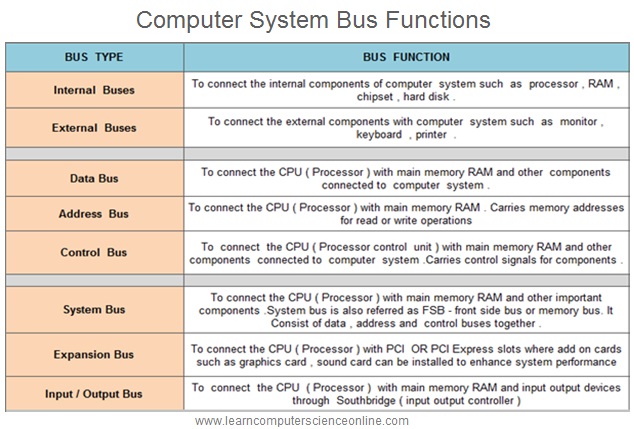
Internal Bus | To connect the internal components of computer system such as processor , RAM , chipset , hard disk . | Internal Bus connects internal components with each other |
External Bus | To connect the external components with computer system such as monitor , keyboard , printer . | External Bus connects the peripheral devices to the CPU. |
Data Bus | To connect the CPU (Processor) with main memory RAM and other components connected to computer system. | Data bus connects CPU to RAM and other components. |
Address Bus | To connect the CPU (Processor) with main memory RAM. Carries memory addresses for read or write operations. | Connects CPU to the RAM. |
Control Bus | To connect the CPU (Processor), control unit with main memory RAM and other components connected to computer system .Carries control signals for components . | Connects CPU to RAM and other components. |
System Bus | To connect the CPU (Processor) with main memory RAM and other important components. System bus is also referred as FSB - front side bus or memory bus. It Consist of data , address and control buses together . | Connects CPU to RAM and other important components. |
Expansion Bus | To connect the CPU (Processor) with PCI OR PCI Express slots where add on cards such as graphics card , sound card can be installed to enhance system performance. | Connects CPU to PCI OR PCI Express slots. |
Input And Output Bus | To connect the CPU (Processor) with main memory RAM and input output devices through Southbridge (input output controller) . | Connects CPU to RAM & Input, output devices. |
What Is Computer Bus ?
The computer system consist of number of internal and external components . These components are physically interconnected and communicate with each other through a network of wires running across the computer system. These wires are referred as computer buses. The buses are essential to the functioning of the computer system.
A computer bus is a communication pathway that allows various components within a computer system to transfer data and signals between each other. It serves as a wired physical connection or set of wires running across connecting various system components.
Computer buses enable the transfer and exchange of information, such as commands, addresses, signals, and data, between the different hardware components in a computer. Computer system makes use of different types of busses as per the system architecture.
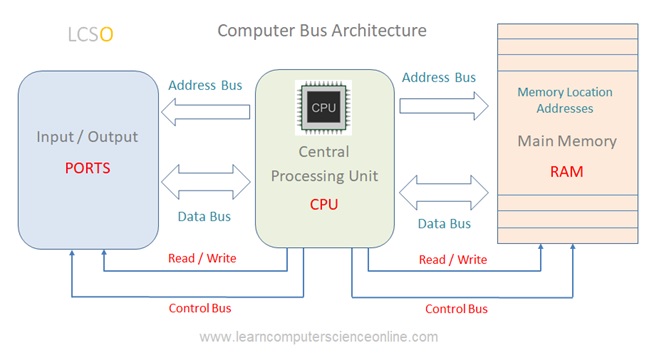
The computer buses can be in the form of wired cables or electrical wires embedded in the computer motherboard PCB ( Printed Circuit Board ) visible on the rear side of motherboard .
It is important for computer science professional to study the computer system bus architecture , technical features of these buses such as bus width and bus speed and its overall impact on the system performance.
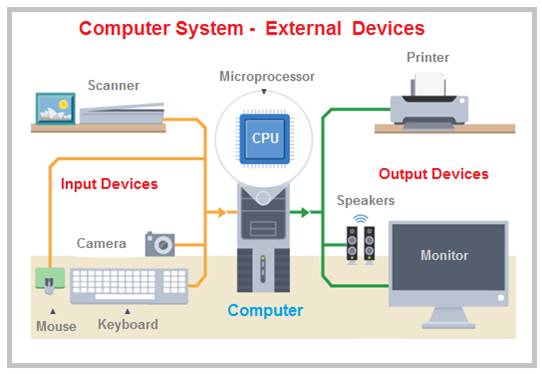

A bus is a common communication pathway used in a computer system through which information flows from one computer component to another.
The computer bus system is a network of buses which physically connect all the components with wires ( actual bus wires OR circuit wires on the motherboard ) .
The bus system consist of different types of buses depending upon the components being connected and the function assigned to the bus .
A bus can consist of set of wires grouped together as connection wire or a printed circuit boards which carry the data and other commands ( instructions ) from the CPU to the memory and to various other components connected to the system.
The bus performance is an important parameter to access the computer system performance . The bus width and the bus speed affects the system performance .
The data bus is a bidirectional bus and can carry the data in both the direction along the data bus. For example , the CPU can send the data to be stored into the RAM .
Similarly, the CPU can also perform the fetch operation for retrieving the data from the specific memory location.
Computer Bus
Types Of Computer Buses
The computer bus system makes use of different types of buses depending upon the purpose and the function of the bus.
The computer system buses can be classified on the basis of number of factors . These factors include :
Bus Types On the Data Being Transmitted
The computer system buses can be classified on the basis of type of the data being transmitted as :
1. Data Bus , 2. Address Bus , 3. Control Bus.
Computer Bus Types
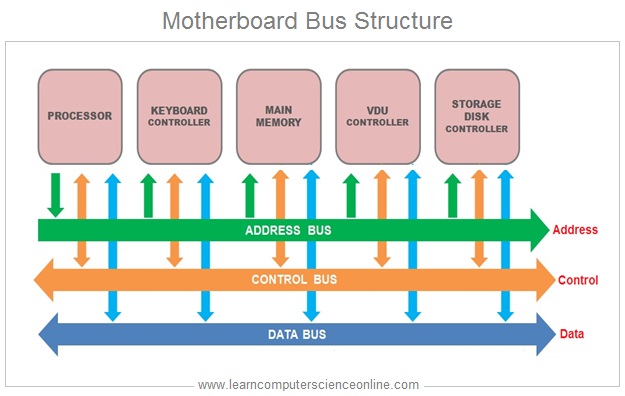
Bus Types Based On the Components Being Connected
The computer system buses can be classified on the basis of type of the components being connected as :
1. System Bus , 2. Expansion Bus , 3. Input And Output Bus.
Bus Types Based On The Location Of Components
The computer system buses can be classified on the basis of location of the component being connected as :
1. Internal Bus , 2. External Bus
Computer Bus
Data Bus
In computer architecture , the data bus is a wired connection dedicated for the transmitting the data between the CPU , peripheral devices and other hardware components . The data bus is a part of the system bus in addition to address bus and the control bus.
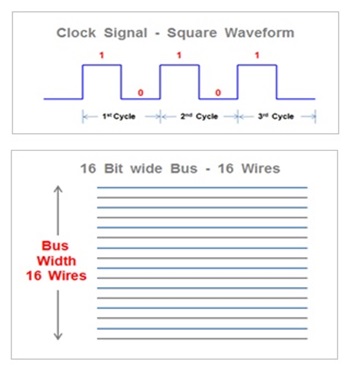
A data bus has many different features , but one of the most important feature is the bus width. The width of a data bus refers to the number of bits ( electrical wires ) that the bus can carry at a time.
For example , a 16 Bit wide data bus can carry 16 bits of data simultaneously between the CPU and the system component such as main memory RAM ( Random Access Memory ).
The Common data bus widths include 8 bit , 16 bit , 32 bit and 64 bit . The wider the bus width , faster would be the data flow on the data bus and thus better system performance.
Computer Bus
Control Bus
The CPU ( Microprocessor ) contains a control unit which controls the functioning of all other components connected to the computer system. The control bus is used to transfer the control signals from one component to another component .
A control bus is a computer bus that is used by the CPU to communicate with the devices that are connected to the computer system. These devices are connected with the help of cables and printed circuits board such as motherboard.
The Control Bus is a part of System Bus in addition to Data Bus and Address Bus.
The Central Processing Unit ( CPU ) transmits different types of control signals to the system components. The devices also communicate with CPU by transmitting the control signals using the control bus.
The control bus is a bidirectional and assists the CPU in synchronizing control signals to the internal components and the external devices connected to the system.
The control bus transmits the control signals such as device interrupt signal , byte enable signal , memory read or write signals and status signals.
Control Bus
How CPU Works ?
Address Bus
What Is A Address Bus ?
The computer program consist of number of program instructions. These instructions direct the CPU to perform desired operation.
The operating system loads the program instructions and the data into the main memory . The CPU executes the program instructions one-by-one by fetching the program instructions from the main memory RAM ( Random Access Memory ) .
In order to perform the memory read or write operation from the main memory RAM , the CPU sends either read or write control signal on the control bus and address of the memory location along the “Address Bus” from where the operation is to be performed .
The address bus is a part of the “System Bus” along with the data bus and the control bus which we have discussed .

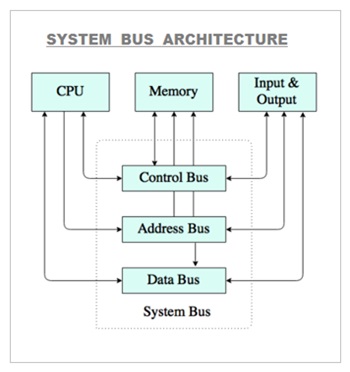
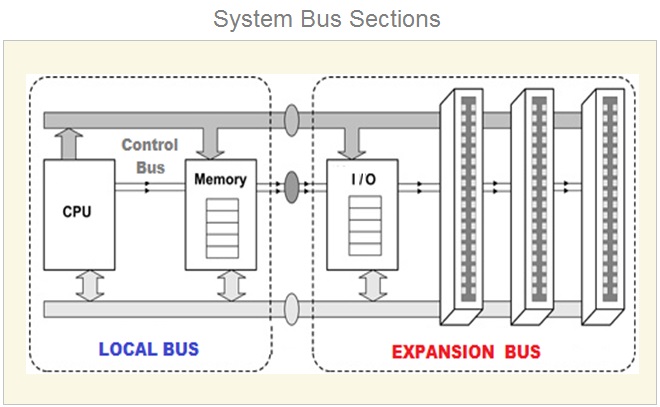
System Bus
What Is A System Bus ?
A System Bus is the main bus which contains Data Bus , Address Bus And Control Bus.
The System bus in computer system connects number of vital internal hardware components placed on the motherboard .
These hardware components mainly include CPU , motherboard , Internal add on cards such as Graphic card , Sound card , Network card , RAM ( Main Memory ) and the internal hard disk .
A system bus is a set of parallel wires which connects the two or more independent major internal components of a computer system. The System bus transfers data , memory addresses and device control instructions.

Computer Bus
Computer Bus Functions
What Are The Functions Of The Computer Bus ?
The computer bus system makes use of different types of buses . Each of these bus is assigned to carry specific type of signal and data depending upon its function.
- Data Sharing .
- Addressing
- Control Signals
- Providing Power to Components .
- Sharing The System Time .
The internal buses connect the various internal system components such as microprocessor ( CPU ) , RAM ( main memory ) , Chipset ( North Bridge And South Bridge ) and disk memory ( Hard Disk ) .
The external bus connects the various external system components such as monitor , keyboard , printer , external hard disk and other components externally connected to the system.
The system bus connects the most important internal system components such as Microprocessor ( CPU ) and main system memory RAM . The system bus is also referred as FSB ( Front Side Bus ) or memory bus. It consist of data bus , address bus and control bus.
The expansion bus connects the most important internal system components such as Microprocessor ( CPU ) and PCI OR PCI Express slots on the motherboard .
The PCI And PCI Express slots are used to connect the add on cards such as graphics card and sound card . These cards are installed to enhance the system performance.
The input and output bus connects the most important internal system components such as Microprocessor ( CPU ) , main system memory RAM and the input / output devises through input and output controller south bridge.
Computer Bus And System Performance
Computer Bus Width And Bus Speed
A bus is a information highway over which information flows and wider the bus , the more information can flow over the channel .
And therefore , a compatible bus width and bus speed is important for the optimal performance of the two most vital system components which includes Central Processing Unit ( CPU ) and main system memory RAM.
This is similar to a multi lane wider highway that can carry more cars due to more number of lanes available for traffic . whereas , a single lane road can carry less number of cars as compared to a multi lane road .
The computer system at the hardware level understands only binary 0 ( zero ) and 1 ( one ) . And therefore , all computer programs are compiled to convert into machine code instructions in binary which computer CPU can decode and execute.
The bus consist of group of cables and each of these cable can carry 1 BIT ( Binary 0 OR 1 ) at a time . Therefore , a bus consist of a group of cables so that a group of bits can be sent at a time through these buses .
Why Computer Bus Use Binary ?
Bus Width
What Is Bus Width ?
The size of a bus is measured in terms number of Bits it can transmit at a time . Each wire can transmit one bit thus more number of wires in the bus can transmit more bits at a time . This number of wires in bus is referred as Bus Width.
The Bus width is an important measure because it determines how much data can be transmitted at one time. For example, a 16 Bits bus can transmit 16 bits of data and a 32 Bit Bus can transmit 32 bits of data at a time.
The bus consist of group of cables and each of these cable can carry 1 BIT ( Binary 0 OR 1 ) at a time . Therefore a bus consist of a group of cables so that a group of bits can be sent through the bus .
This is similar to a multi lane wider highway that can carry more cars due to more number of lanes available for traffic .
Bus Speed
What Is Bus Speed ?
The Bus performance is important for optimal CPU performance . The Bus performance is measured on two factors ( Bus Width And Bus Speed ) .
The bus speed is another important parameter for the bus performance . The bus speed is defined by its frequency expressed in Hertz .
The bus frequency is the number of data packets sent or received per second. Each time that data is sent or received , It is called as one cycle.
The bus speed is generally referred to the FSB – Front Side Bus speed . The Front Side Bus connects the CPU to the memory controller chip North-bridge .
What Is Bus Bandwidth ?
Let us summarize the bus width and the bus speed using the highway analogy. If the bus width is the number of lanes available for the traffic and the bus speed is how fast the vehicles are moving on each of these lanes.
The bandwidth is the product of Bus Width And Bus Speed and reflects the amount of traffic that the channel can convey per second.
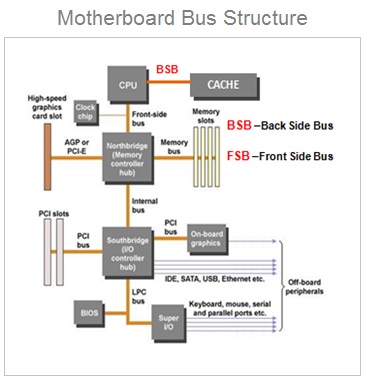
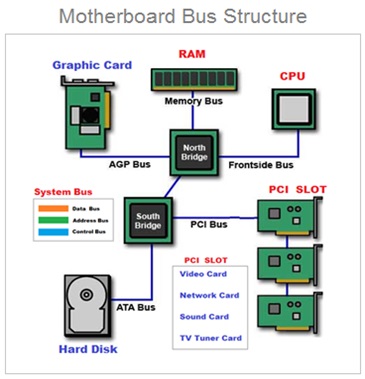
Motherboard Bus Architecture
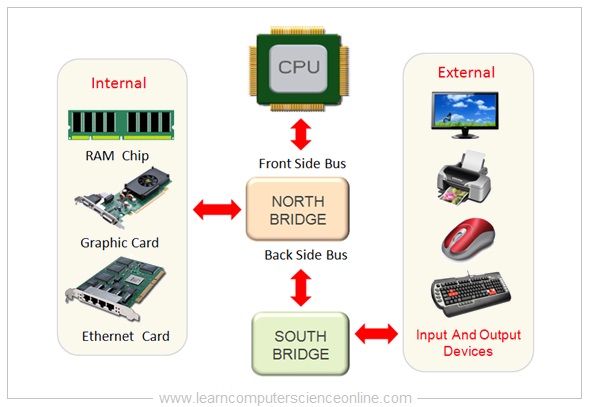
The CPU is connected to the internal system components ( RAM , Graphics Card Network card ) and external peripheral devices ( Monitor , Printer , Mouse , Keyboard ) by using device controller circuits placed on the motherboard .
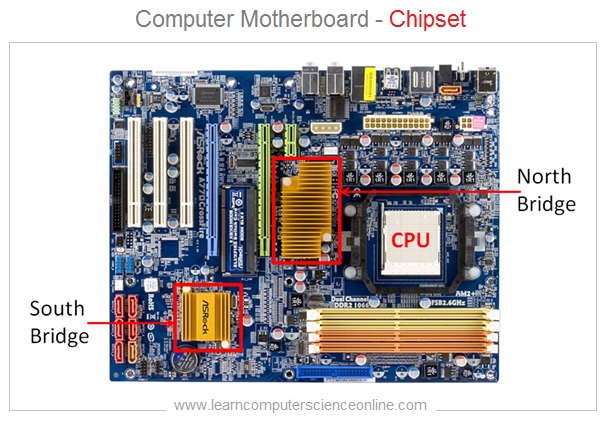
All the device controller chips are now integrated into only two controller chips called chip-set . The chip-set consist of two prominently visible IC Chips called North-bridge and South-bridge placed on the motherboard .

The memory controller chip North-bridge and input / output controller chip South-bridge circuits are placed on the motherboard.
The internal components ( CPU , main memory RAM , Graphics Card ) are connected through North Bridge.
And other peripheral devices ( Display monitor , printer , keyboard , mouse ) are connected through the input & output controller chip South Bridge.
All these components are connected by using the system of bus wires which essentially carries three different types of information :
1. Memory Addresses , 2. Control Instructions And 3. Data.
Expansion Bus
What Is Expansion Bus?
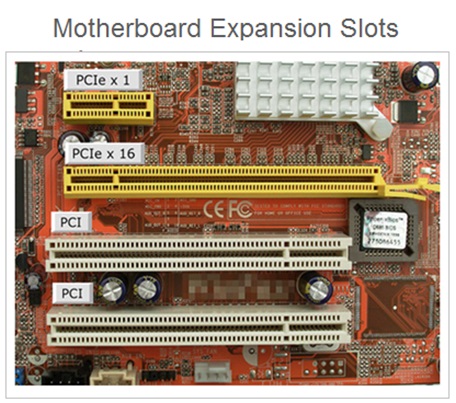
The performance features and functionality of a computer system can be extended by adding an additional cards such as graphics card Or sound card.
The expansion slots are the ports located on the motherboard of a computer system in which an expansion cards can be installed . The user can use these slots to insert additional expansion cards as per the functional requirements .
An expansion bus is a group of wires OR PCB used to connect with the expansion slots on the motherboard. These expansion slots are used for installing the expansion cards .
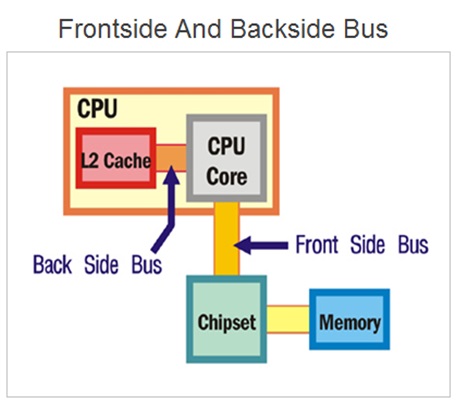
Front Side Bus
What Is Front Side Bus ( FSB ) ?
The front side bus ( FSB ) represents one of the most important communication bus that connects some of the most vital components of the system. And hence , the FSB is also referred as system bus.
The front side bus connects the computers central processing unit ( CPU ) with the main system memory RAM . The FSB also connects PCI slots and DIMM slots on the motherboard with the processor socket .
And therefore , the FSB is an important communication bus that connects some of the most important components such as CPU , main memory RAM , graphics card and other components connected through PSI slots.
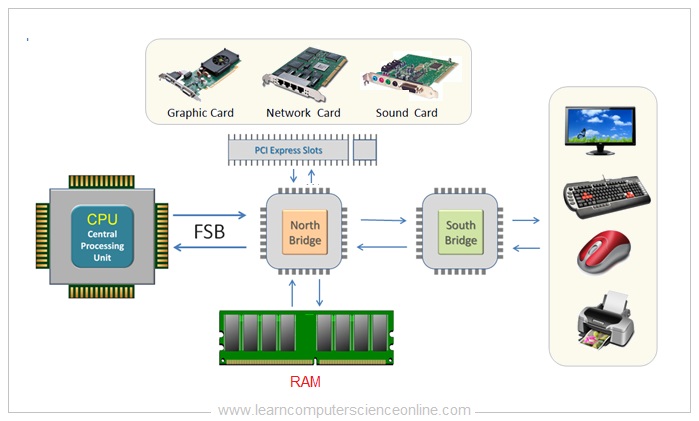
These components are connected using the FSB through one of the memory controller chip called the north bridge. The motherboard chip set consist of two controller chips.
The front side bus is present on the motherboard embedded as a printed circuit board ( PCB ) wired connections running across the motherboard PCB .
The FSB speed is considered as an important parameter that significantly affect the CPU performance . The FSB speed is measured in Megahertz ( MHz ).
The FSB speed is generally ranges between 66 MHz to 800 Mhz. It can also be expressed as a ratio to CPU speed.
RAM Standard | RAM FSB Speed | RAM Code |
DDR | 100 MHz | PC - 1600 |
DDR | 266 MHz | PC - 2100 |
DDR | 333 MHz | PC - 2700 |
DDR | 400 MHz | PC - 3200 |
DDR2 | 400 MHz | PC2 - 3200 |
DDR2 | 533 MHz | PC2 - 4200 |
DDR2 | 667 MHz | PC2 - 5300 |
DDR2 | 800 MHz | PC2 - 6400 |
DDR2 | 1066 MHz | PC2 - 8500 |
DDR3 | 800 MHz | PC3 - 6400 |
DDR3 | 1066 MHz | PC3 - 8500 |
DDR3 | 1333 MHz | PC3 - 10600 |
DDR3 | 1600 MHz | PC3 - 12800 |
DDR3 | 1867 MHz | PC3 - 14900 |
DDR4 | 1867 MHz | PC4 - 14900 |
DDR4 | 2133 MHz | PC4 - 17000 |
DDR4 | 2400 MHz | PC4 - 19200 |
DDR4 | 2666 MHz | PC4 - 21300 |
DDR4 | 4000 MHz | PC4 - 32000 |
The front side bus ( FSB ) is bi-directional bus . The FSB is used to by the CPU to either receive or send the data from various components connected to the CPU.
The CPU frequently communicates with system main memory RAM and other devices during the program execution. And therefore , the FSB speed matters for the CPU performance.
Join The Best Seller
Computer Science Online Course
This is the most comprehensive and unique Computer Science And Programming Fundamentals course Online which will give you in depth understanding of most important fundamental concepts in computer science And Programming .