Relational Database
Relational Database Management System
RDBMS | Relational Model | Data Modelling | Normalization
The Relational Database is a database that is designed and developed based on the relational database model .
The Relational Database Model was proposed and developed by E.F. Codd who was an English computer scientist while he was working with IBM .
The Relational Database Management System ( RDBMS ) is a database management system ( DBMS ) that allows the creation , management and administration of Relational Databases.
What Is Relational Database ?
The Relational Databases are the most commonly used databases in the industry today. Some of the most popular DBMS being used are based on the relational model .
The most popular and widely used RDBMS includes MySQL , Oracle MS SQL server and there are many more.
In this tutorial , you will learn what are relational databases , design principles , relational database terminology , database keys , database normalization and other important topics related to the relational databases.
Relational Database
Table Of Contents
What Is Data ?
The data is the central core of any database software application. The database applications are designed and developed to process large volumes data . let us first start with getting the clarity and understand the meaning of term data.
The data is the most important element of any database system. It is important to understand the meaning of term data and what it means to different database users .
The database users include end users , database designers , database application developers , system analysts and database administrators.
The term data usually refers to raw data that has not been processed and therefore cannot be directly used for some meaningful work such as analyzing trends and decision making within an organization.
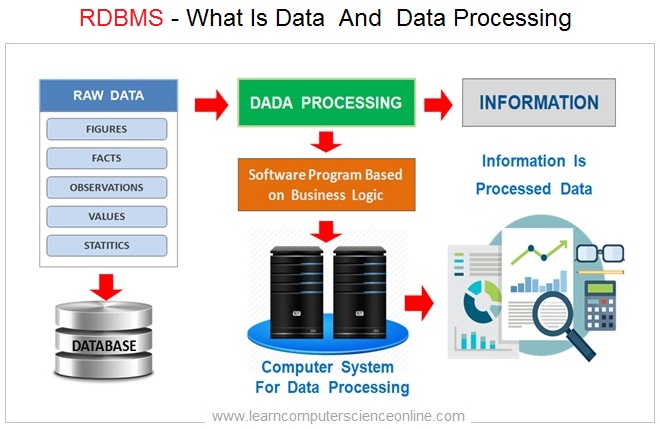
The data is scientifically collected and recorded as facts , observations , factual information , set of values and figures about any real world objects.
The data must be stored and digitally processed with the help of a computer system and software application to operate on the data.
For example if we are designing a database system to store the employee information, then all the employee related data such as employee Name , address , designation , DOB , Salary will be stored in a database as employee data.
What Is Database ?
The database is a key component of most of the software applications which are designed to store the information about some real world business entities such as employee database , customer database , student database , inventory management system and so on .
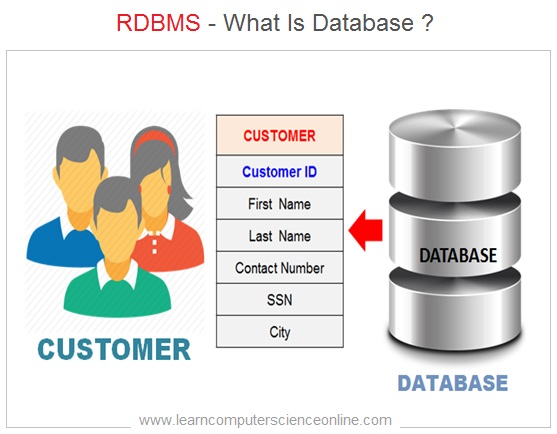
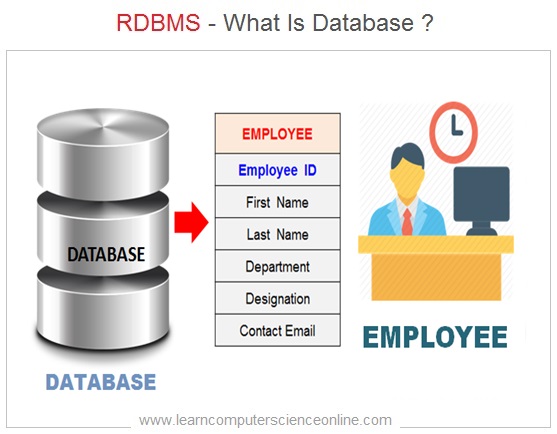
The data within a database can be easily accessed and processed , since the data in a database is logically organized and inter-related. A Database is a computer based record keeping system which is used to record , maintain and retrieve data .
The database is a vital component any database management system ( DBMS ) that actually stores the data . The database allows various operations for efficiently storing , retrieving and managing the data within a database .
What Is Relational Database ?
The relational databases implement the relational model invented and proposed by E F Codd . The relational databases are designed as per the set of rules and principles defined by E F Codd.
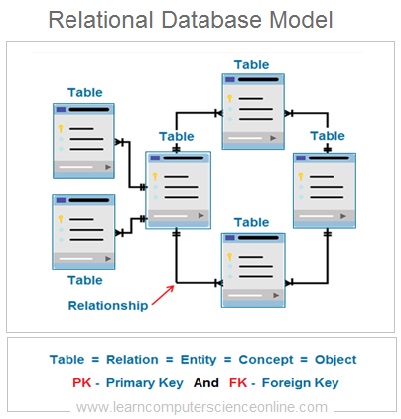
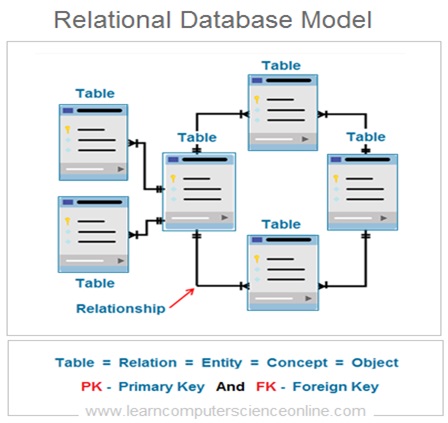
In relational database management system the logical structure of the database consist of number of inter-related tables .
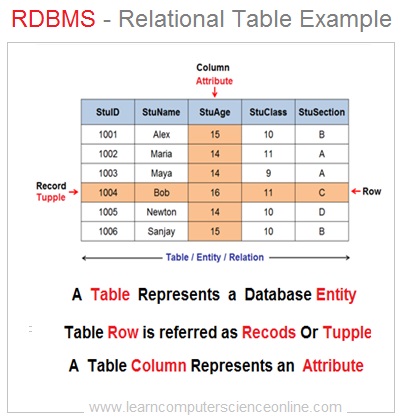
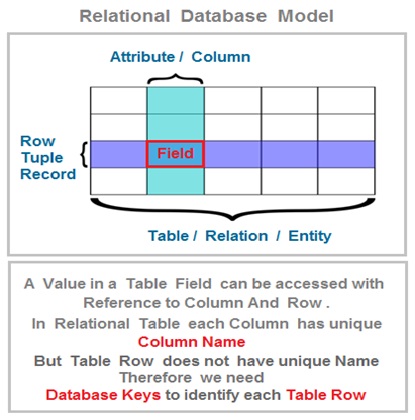
A Table represents a relation or database entity. A table is a collection of records and each table row represents a record . Each table in a relational database consist of number of rows and column .
What Is RDBMS ?
Relational Database Management System
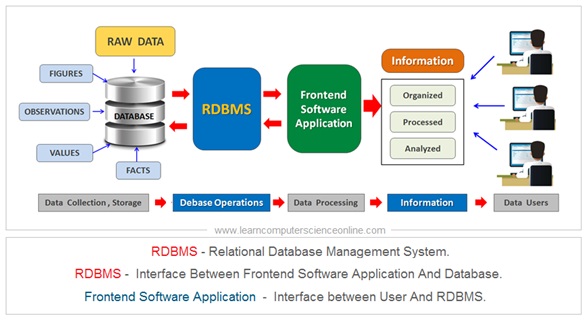
The RDBMS stands for Relational Database Management System. The RDBMS is a software application designed to create , manage and administer the relational databases .
The RDBMS internally might consist of number of sub-programs and each of these program performs a specific operation of the RDBMS.
The RDBMS is a database management system that is based on the relational model proposed and developed by E.F. Codd who was an English computer scientist. He invented and proposed the theory of Relational Databases while he was working with IBM .
The user interacts with the database through application software ( Front End ) . The application software in turn use SQL which is database query language .
The DBMS in turn interacts with the database and perform various database operations . The RDBMS provides a layer of abstraction between database and application software.
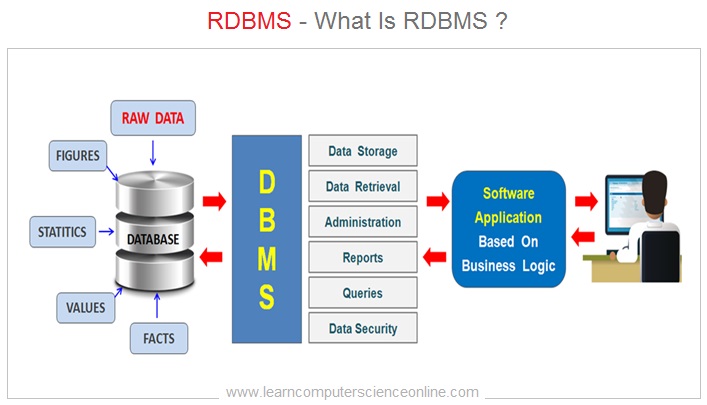
The Relational Database Management System ( RDBMS ) is the most commonly used DBMS in the industry today. Some of the most popular and widely used RDBMS include MySQL , Oracle and MS SQL Sever.
The RDBMS supports only relational databases . The relational databases are based on the relational model . The relational databases must comply the set of rules defined by E F Codd in order to qualify as relational database.
Most Widely Used RDBMS
The database technology has evolved over a period of last few decades and seen the advent of different types of database management systems such as NoSQL and Object oriented databases .
However, despite these developments , the RDBMS technology has retained its popularity.
The RDBMS market has seen a steady growth despite the advent of new players. The RDBMS market is dominated by some of the largest players such as Oracle , IBM and Microsoft .
The most popular and widely used RDBMS include :
Relational Database Terminology
In order to understand the relational database structure , It is important to first understand the relational database terminology. This terminology includes the frequently used technical terms . Some of the frequently used terms include :
- Data Modelling.
- Conceptual Data Model.
- Logical Data Model.
- Physical Data Model.
- Database Integrity.
- Database Consistency.
Entity
What Is Entity In Database Design ?
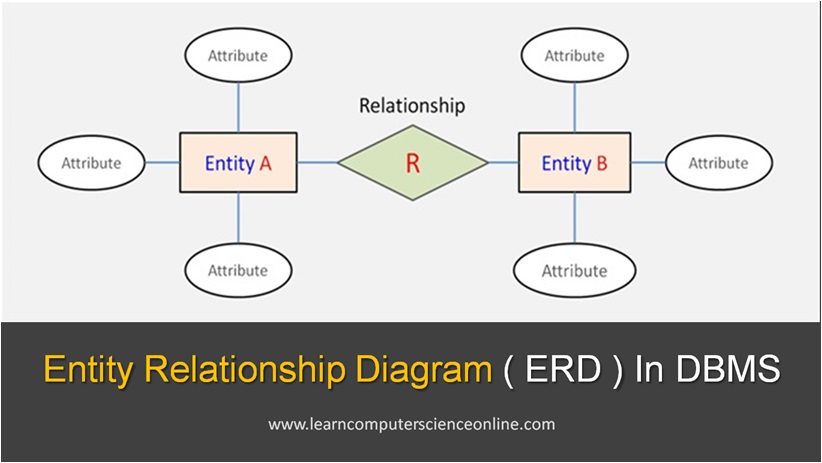
A database entity is any object or business concept that needs to be represented within a database system .
An entity can also be an object or concept that we want to model and store information about. A database entity could be any recognizable concepts which may be either concrete ( Tangible ) or abstract ( Intangible ) .
For example let us consider a database for a college . The student , teacher , principal , department , major are all examples of valid objects or database entities . The database stores information about various entities within a database .
Attributes
What Are The Attributes Of An Entity ?
Each database entity has many attributes which highlight a specific feature of the database entity . Each table column represents one attribute of database entity.
For example , let us consider a students database. The student is a valid database entity and the first name , last name , DOB , SSN are some the attributes which are represented by respective column in the student table.
Relationship
What Is Relationship In Relational Database ?
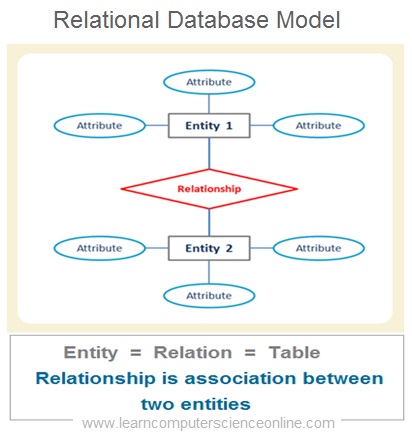
In relational database the logical structure of the database consist of number of interrelated tables . Each table represents an entity . The relationship is an association between the two database entities .
In relational database , an entity is represented by a table which is also commonly referred as a relation . So each entity is a type of relation . Since the relation is a mathematical construct , it can easily be represented as two dimensional table .
The relationship between the two tables ( Entities ) is defined by using the database keys that is primary key and foreign key .
Relational Database
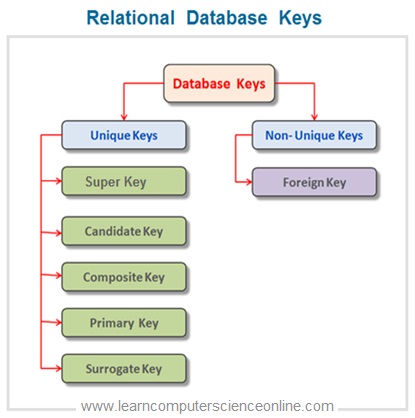
Database Keys
What Are Database Keys ?
The relational database consist of number of inter related tables . The relationship is an association between the tables , which depends upon the functional dependencies.
In relational database , an entity is represented by a table which is also commonly referred as a relation . So each entity is a type of relation . Since the relation is a mathematical construct , it can easily be represented as two dimensional table .
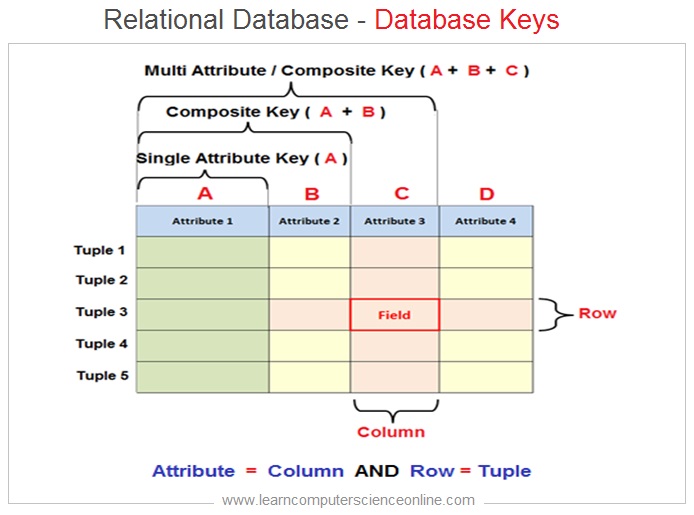
The DBMS can access a specific data value stored into a data field ( intersection of row and column ) with reference to column name and a unique row for each record .
This unique attribute for each record in a table is defined as database key . The database key has a unique value for each table row (Record / Tuple).
Types Of Database Keys
Relational Database
Types Of Database Keys
The database designers define the relationship between the tables , with the help of different types of database keys.
In relational database , the database keys can be fundamentally grouped in to two categories ( Unique Keys And Non Unique Keys ) based on the uniqueness of the column ( Attribute ) values.
The unique keys can be further subdivided as Super Keys , candidate key , Composite key , Primary Key and Surrogate key And Foreign key is a Non unique key.
- Super Key
- Candidate Key
- Composite Key
- Primary Key
- Foreign Key
- Surrogate Keys
READ MORE
Relational Database
What Is SQL ?
Structured Query Language
The SQL stands for Structured Query Language . In simple terms ,it is a database query language ( type of computer language ) used by the software applications to communicate with the database management system ( DBMS ) .
The DBMS in tern communicates with the database . The DBMS also manages the actual database that stores the data.
The RDBMS – Relational Database Management System are extensively being used for providing web server based database functionality to some of the largest and popular web applications .
The RDBMS internally makes use of SQL – Structured Query Language which is a database query language used for performing various database operations on the relational databases.
The Structured Query Language ( SQL ) is a database query language used for storing and managing data the using any RDBMS. SQL was the first commercial language introduced for E.F Codd’s Relational Database Model. The SQL is supported by almost all RDBMS currently operational.
Today, almost all RDBMS ( MySql, Oracle, MS SQL Server , Sybase, MS Access ) use SQL as the standard database query language. SQL is used to perform all types of database operations in RDBMS.
Relational Database
Data Modelling
What Is Data Modeling ?
Similar to an architect , the database designers also create a data model during database design process to visualize and communicate the design features of the database being designed . These data models are later on used as blue prints for building the database.
In the context of database design , a data model is simply a diagrammatic representation of the database’s internal structural details . In other words , a data model is simply a diagram that displays a set of tables ( database entities ) and the relationship between these tables .
The data model makes it very easy to understand how different database entities are being represented by tables and Relationships ( functional dependencies ) that exists between these tables .
Types Of Data Models
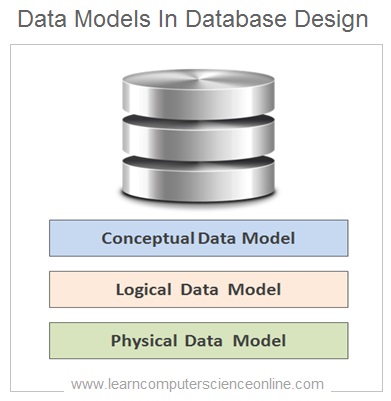
Data Models In DBMS
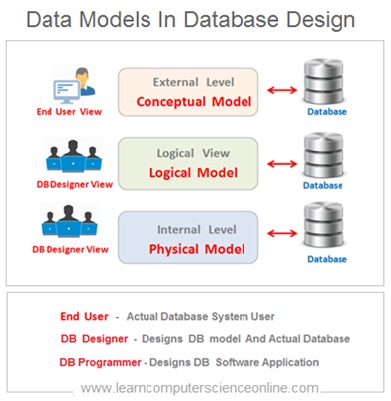
Data Modelling
Conceptual , Logical And Physical Data Model
A data model is constructed as conceptual data model, logical data model and physical data Model . Each data model highlights different database design features and presents different abstraction view.
The conceptual, logical and physical data models are three different ways of modelling data during database design process .
Conceptual Data Model
During the database design process the database designers create a conceptual data model to capture the end user data requirements that user needs to perform specific role within an organization.
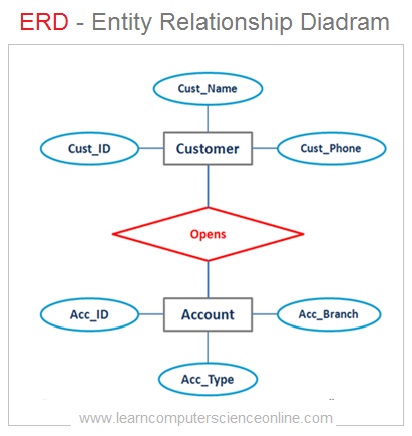
The Entity Relationship Diagram ( ERD ) is a graphical conceptual representation of the database used by the database designers to define the database view at the end user level.
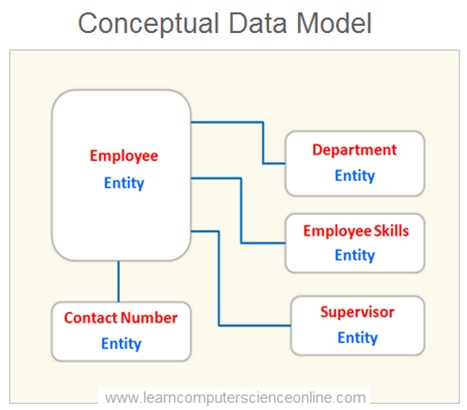
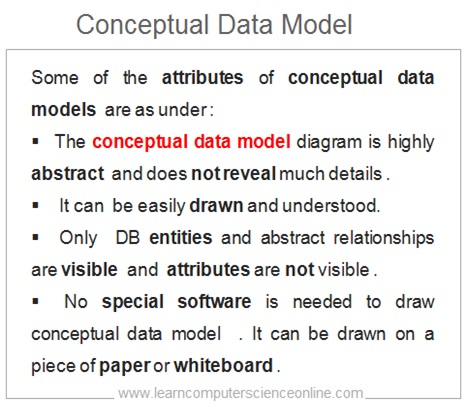
In other words, the conceptual data model is a graphical description of the business . The conceptual data model helps to identify the key business entities and systems that needs to be represented in the database.
The conceptual data model is a highly abstract and provides a high-level view of the key business and system entities and the association between them in terms of existing relationships.
The conceptual data model is DBMS independent and can be implemented on any DBMS .
Logical Data Model
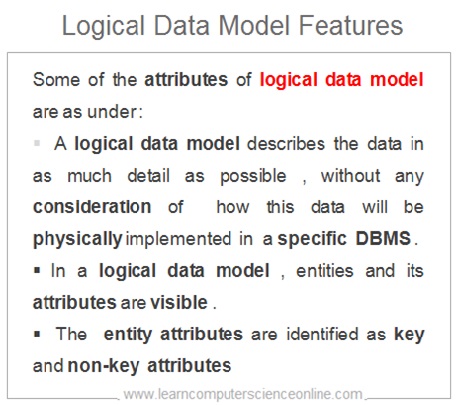
The logical data model is the second stage of the database design process and can be implemented on any DBMS .
The logical data model is created from conceptual data model . The conceptual data model is further expanded by database designers by adding more details which brings further clarity and detailing about the database structural elements .
A logical data model describes the relationships between the various tables ( entities ) by identifying the primary key and foreign keys for each table and the relationships are defined with the help of connecting arrow depending upon the functional dependencies .
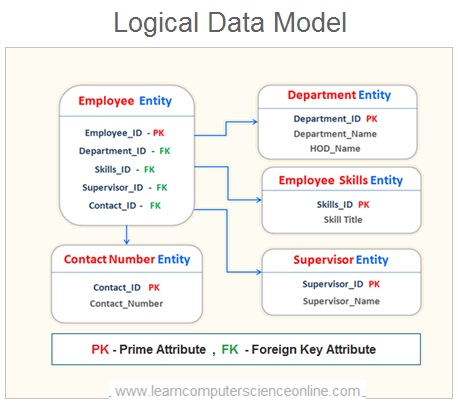
A logical data model diagram can be drawn with the help of a special software such as Erwin , ER/One and many more .
The logical data model is DBMS independent and can be implemented on any DBMS .
Physical Data Model
The physical data model is the third stage of the database design process and can be implemented only on specific DBMS .
The physical data model is created from logical data model . The logical data model is further expanded by database designers by adding more details which are required to create a database using specific DBMS such as data type and size for each data field.
A physical data model refers the database entities as tables and entity attributes as table columns .
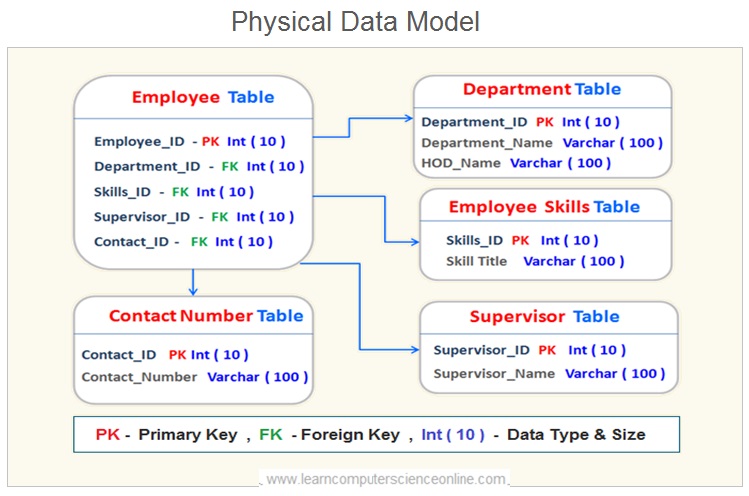
In physical data model , the column names are not user friendly names but column names must be database compatible names in which the database will be created such as MySQL Or Oracle Or any other database .
In physical data model the data type and size should also be fully compatible with the DBMS used to create the database .
The physical data model constrains database developers to define the data type and size . And therefore , the physical data model is DBMS dependent and can be implemented only on specific DBMS that supports the same data type.
Introduction To Relational Database Model
The Relational Database Model is one of the most important database model and the relational databases are extensively being used in the industry .
The relational database model offers major advantages as compared to traditional computer based record keeping system .
In order to understand the advantages offered by the relational databases , the database student needs to be aware of the limitations of traditional single table databases .
Flat File Database
Limitations Of Flat File Databases
The traditional computer based record keeping system used to store the data is single flat file or in a single table . The single table database has some major limitations and it is difficult to establish relationship between between various data elements .
Further , In a single table database it is difficult to control the repetition of data in a multiple rows and columns . These duplication of same data at multiple places leads to problem of data redundancy.
The data redundancy is the root cause of many database problems ( Database Anomalies ) and inconsistent state of the database.
Data Redundancy
What Is Data Redundancy ?
The presence same data in multiple records is referred as redundant data . This repetition of data at multiple places within a table is the root cause of many potential problems .
The redundant data can be either present at multiple fields of the same table or it can be present in number of tables.
The data redundancy problem must be resolved to avoid various database anomalies . The database anomalies leads to inconsistent state of the database when database contains two different values for same data field.
These problems due to the presence of redundant data in a table are referred as database anomalies.
In single large table database , it is difficult to avoid redundant data . And therefore , in relational database, the larger tables are decomposed to smaller tables in order to normalize the database.
Example Of Data Redundancy
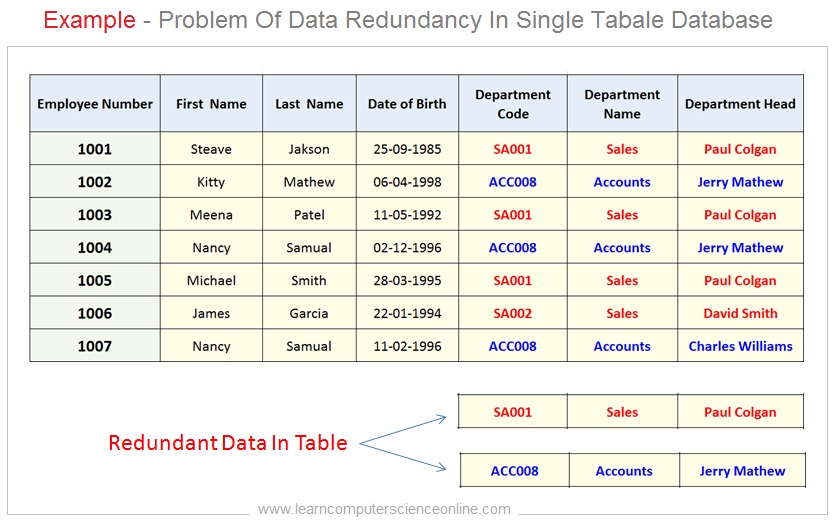
Let us consider one example to illustrate the existence of redundant data in a table .
As we see in this table , the table columns Department Code , Department Name and Department Head are being repeated as duplicate data fields for each employee record which is a redundant data.
This duplication of data in multiple records is referred as redundant data . The redundant data is the root cause of many database anomalies. The data redundancy must to be treated and reduced to minimum.
Database Anomalies
What Are Database Anomalies ?
The DBMS’s are mainly used to efficiently organize the data for its optimum utilization .
In RDBMS , the data is logically organized as group of inter related tables . The database developers split the larger tables into smaller but more meaningful tables to avoid the duplication of data in tables .
The presence of redundant data in a table can cause many potential problems commonly referred as database anomalies in the database world .
The database anomalies caused due to redundant data adversely affect the database performance and consequently the applications which makes use of the database .
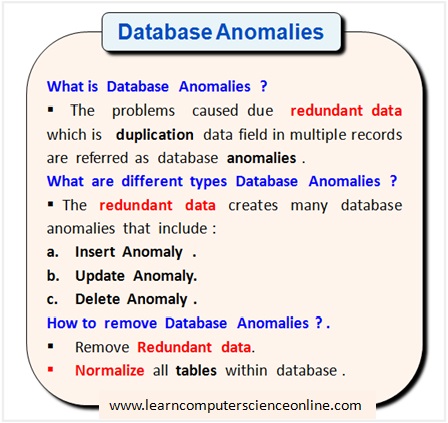
And therefore , during the database development process , the database is designed by applying a set of rules ( Database Normalization Rules ) and by splitting the larger tables into smaller tables to avoid the data redundancy.
Relational Database
Types Of Database Anomalies
The presence of duplication of data in a table can cause different types of database anomalies . The three database anomalies needs to be treated in order to normalize the database :
Insertion Database Anomaly
An insert anomaly is said to be present in a table when certain attributes cannot be inserted into the database table without the presence of other attribute . An insertion anomaly is the inability to add data to the database due to absence of other data .
An insertion anomaly makes it mandatory to first insert some other data fields in order to insert the required data . An insertion anomaly is caused due to the presence of redundant data in a un-normalized table .
Update Database Anomaly
An update anomaly is said to be present in a table when the database operation fails to update all the records resulting inconsistent state of the database.
The update ( Also referred as Modify Anomaly ) is caused due to the presence of redundant data in a table containing duplicate fields in multiple records .
An update anomaly is the inability to update all records within a database table during update operation.
An update anomaly is caused due to presence of redundant data in a un normalized table and can be resolved by normalizing the tables.
Deletion Database Anomaly
A delete anomaly is said to be present in a table when the one database delete operation on one attribute also deletes another attribute .
A deletion anomaly is the unintended loss of data during the one database delete operation on one set of data that causes deletion of other data .
An delete anomaly is caused due to the presence of redundant data in a un normalized table and can be resolved by normalizing the tables.
Relational Database Design
The Relational database is logically structured as group of inter-related tables. The each table in a database represents a database entity .
The relation is established between the tables by defining a primary key for each table which has a unique value for each row ( record ) in a table .
A relationship is created when the primary key of one table is included as foreign key in another table as non-prime attribute .
Each table can have only one primary key and many foreign keys as non prime attribute.
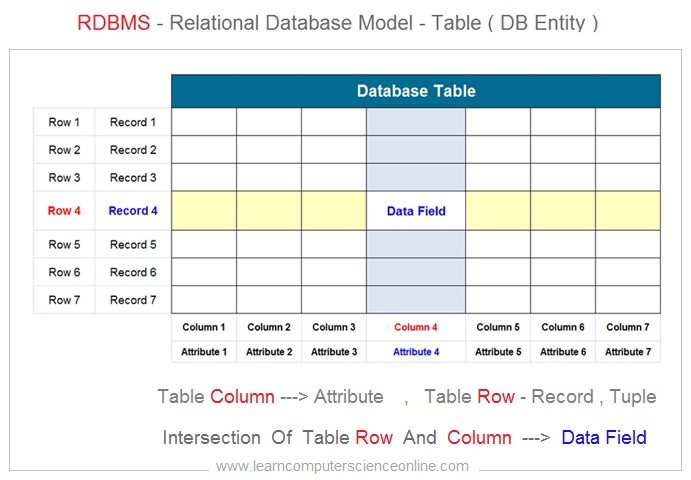
Each table represents an entity . Each table consist of number of rows and columns . Each table row represents a unique record ( an instance ) which is uniquely identified by its corresponding primary key .
Each table represents an entity and each database entity can have many attributes . These attributes are represented by table columns for a relational table . Each attribute of the entity represents one table column.
Each intersection of table row and column represents a data field that can be uniquely identified with reference to primary key ( row ) and attribute name ( Column ) . And therefore , each data field ( Table Cell ) has unique identity .
E F Codd's 12 Rules For Relational Databases
The Relational Databases are well known for its reliability , simplicity , robustness and security features . E F Codd inventor of relational database model defined rules that relational database must comply.
The Codd’s twelve rules are a set of rules was proposed by EF. Codd, , who introduced the relational database model . A DBMS must conform to these rules in order to qualify as a relational database .
The databases designed using RDBMS are based on relational model and referred as relational databases . These twelve rules include :
- Information Rule.
- Guaranteed Access Rule.
- Systematic Treatment of NULL Values.
- Active Online Catalog.
- Comprehensive Data Sub-Language Rule.
- View Updating Rule.
- High-Level Insert , Update, and Delete Rule.
- Physical Data Independence.
- Logical Data Independence.
- Integrity Independence.
- Distribution Independence.
- Non-Subversion Rule.
Relational Database
Database Normalization
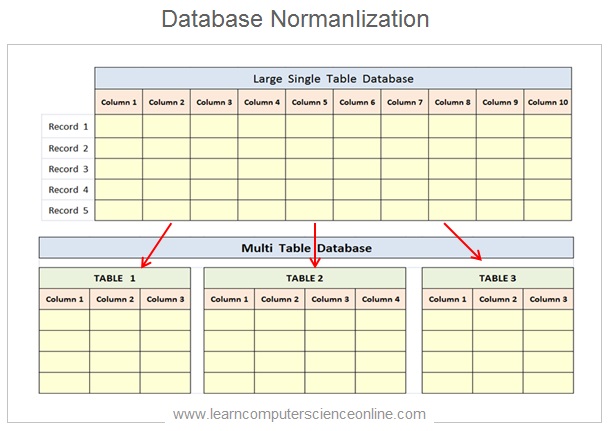
The database normalization is an important step in the design process of relational databases . To normalize the database the larger tables are split into the smaller tables to minimize the problems caused due to duplication of data in tables. The main objective of the normalization process is to eleminate the database anomalies.
During the database design stage , the database designers main task is to reorganize the tables in such a manner that , the data redundancy minimized or completely eliminated .
The redundant data in table is the main cause of various database anomalies and such problems must be resolved in the database design stage .
The process of reorganizing the data in a tables by splitting larger tables in to smaller meaningful tables with well defined relationships is referred as database normalization.
The main objective of the database normalization process is to minimize the problem of data redundancy in larger tables that causes database anomalies.
During the database normalization , the larger tables are decomposed to smaller meaningful tables by applying the database normalization rules .
Read More
E F Codd's
Database Normalization Rules
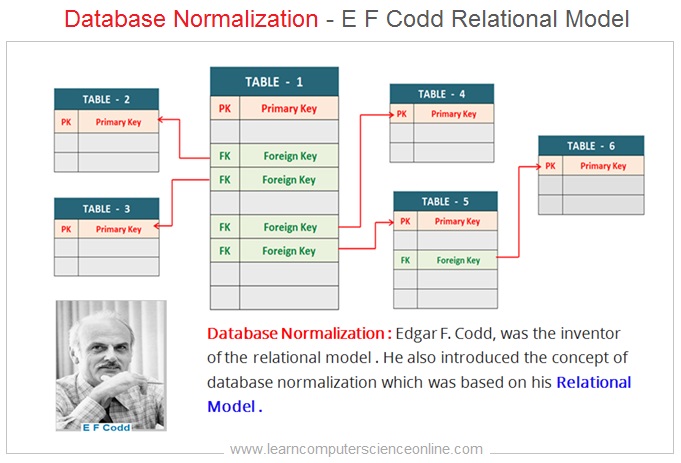
Edgar F. Codd, was the inventor of the relational model . He also introduced the concept of database normalization which was based on his relational model .
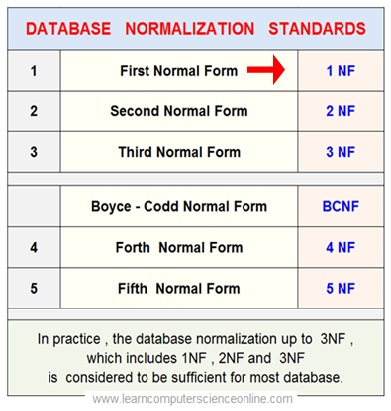
E F Codd proposed three forms ( three stage process ) for database normalization what we today know as the First Normal Form ( 1NF ) in 1970.
He subsequently also went on to define the Second Normal Form ( 2NF ) and Third Normal Form ( 3NF ) in 1971 for database normalization .
Database Normalization Forms
E F Codd was the inventor of relational model and proposed three types of normal forms ( 1NF , 2NF and 3NF ) for the normalization of tables within a relational database .
He also defined the normalization rules that each table in a relational database must satisfy and also the corrections to be applied to the table so that the table qualify to the different criterion defined for normalization ( 1NF , 2NF and 3NF ) .
The table which is in 2NF is also considered to be in 1NF and the table which is in 3NF is also considered to be in 1NF and 2NF .
Database Normalization Rules
Database Normalization
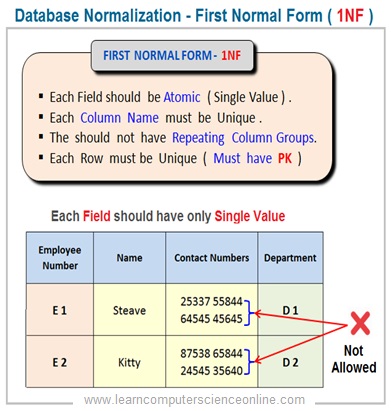
First Normal Form ( 1NF )
The relational table is said to be in First Normal Form ( 1NF ) if it satisfy the following criterion :
1. Each field ( Intersection of column and row ) can have only one single value ( Atomic value ) and multiple vales are not allowed .
2. Each relational table Column ( Attribute ) should have unique name and repeating column groups creates redundant data and therefore not allowed .
3. Each Row should have key Attribute ( PK ). So that each record can be uniquely identified with reference to key attribute ( Primary Key ) .
Database Normalization
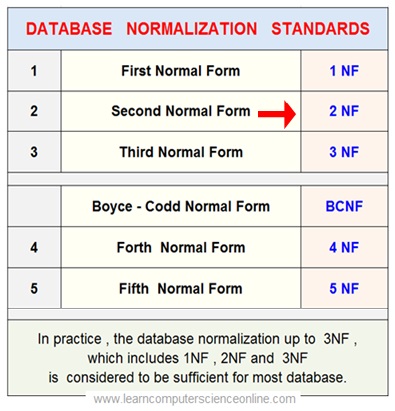
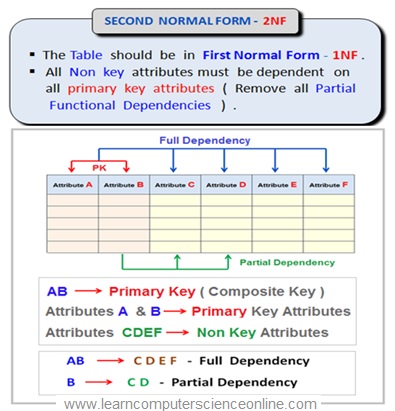
Second Normal Form ( 2NF )
The Relational Table is said to be in Second Normal Form ( 2NF ) if it satisfy the following Conditions :
- First , the table must be in the First Normal Form ( 1NF ) . That is table must fulfill all the criterion for First Normal Form ( 1NF ).
2. All Non-key attributes ( Column C, D, E, F ) must be totally dependent on the primary key ( AB ) and Not just on one of the prime attributes ( either A or B ).
In Second Normal Form ( 2NF ) , The partial dependencies are moved to a separate table .
The partial dependency can occur only if the primary key is a composite key.
Database Normalization
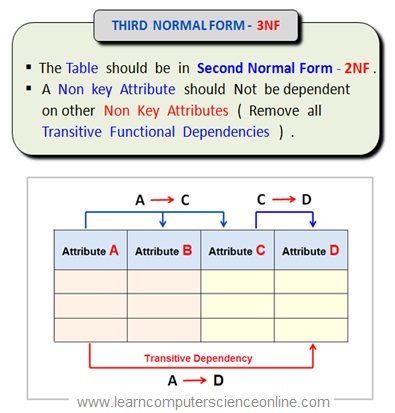
Third Normal Form ( 3NF )
The Relational Table is said to be in Third Normal Form ( 3NF ) if it satisfy the following Conditions :
1. The table must be in the Second Normal Form ( 2NF ) and First Normal Form ( 1NF ). That is table must fulfill all the criterion for First Normal Form ( 1NF ) And Second Normal Form ( 2NF ).
2. Remove all Transitive Dependencies
If one non key attribute ( C ) determines another non key attribute ( D ) then transitive dependency exist .
The 3NF criterion can be achieved by moving all transitively dependent attributes to a new separate table to avoid database anomalies due to transitive dependencies .
Relational Database
Database Normalization
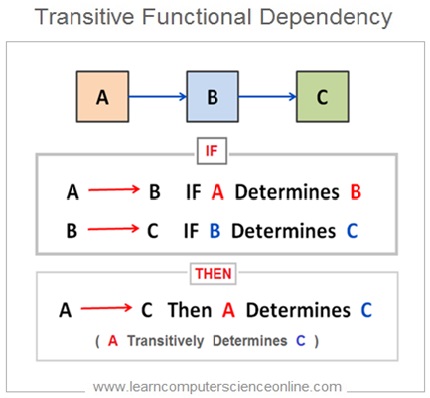
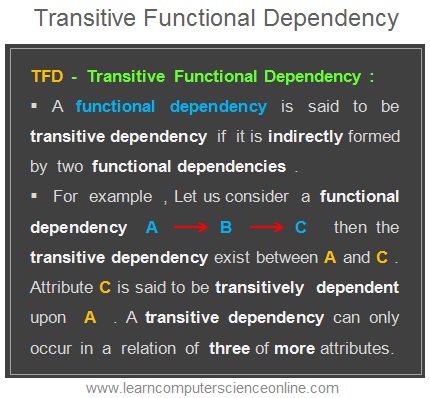
What Is Transitive Dependency ?
A transitive dependency is defined as If one non key attribute ( C ) determines another non key attribute ( D ) then transitive dependency exists in a table .
A functional dependency is said to be transitive dependency when one non key attribute determines another non key attribute .
Join The Best Seller
Computer Science Online Course
This is the most comprehensive and unique Computer Science And Programming Fundamentals course Online which will give you in depth understanding of most important fundamental concepts in computer science And Programming .